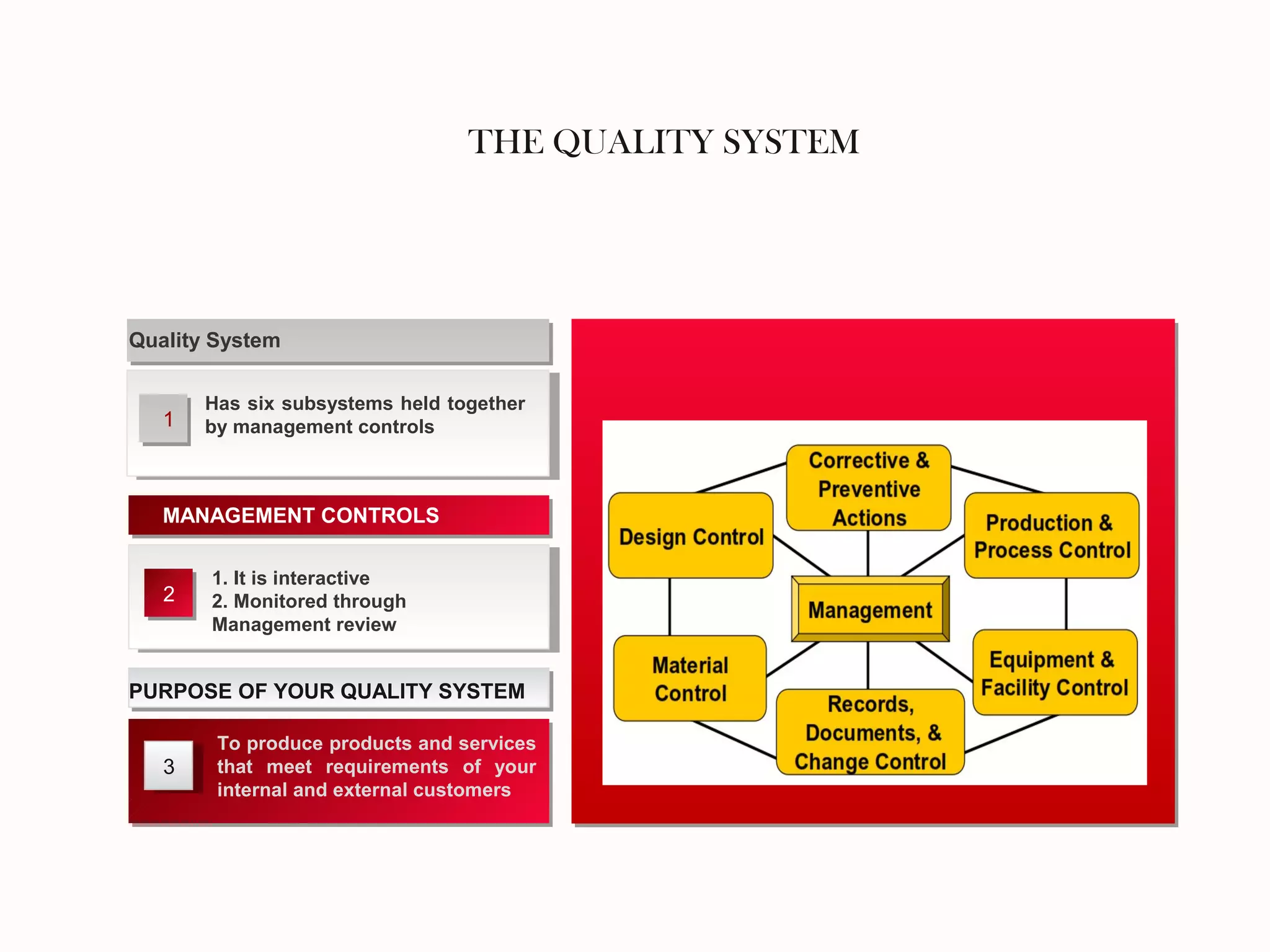
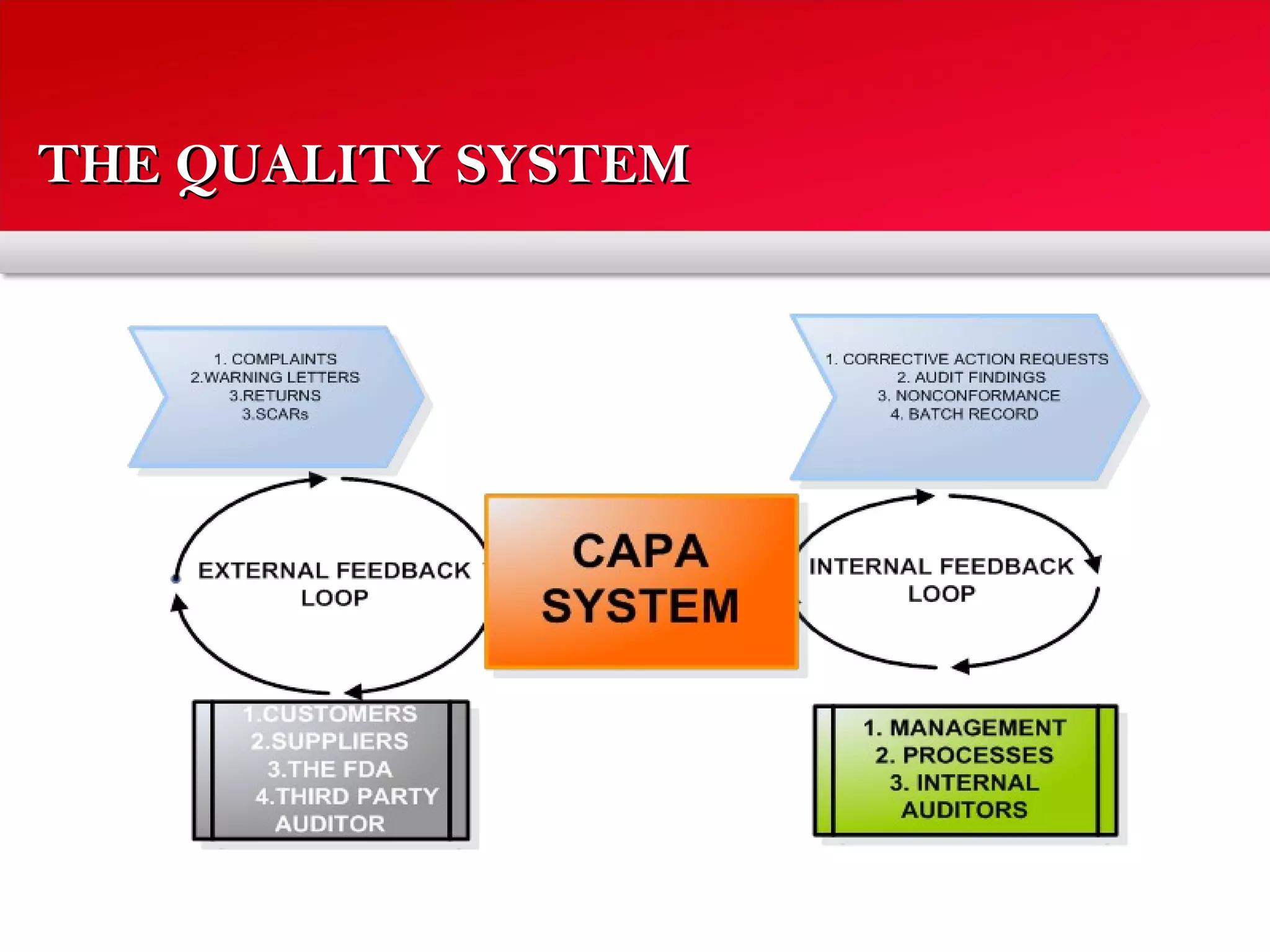
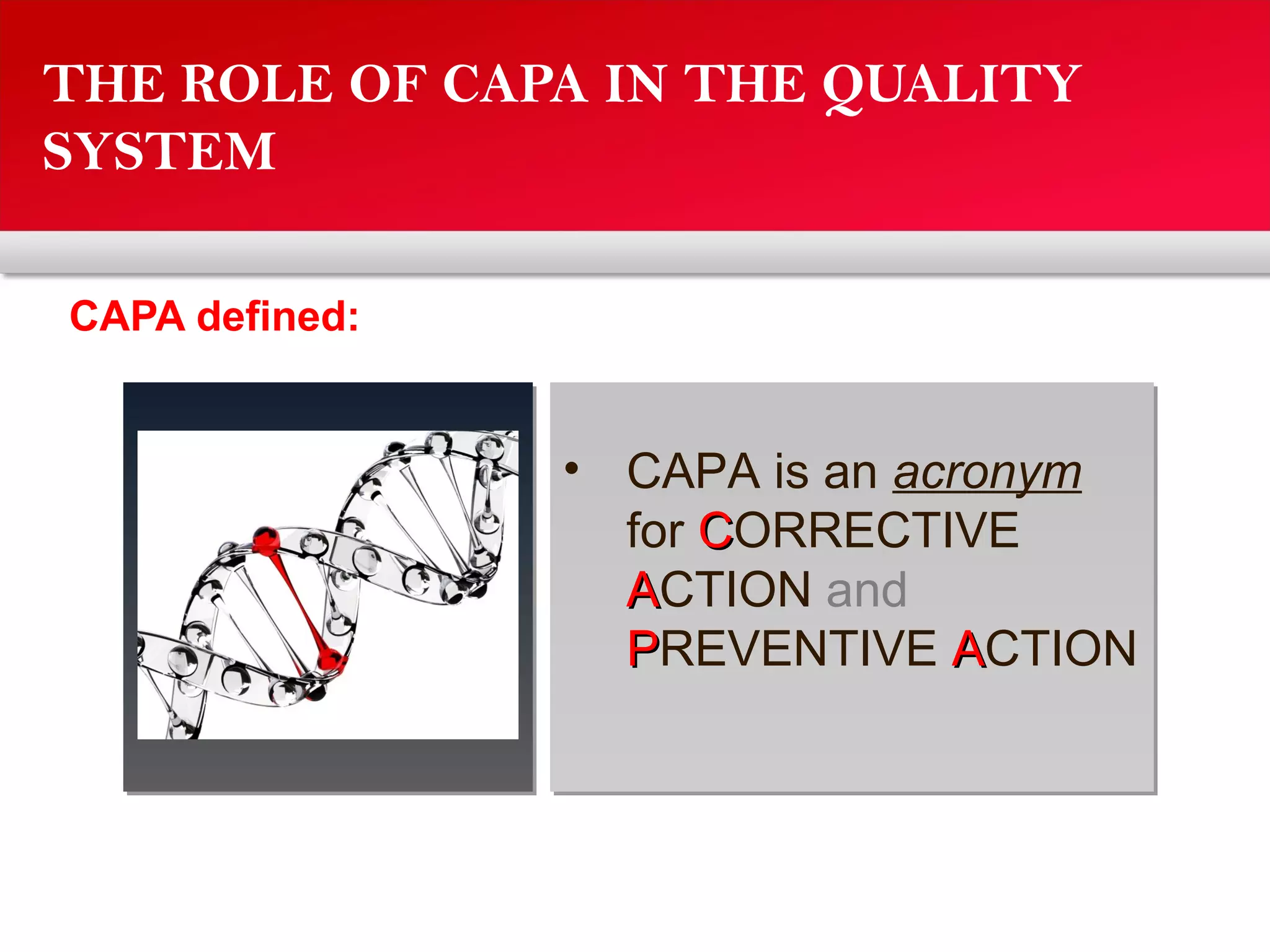
