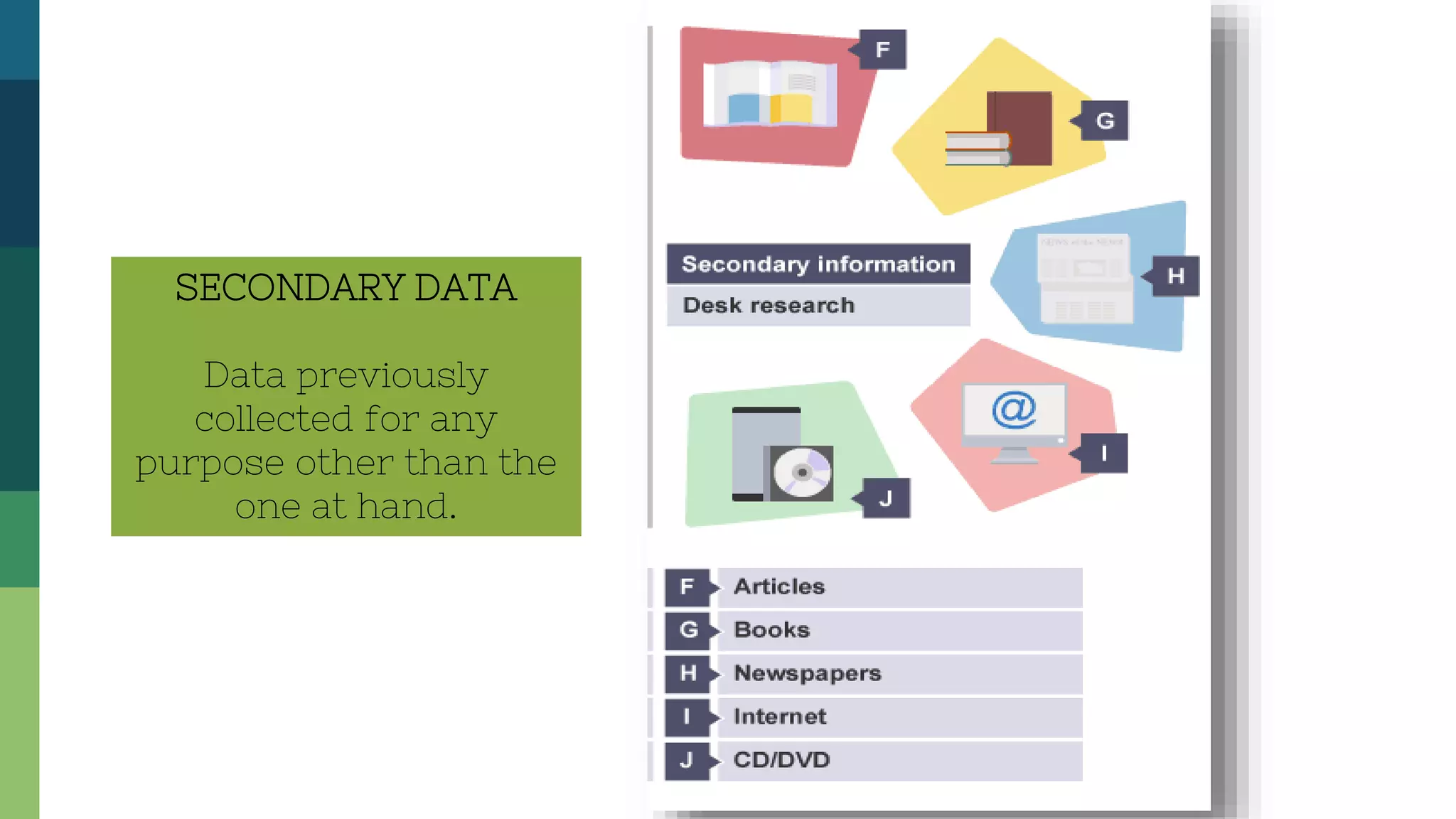
The document outlines the key steps in conducting research:
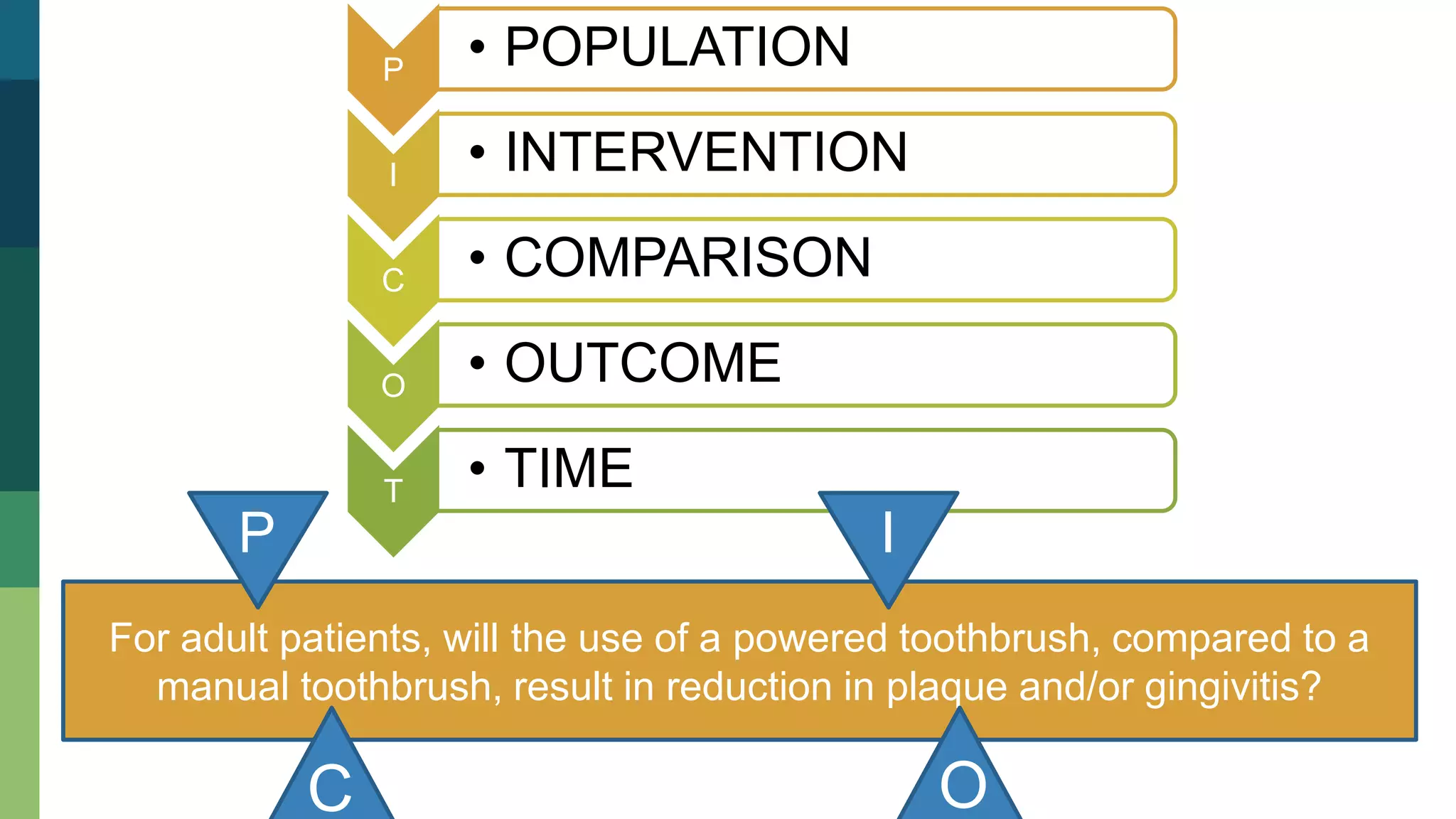
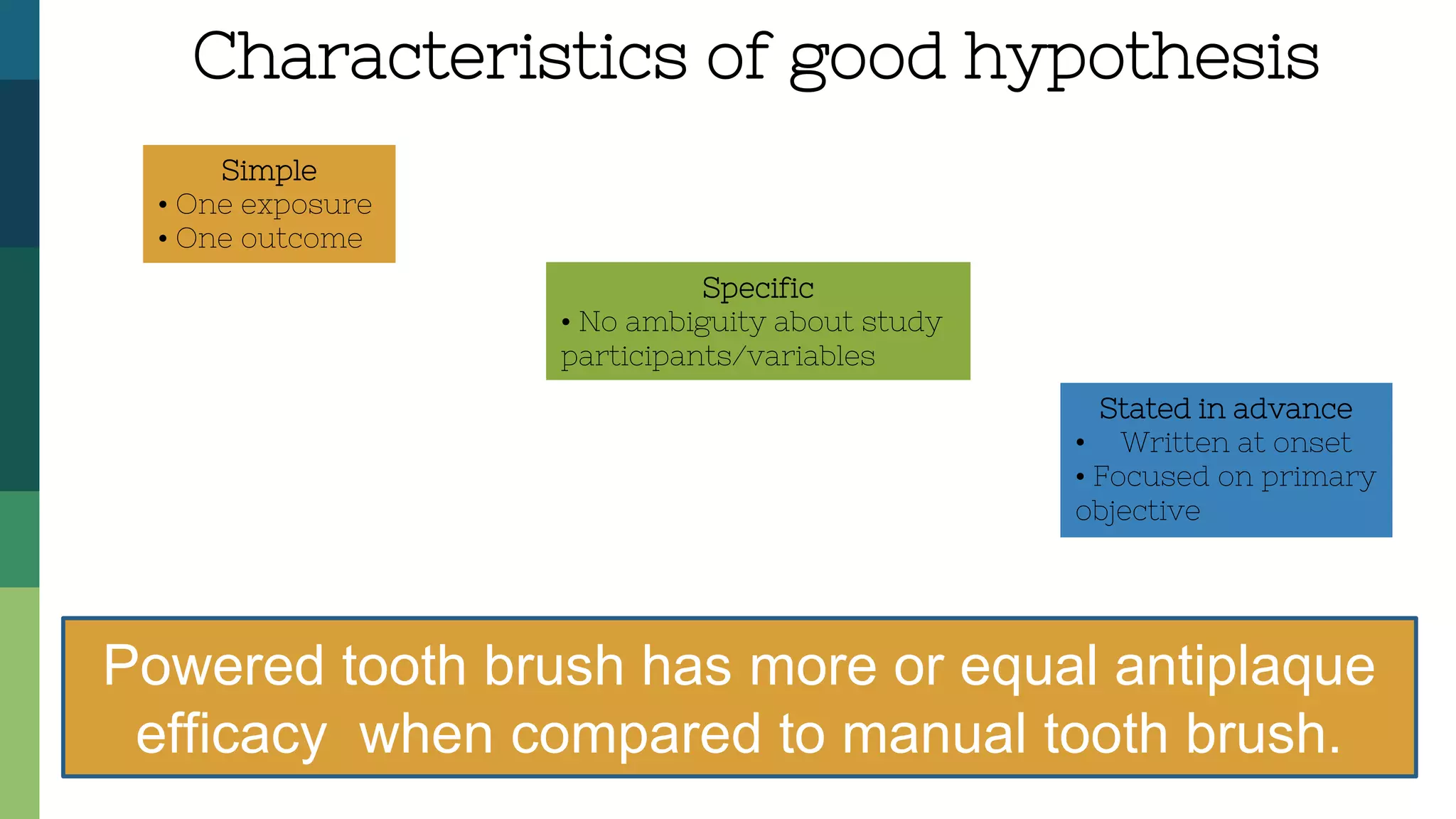
1) Choosing a topic of interest and reviewing relevant literature to form a research question and hypothesis.
