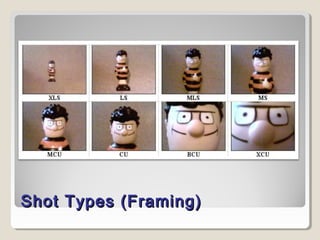
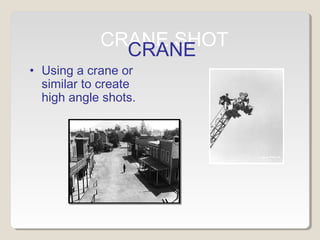
The document discusses how to analyze camera use in two ways: framing and movement. It defines various types of shots defined by camera distance and angle from the subject. These include extreme long shot, long shot, medium long shot, mid shot, medium close up, close up, and extreme close up. It also defines high angle, low angle, and wide angle shots. The document then discusses various camera movements like panning, tilting, rolling, tracking shots, crane shots, and aerial shots. It provides examples of different shot types and their purposes.