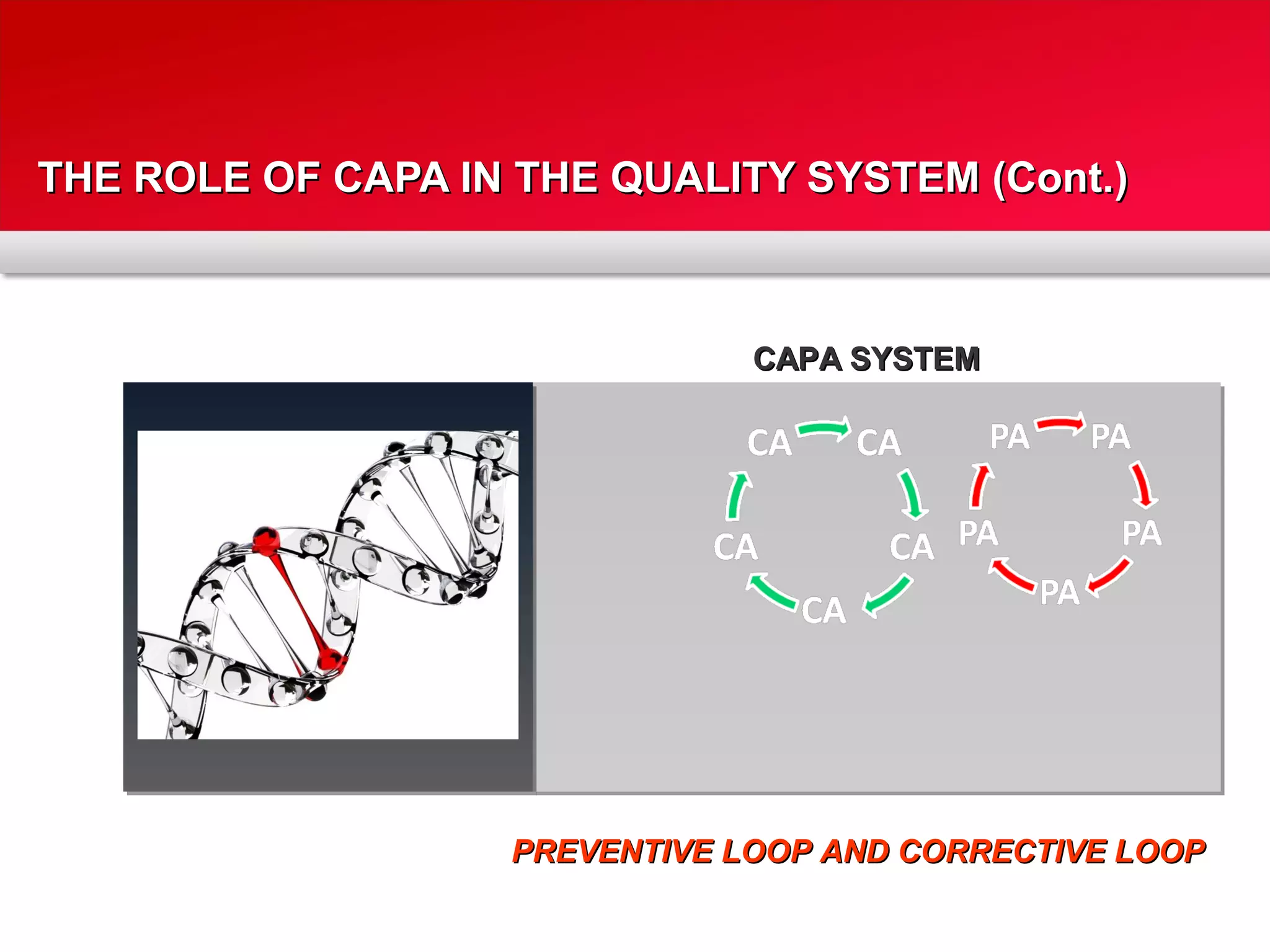
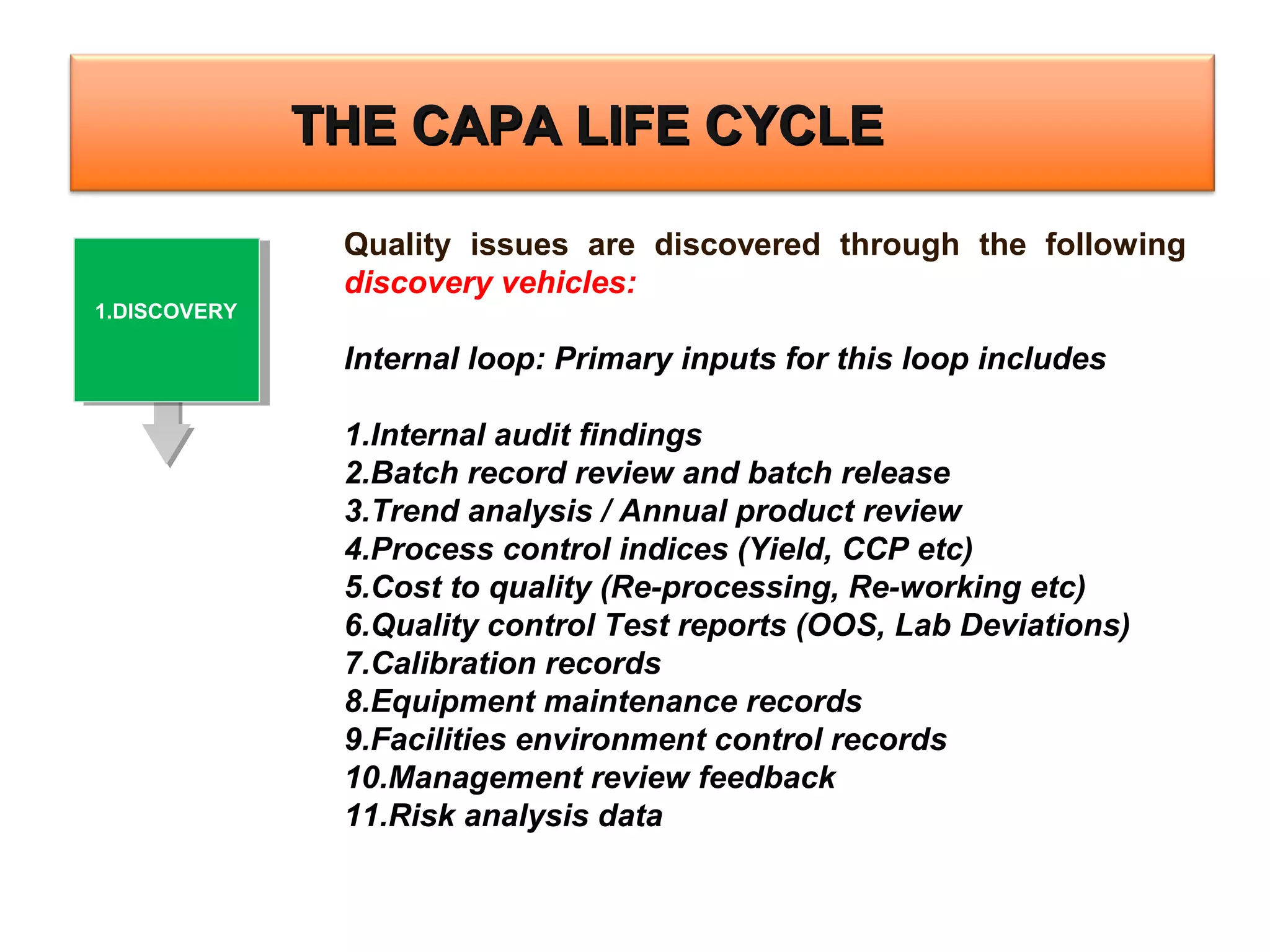
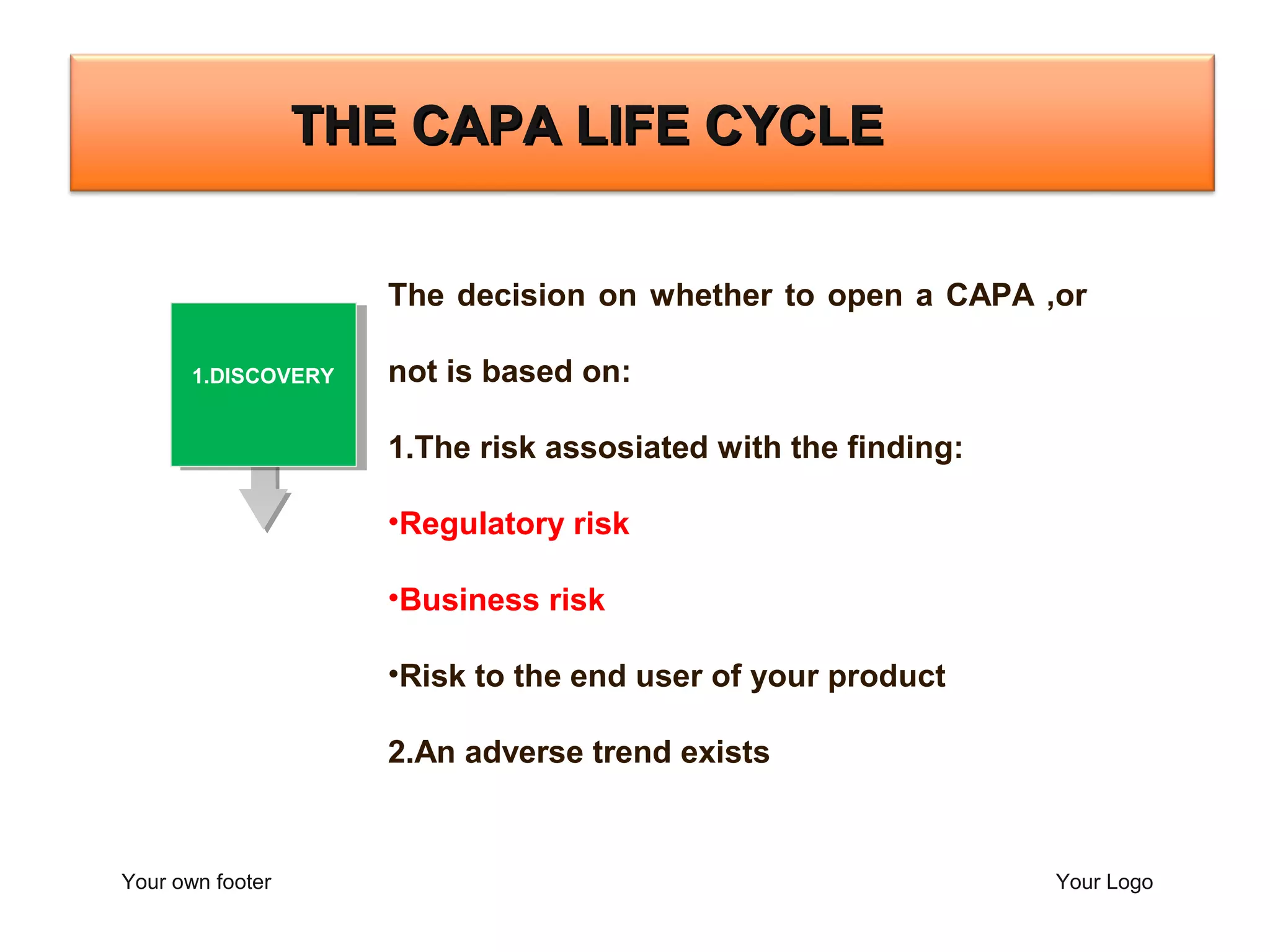