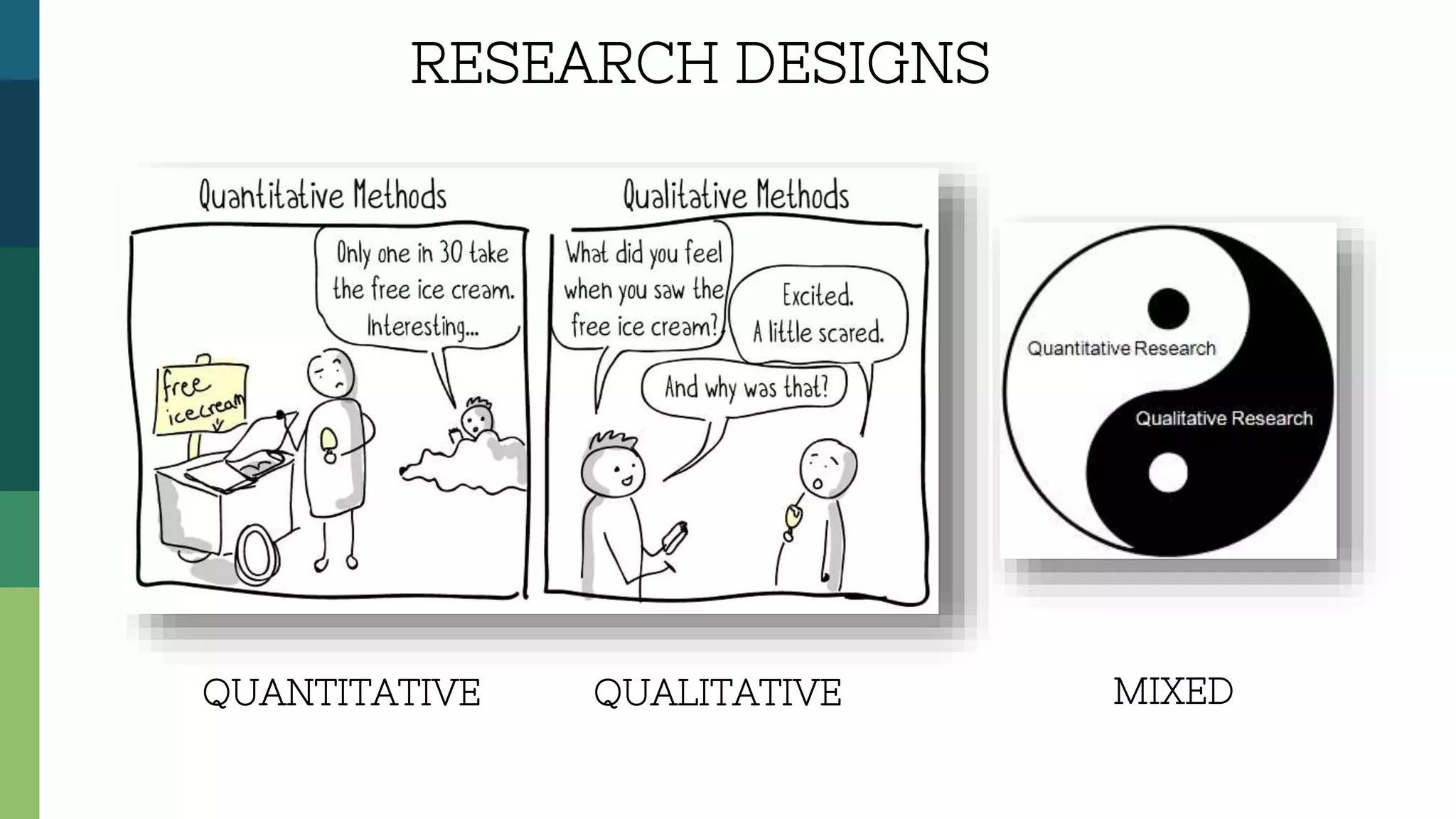
2) Developing a research design that determines how data will be collected, such as through qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods.
3) Implementing the study by collecting and analyzing data, then preparing and publishing a report of the findings. The goal is to advance scientific knowledge while upholding high ethical standards throughout the research process.