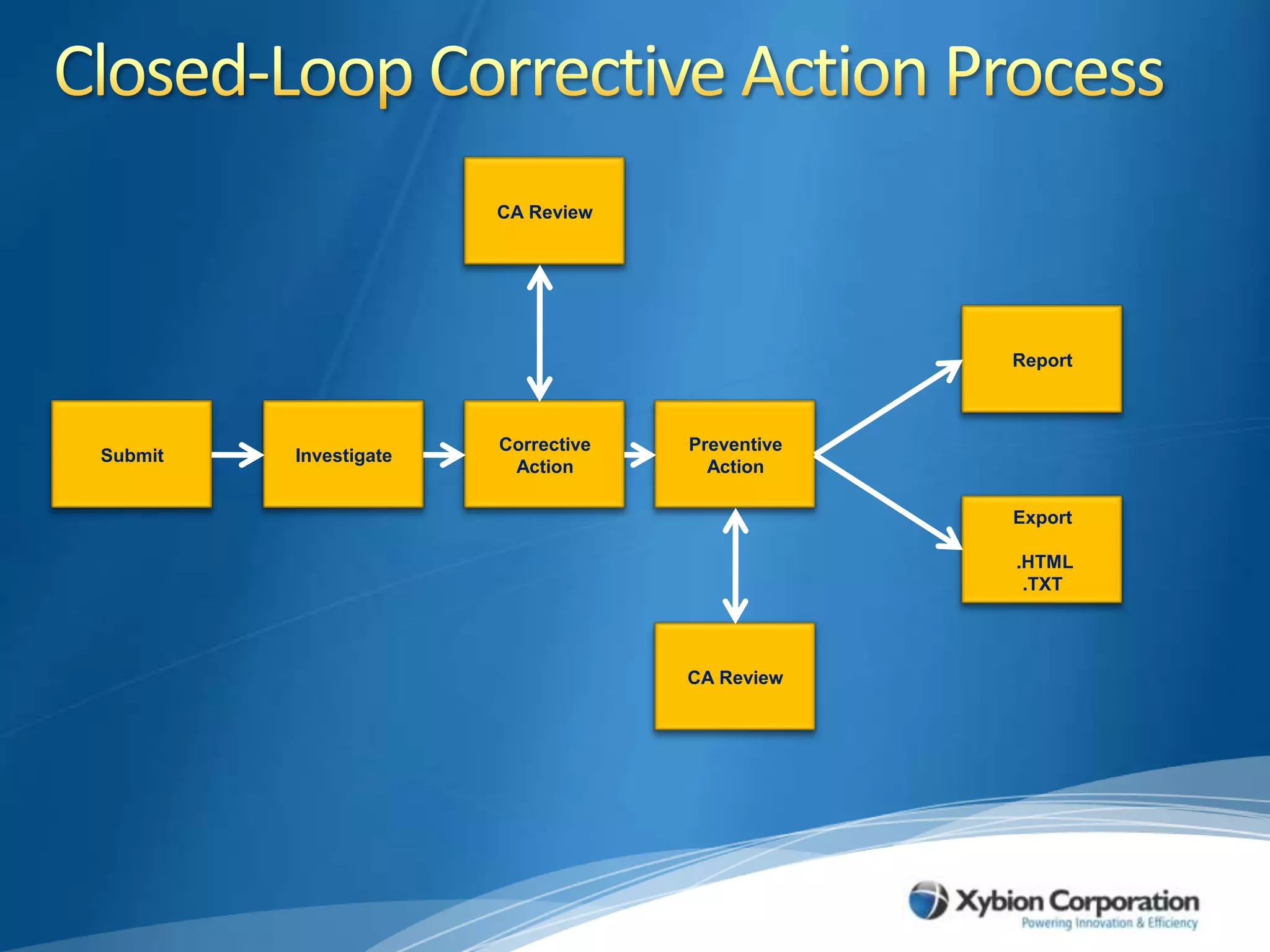
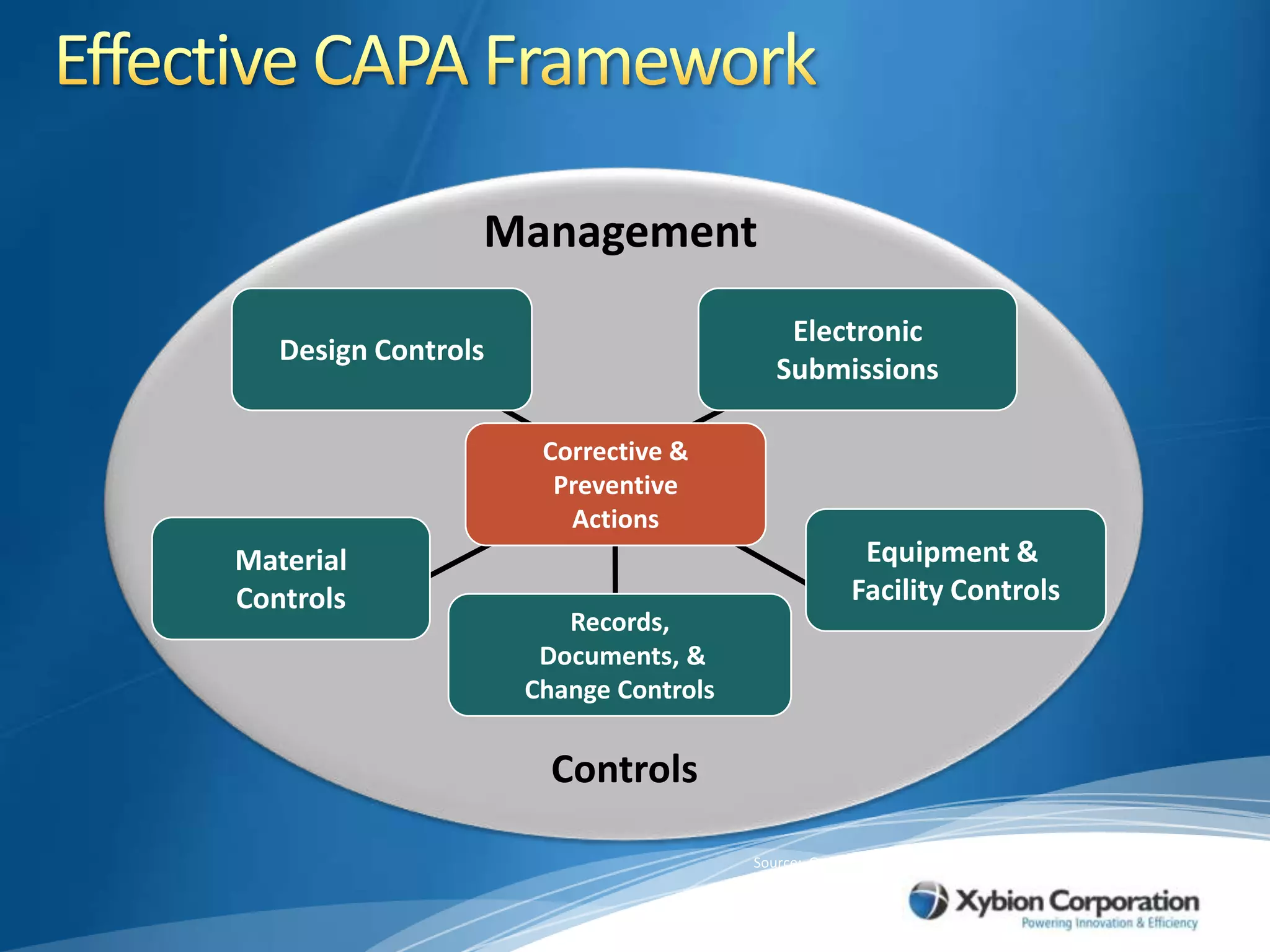
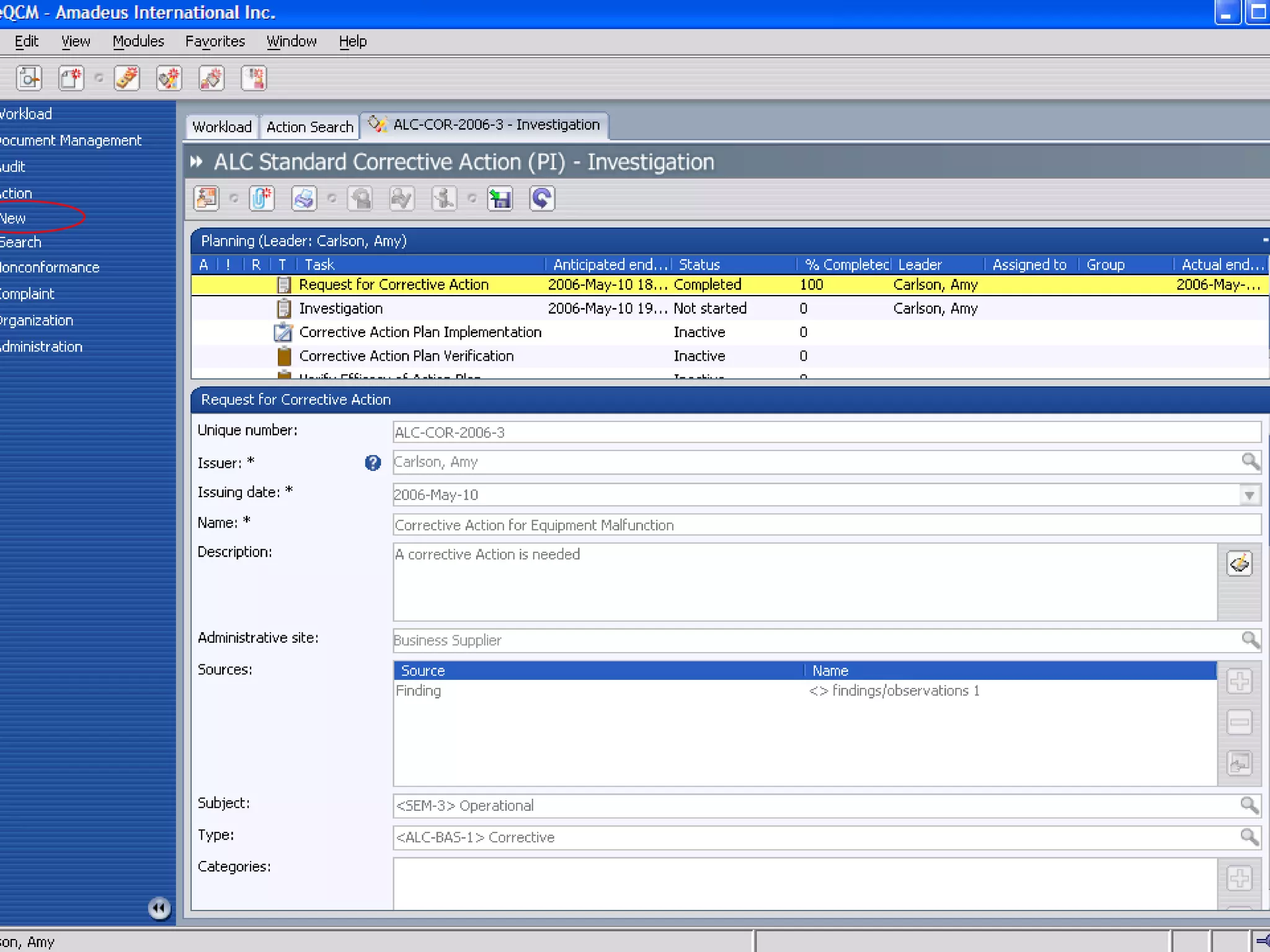
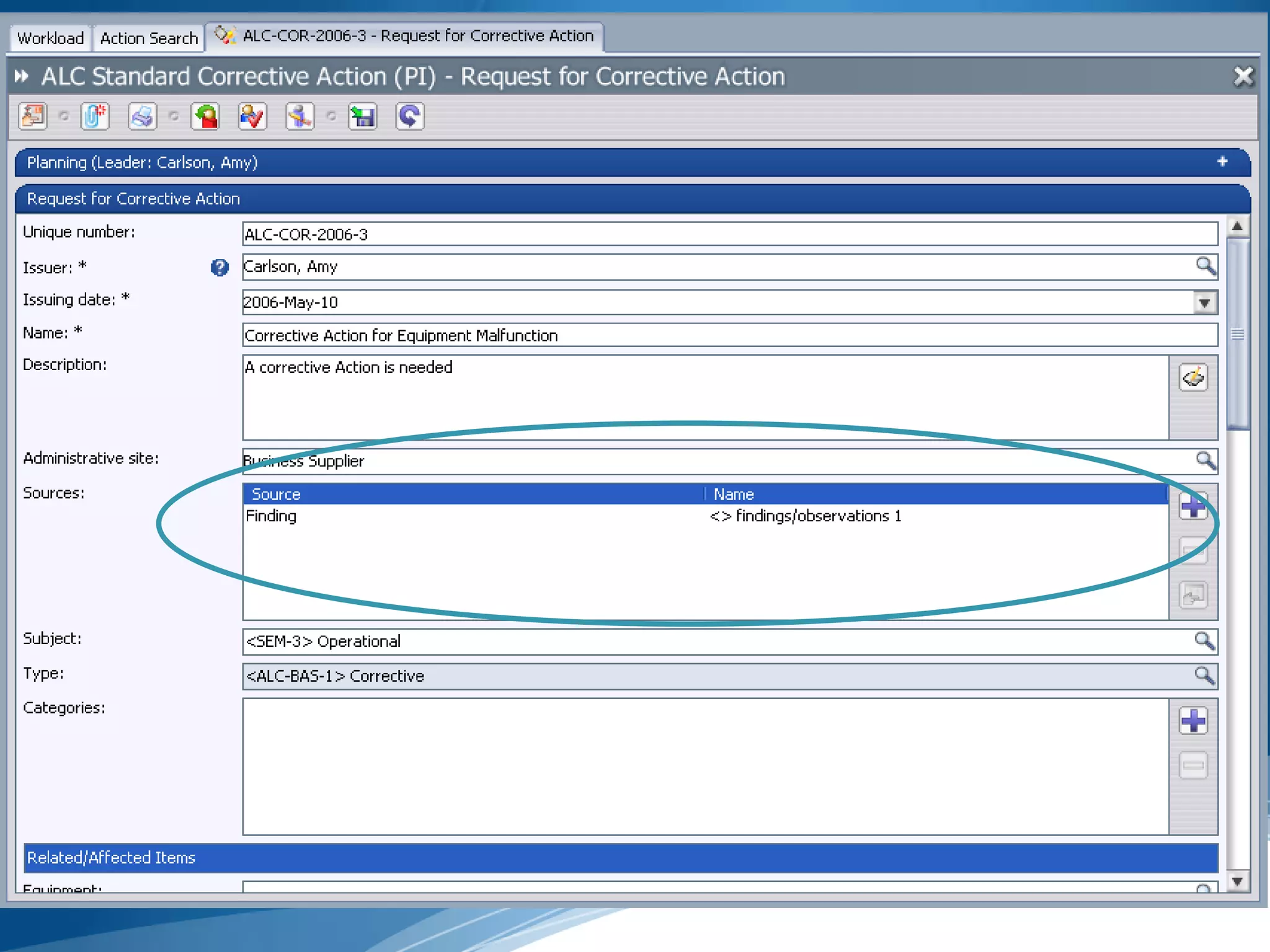
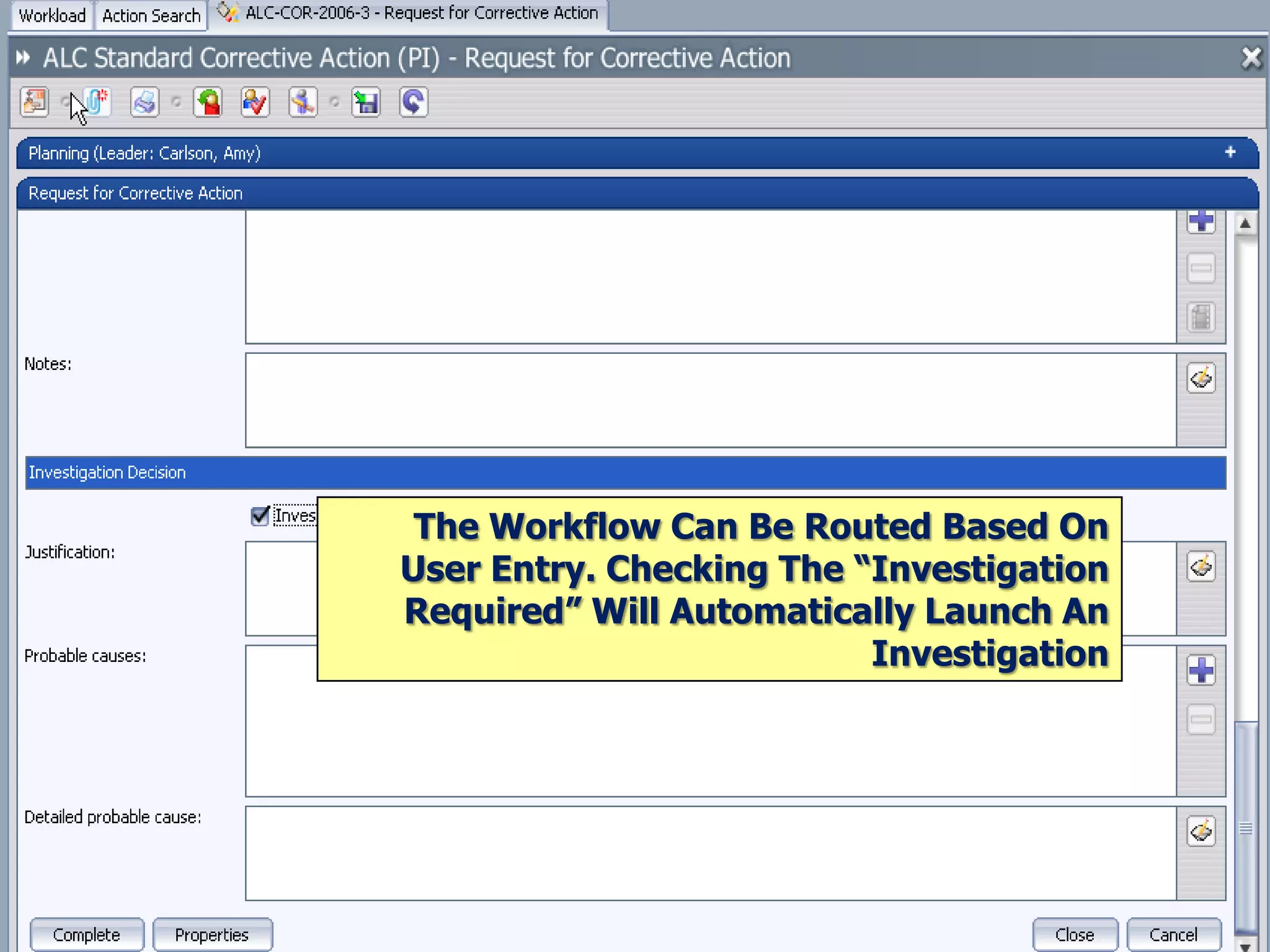
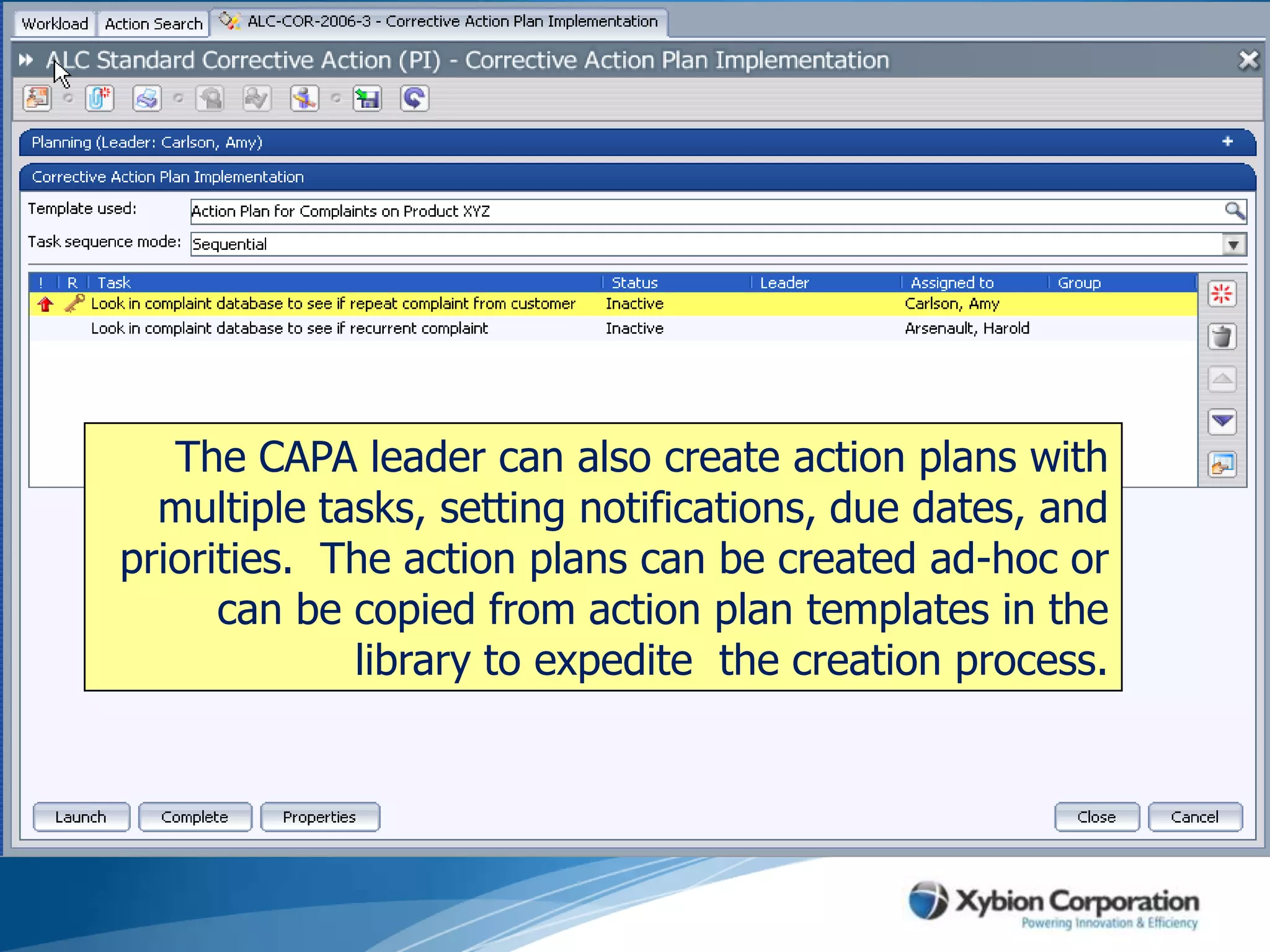
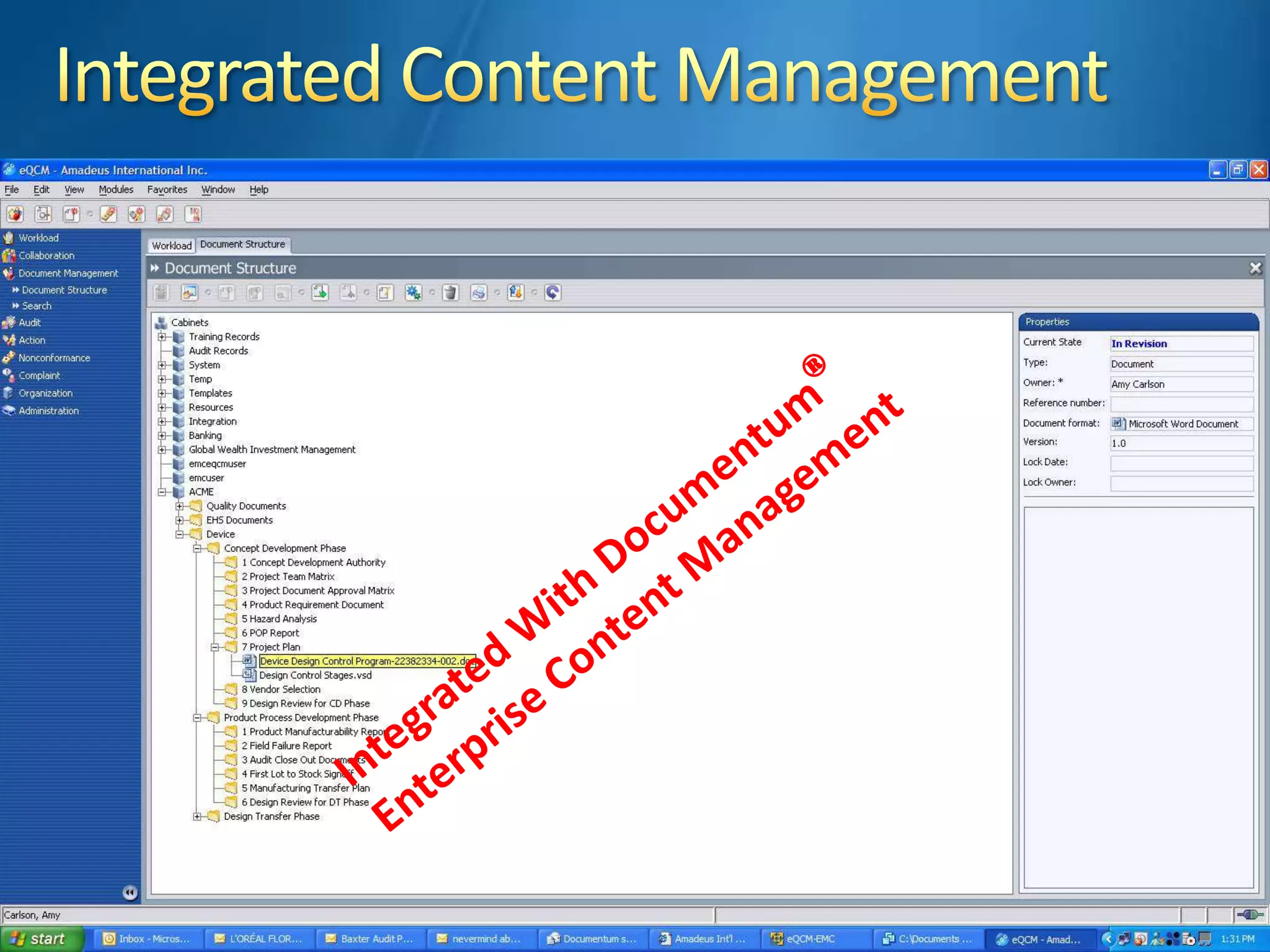