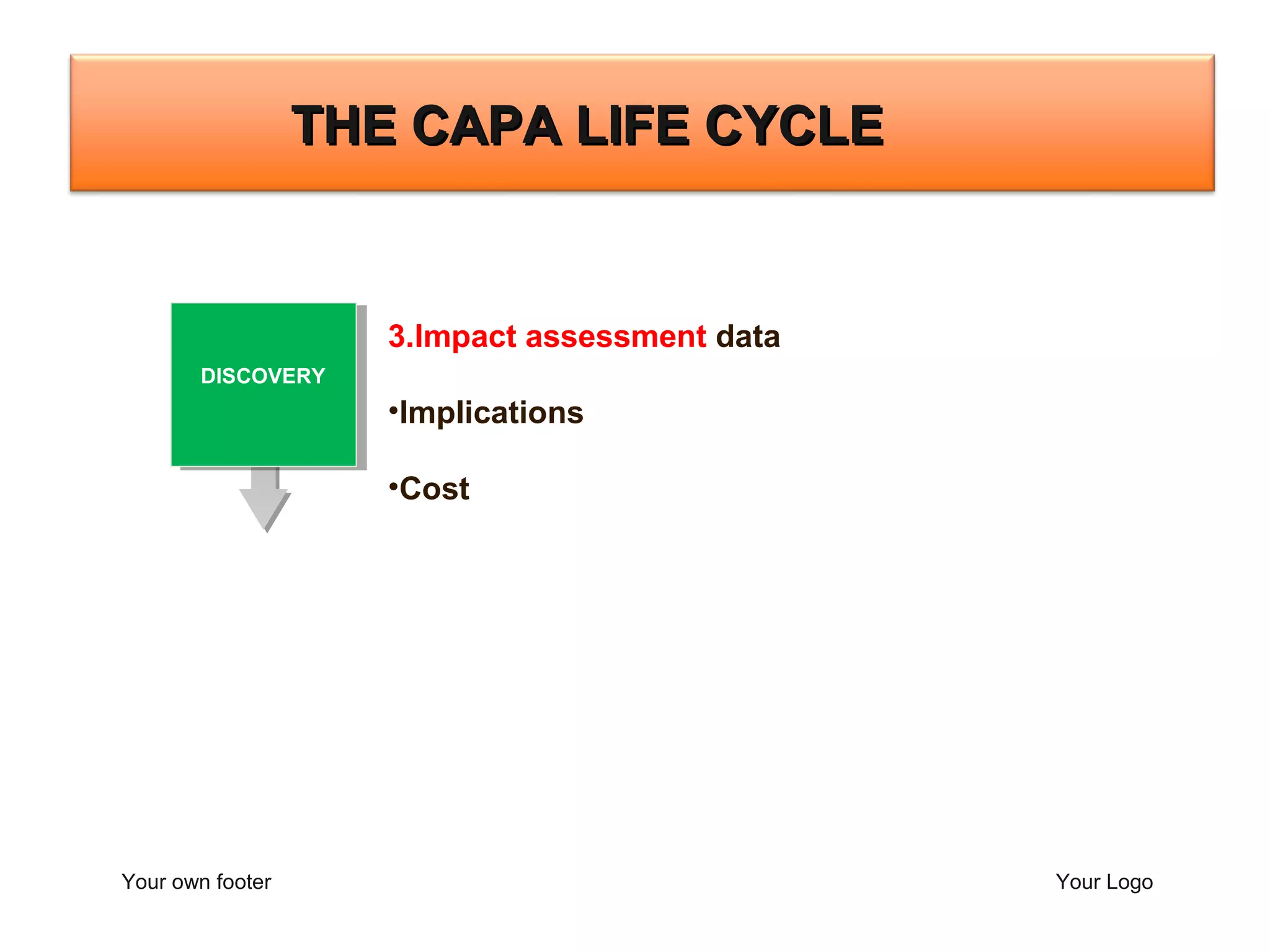
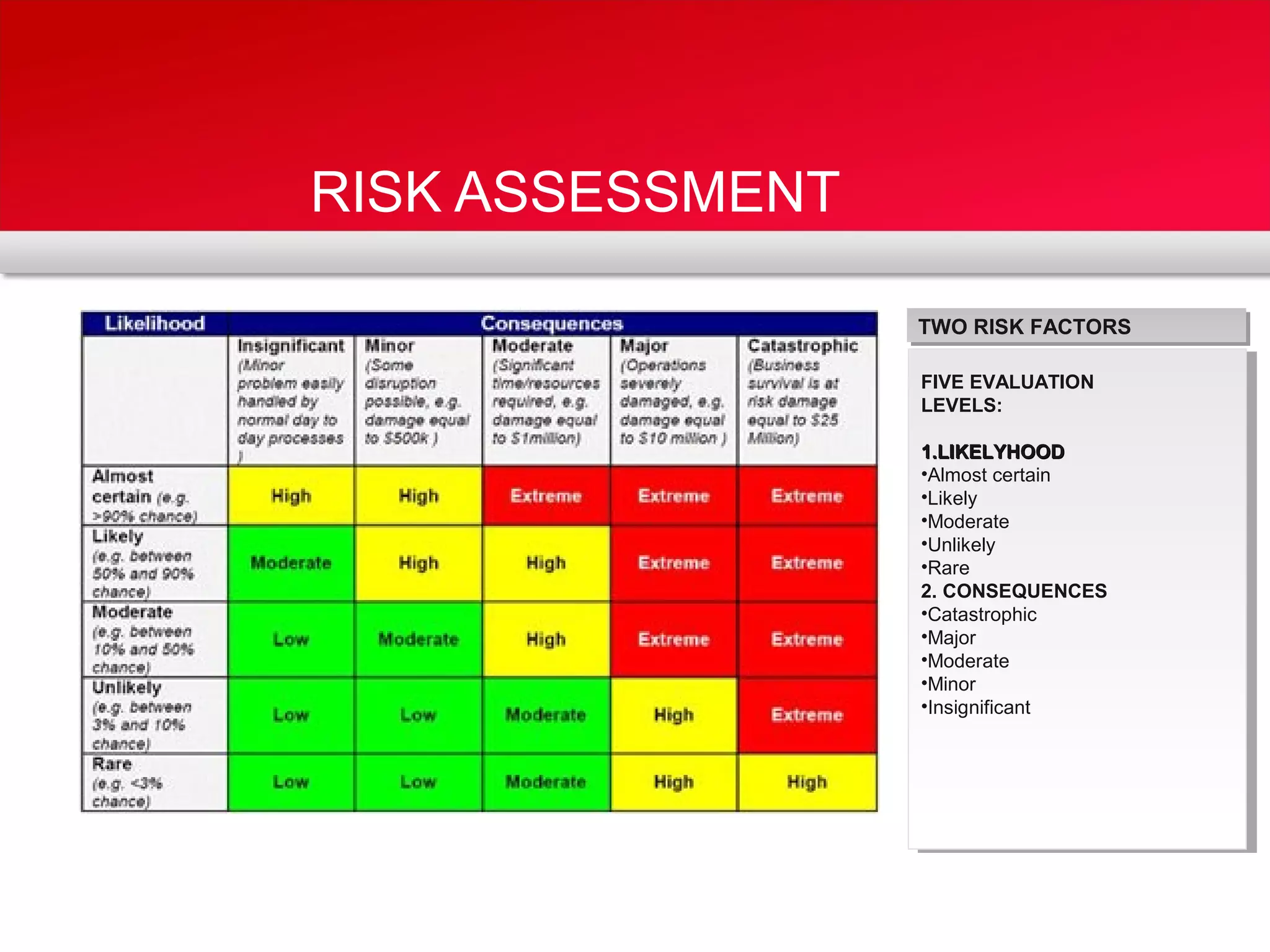
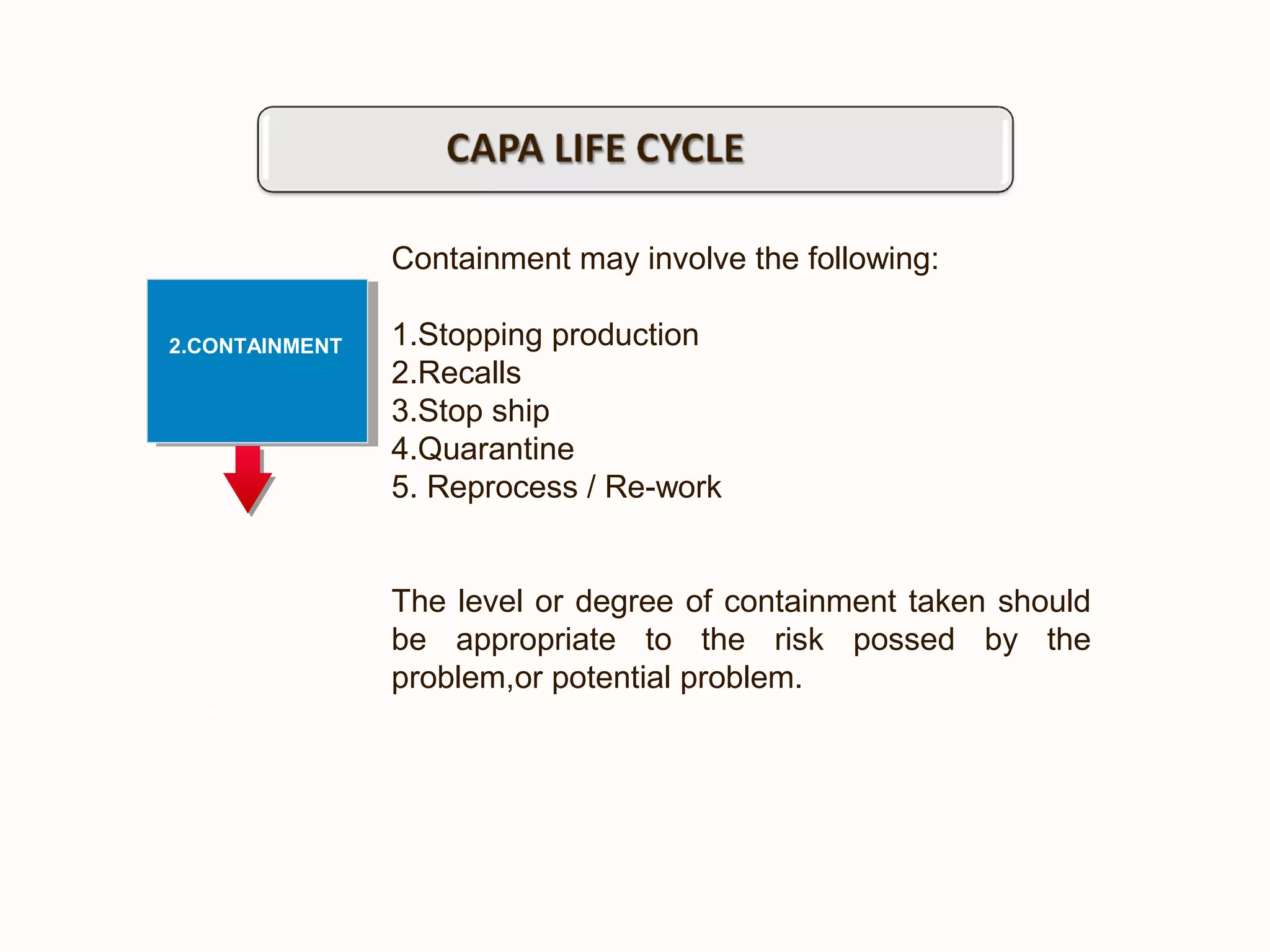
