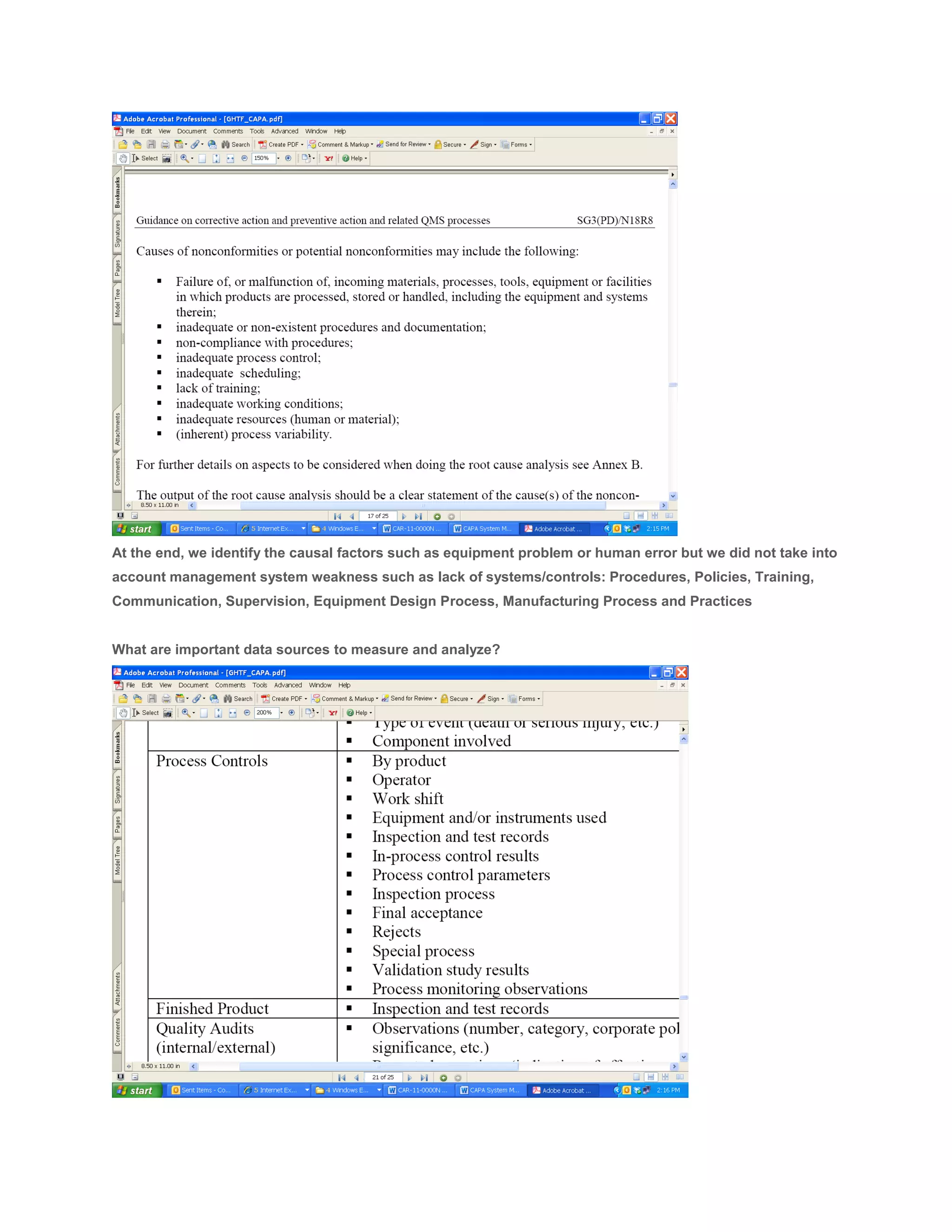
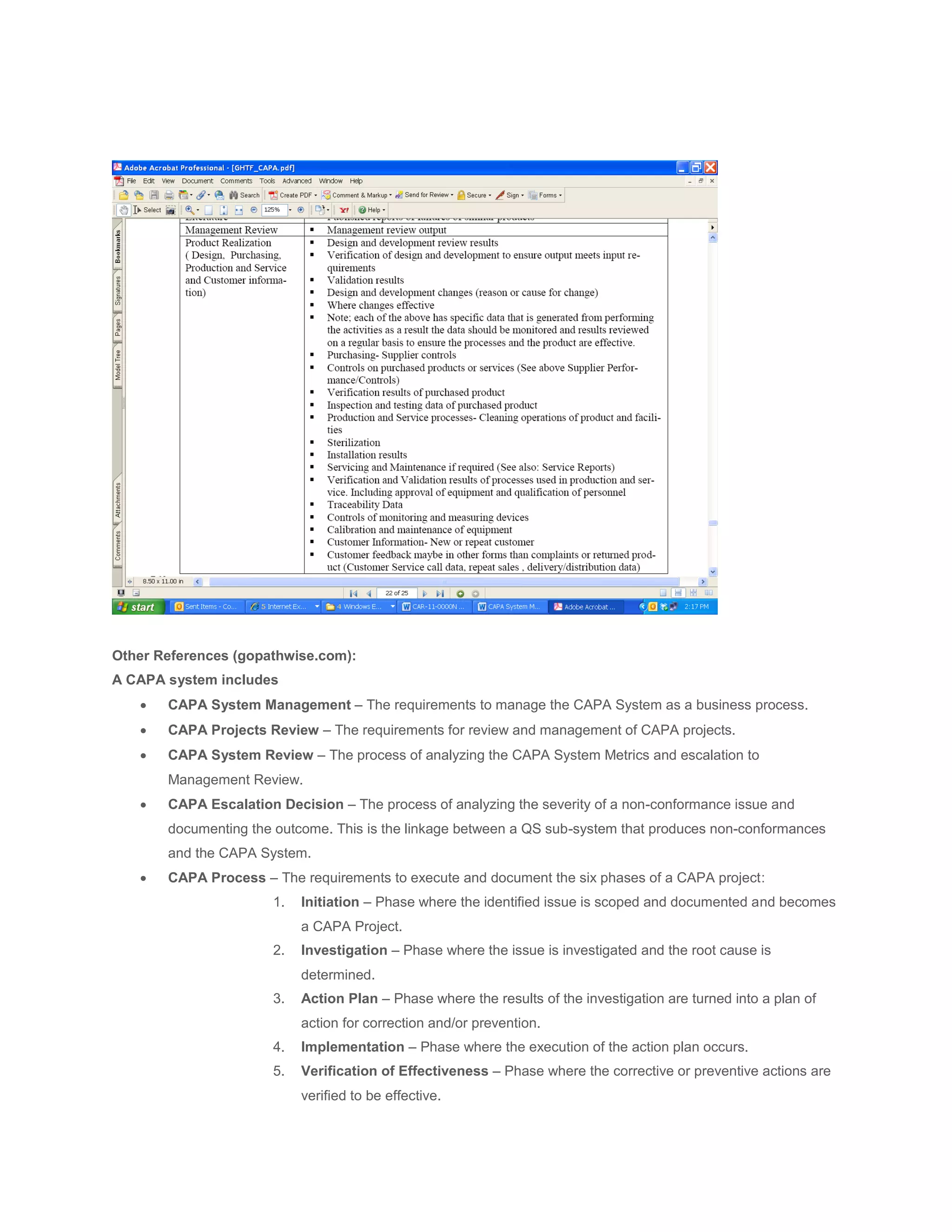
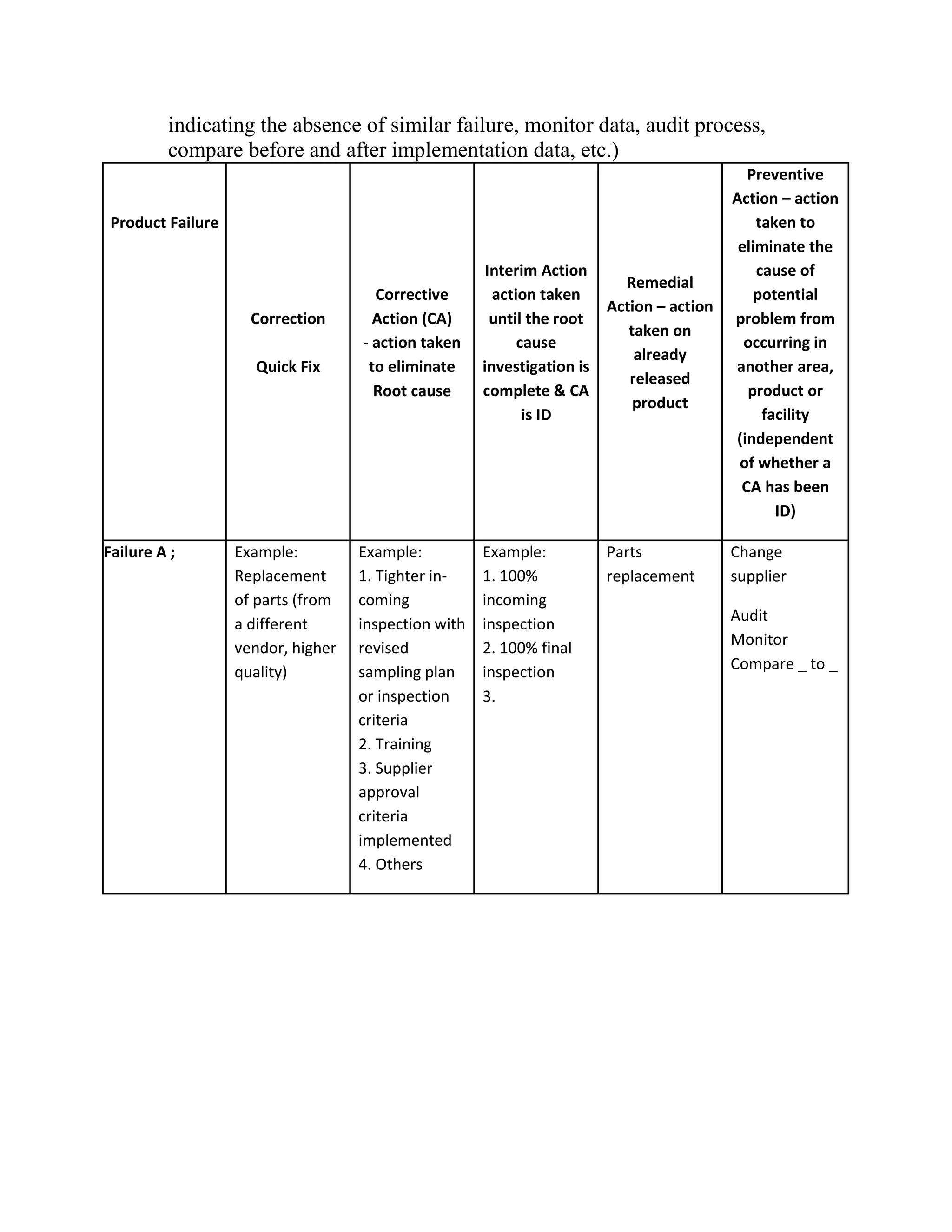
The document discusses Corrective and Preventive Action Plans (CAPA) used to improve organizations and address issues found through failure rates, customer complaints, and supplier definitions. CAPA helps find core issues and actions for improvement programs. Root cause analysis is used to identify the underlying cause of problems in order to implement targeted action plans. Effective CAPA systems include escalation processes, separate phases for investigation and action planning, and trend analysis to identify common issues requiring preventative improvement initiatives. Documentation of CAPA plans should include a root cause analysis, identification of corrective/preventative actions, verification of actions, implementation, and effectiveness checks.