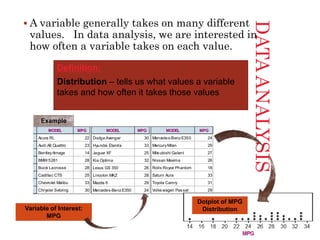
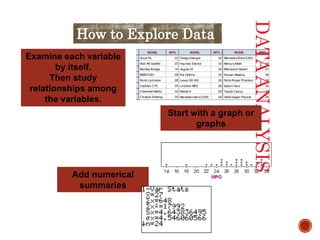
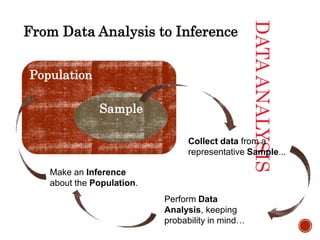
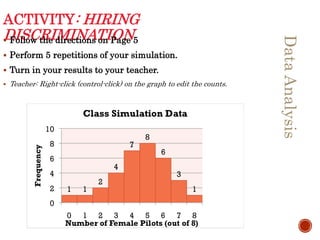
This document introduces the concepts of data analysis. It defines key terms like individuals, variables, categorical vs. quantitative variables, and distribution. It explains that the goal of data analysis is to organize, display, summarize and ask questions about data in order to make inferences about populations based on samples. The next sections will cover analyzing categorical data with graphs and tables, as well as describing quantitative data with numerical summaries.