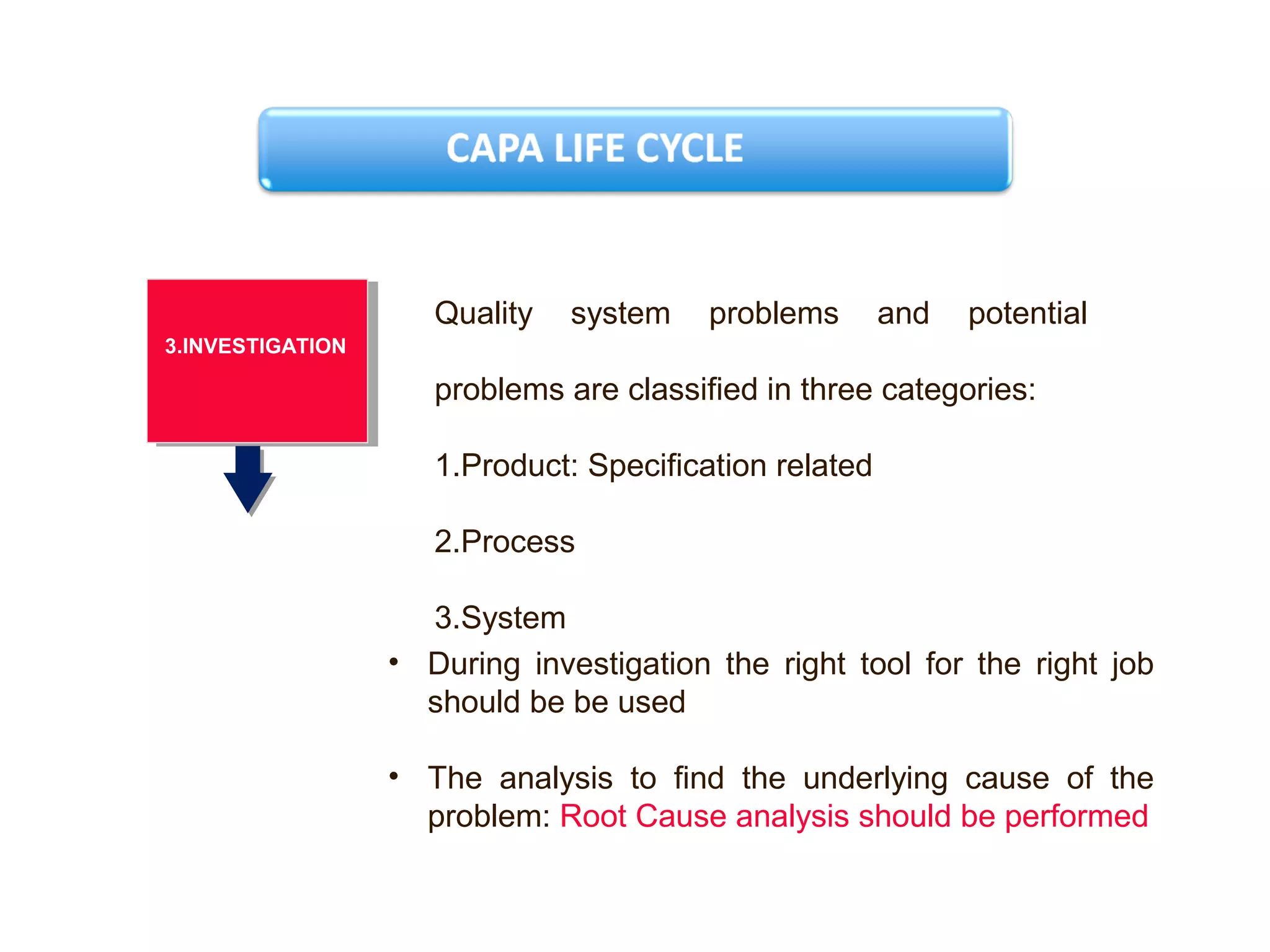
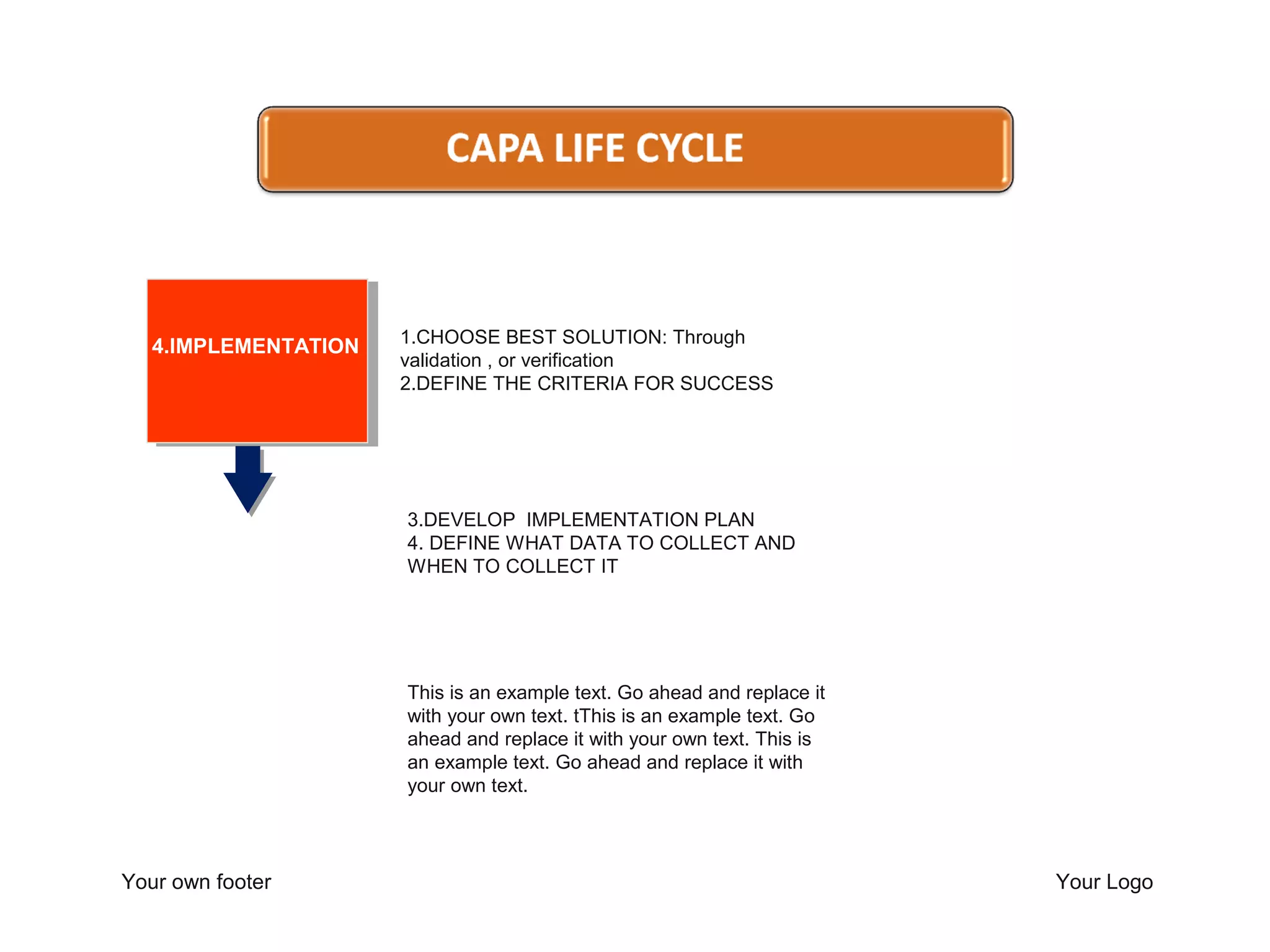
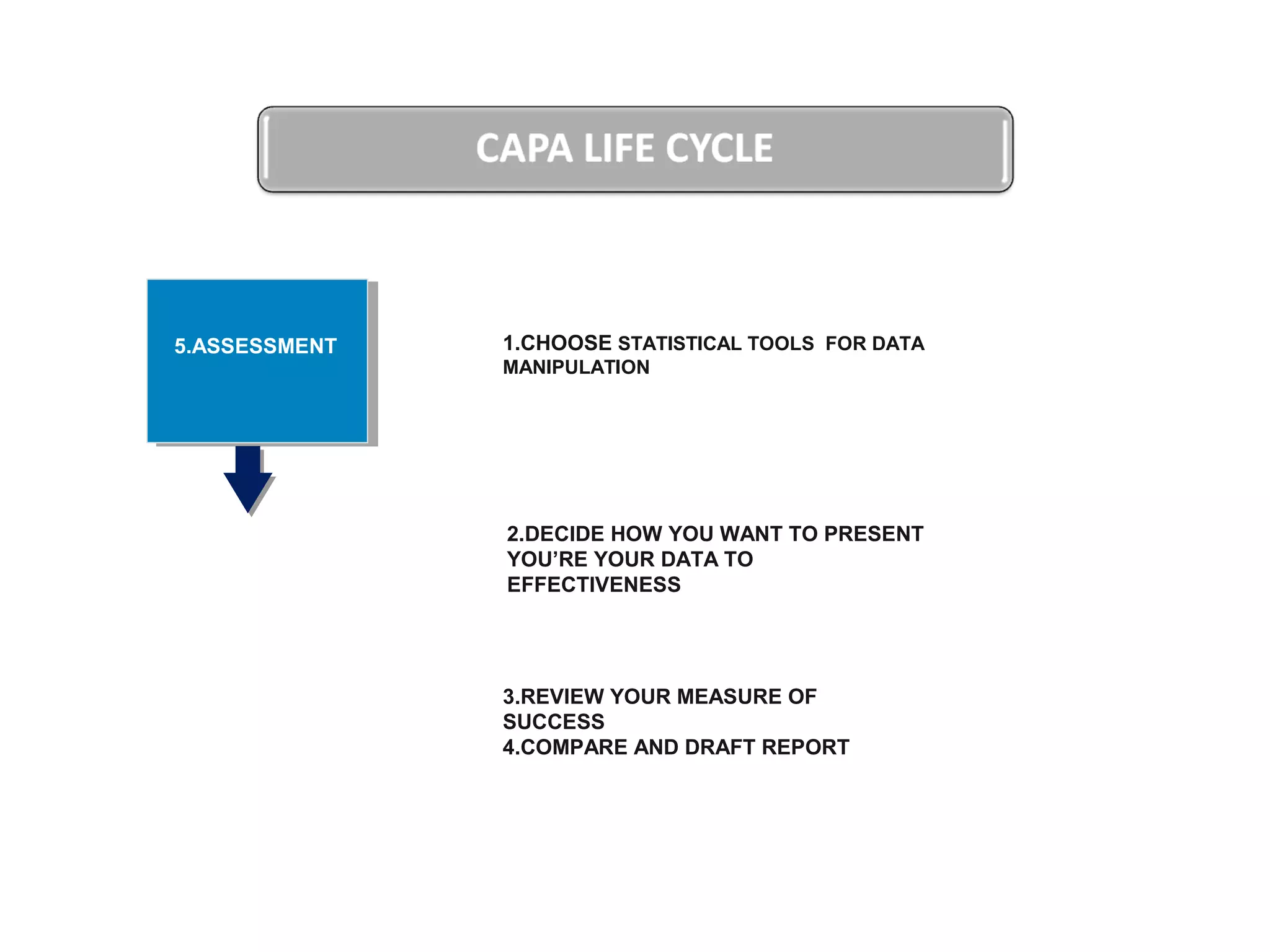
