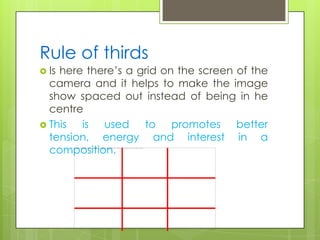
The document discusses various camera shots, angles, movements, and composition techniques used in filmmaking. It defines shots like establishing shots, wide shots, long shots, mid shots, close ups, and extreme close ups. It also covers camera angles like low angles, high angles, and canted angles. Common camera movements such as pans, tilts, tracks, zooms, dollies, and cranes are explained. Principles of composition like balance, symmetry, asymmetry, and the rule of thirds are also outlined.