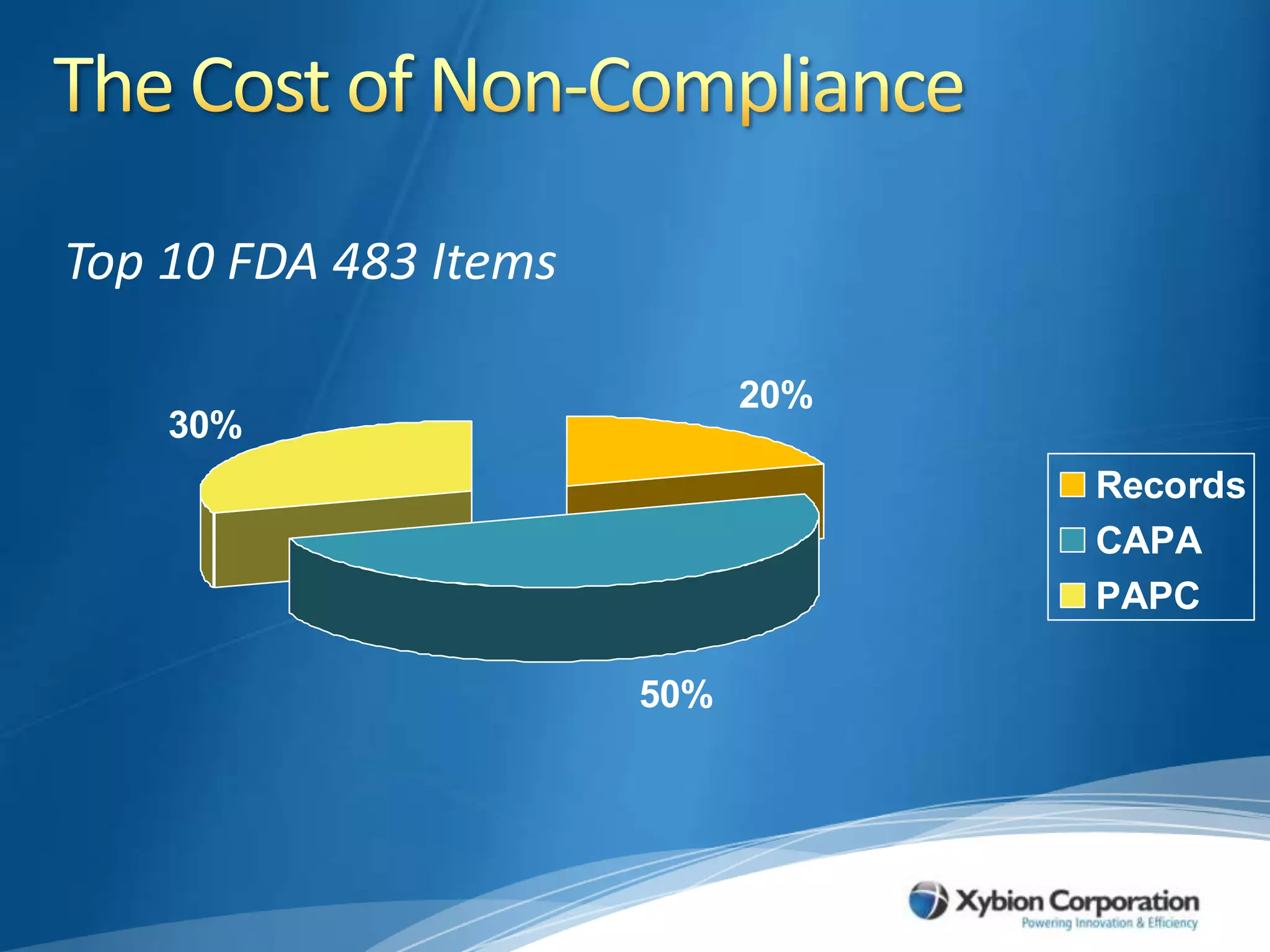
The document discusses best practices for establishing effective Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) programs, highlighting the importance of risk assessment and compliance with regulatory requirements from