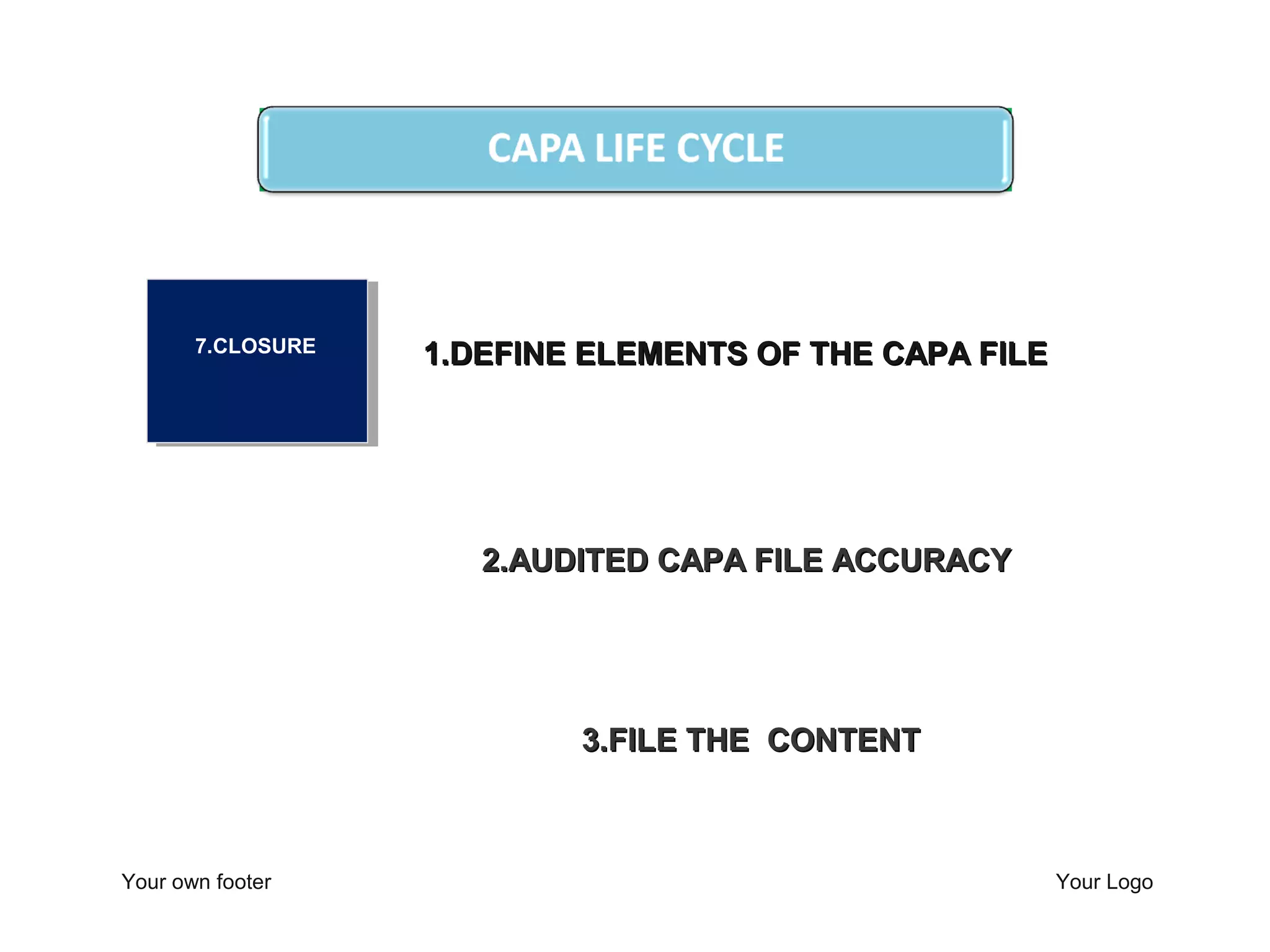
The document outlines a training program focused on Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) within a quality system framework. It details the roles, functions, and requirements of CAPA, emphasizing its importance in continuous improvement and risk assessment related to product and process quality. Additionally, it discusses the lifecycle of CAPA, including discovery, containment, investigation, implementation, and closure phases.