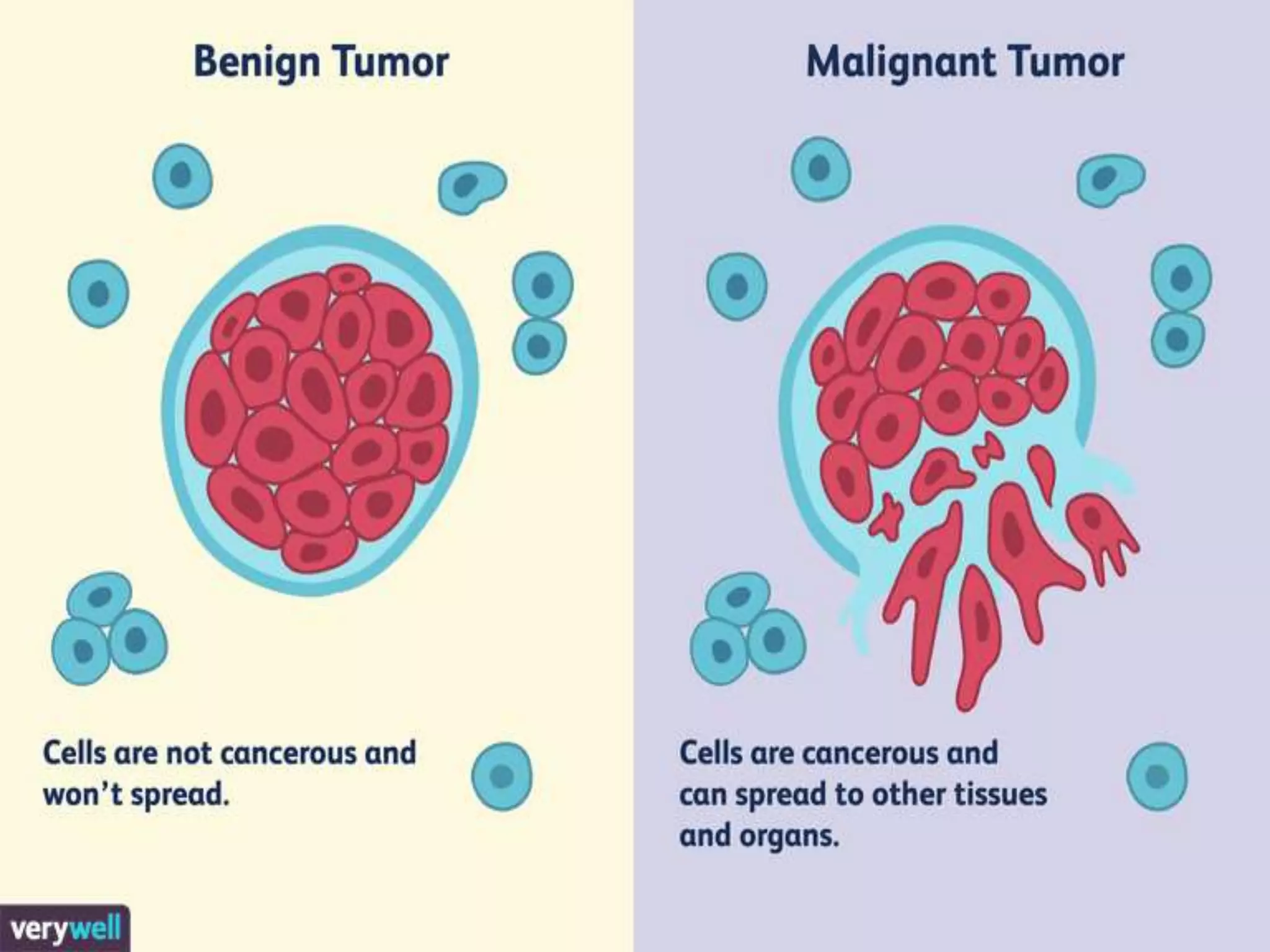
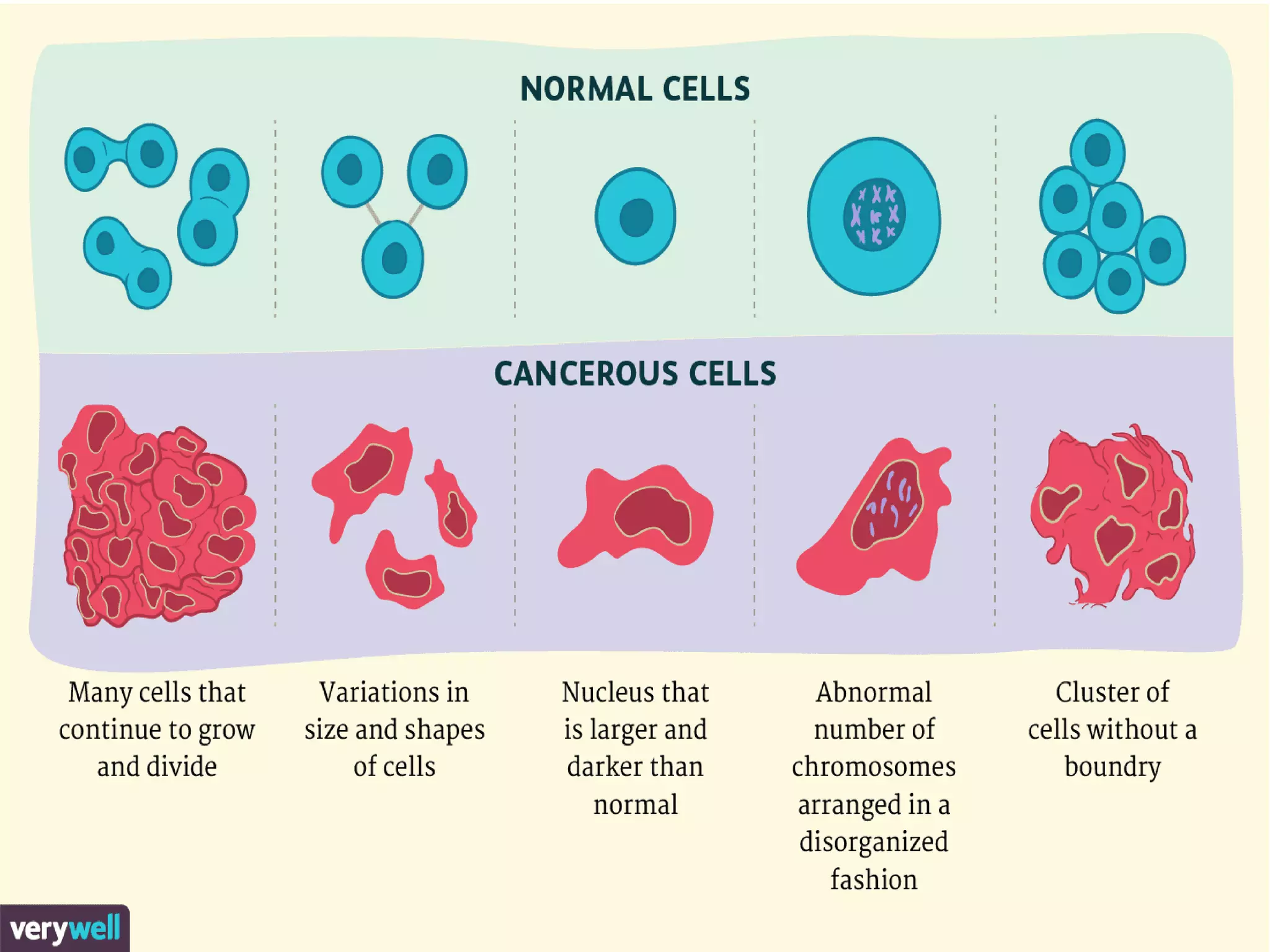
This document provides information about cancer including its types, symptoms, treatment, and spread. It discusses how cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can be caused by various factors. The most common cancers are listed for men, women, and children. It also describes the main types of cancer - carcinoma, sarcoma, leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma - and how they can spread through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to form secondary tumors in other parts of the body. The key properties of cancer cells that enable uncontrolled growth and spread are also outlined.