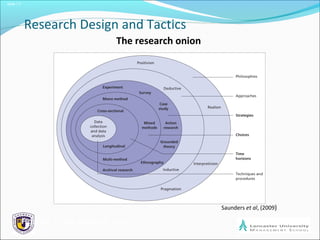
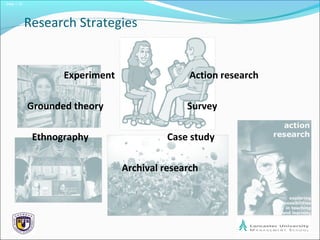
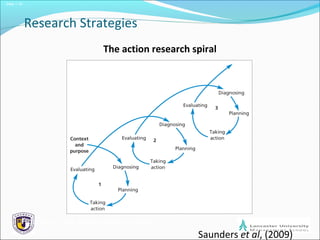
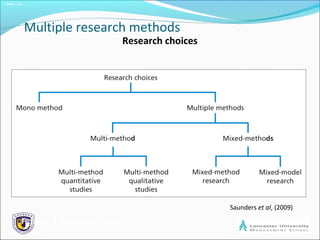
The document outlines the process of formulating a research design, emphasizing the importance of relevant and clear research questions. It discusses various research strategies such as experiments, case studies, and surveys, and highlights considerations like time horizons and ethical issues. Finally, it notes the significance of combining multiple research methods to enhance validity and reliability of findings.