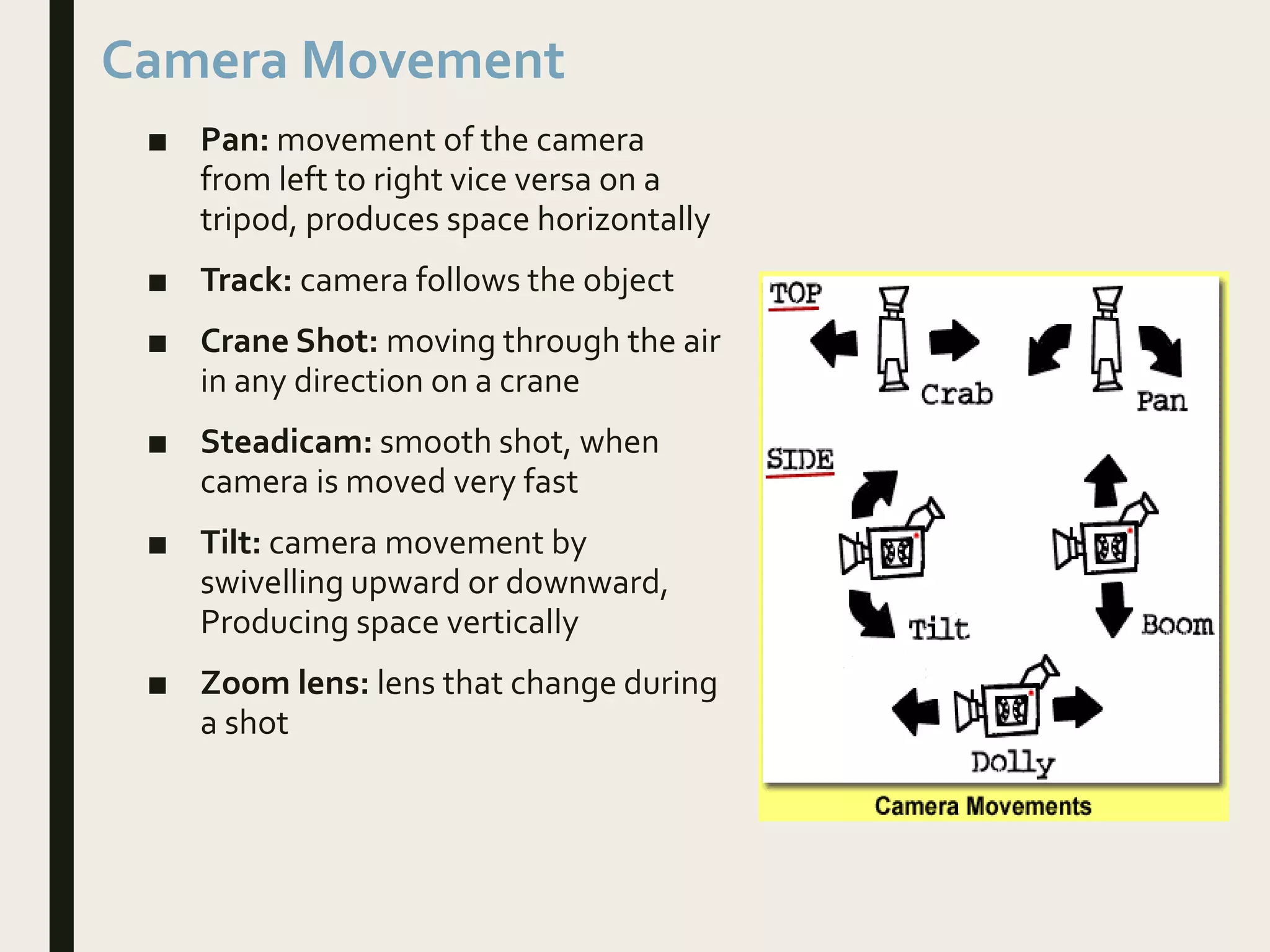
The document provides an overview of the course objectives and assessments for an A Level Film Studies course. Students will study textual analysis, genre, narrative, and representation. They will be assessed through two 2-hour examinations on film history and critical perspectives, worth 35% each. Students will also complete a non-examined assessment involving producing a short film or screenplay and analyzing it in relation to professional examples. The document outlines micro and macro elements that students will analyze in films, including technical codes like shots, editing, and lighting, as well as narrative structure and themes. It provides definitions and examples of different shot types and camera angles and movements.