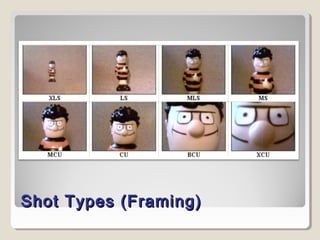
This document discusses techniques for analyzing camera use in micro detail. It examines framing and movement. For framing, it discusses camera distance, angle, and point of view. It provides examples of different shot types defined by distance and angle. It also examines types of camera movement like panning, tilting, rolling, tracking, craning, and aerial shots. Key terms for both framing and movement are defined. Different shot types and their functions are also outlined.