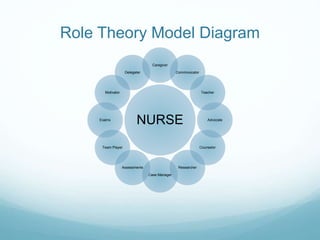
This document summarizes two nursing theories - Human Caring Theory and Role Theory - and their application to clinical practice. Human Caring Theory, developed by Jean Watson, focuses on compassionate care, dignity, and healing relationships between nurses and patients. Role Theory examines how individuals behave in social and work situations. The document compares the key concepts of each theory and provides examples of how they inform nursing assessments, diagnoses, and interventions. It also discusses areas where further research is needed, such as boundaries in caring relationships.