entities like the FDA and ISO. It outlines seven essential habits of effective CAPA systems, including problem identification, root cause analysis, and action plan implementation, while also addressing common causes of CAPA program failures and strategies for continuous improvement. Additionally, the document emphasizes the need for collaboration and proper documentation within an integrated system to enhance overall quality management.










![CAPA [21CFR 820.100] Includes Actions Needed To: Correct (“Correction”) Nonconforming Product And Other Quality ProblemsPrevent Recurrence (“Corrective Action”) Of Nonconforming Product And Other Quality ProblemsEliminate The Cause Of Potential (“Preventive Action”) Nonconforming Product And Other Quality Problems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011xybionwebinar-capabestpractices-final2-110407154513-phpapp01/75/Xybion-Webinar-7-Habits-of-Highly-Effective-CAPA-Programs-12-2048.jpg)
![Corrective Action Action Taken To Eliminate The Causes Of An Existing Non-conformity, Defect Or Other Undesirable Situation In Order To Prevent Recurrence. [ISO 8402]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011xybionwebinar-capabestpractices-final2-110407154513-phpapp01/75/Xybion-Webinar-7-Habits-of-Highly-Effective-CAPA-Programs-13-2048.jpg)
![Preventive Action Action Taken To Eliminate The Cause Of A Potential Non-conformity, Defect, Or Other Undesirable Situation In Order To Prevent Occurrence [ISO 8402]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011xybionwebinar-capabestpractices-final2-110407154513-phpapp01/75/Xybion-Webinar-7-Habits-of-Highly-Effective-CAPA-Programs-14-2048.jpg)