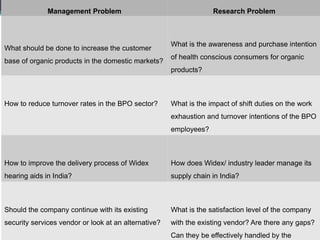
The document discusses various aspects of business research methods. It defines business research as the systematic and objective process of generating information to aid in making business decisions. Some key points include:
- Business research involves acquiring information and knowledge for professional or commercial purposes such as determining opportunities and goals for a business.
- It must be conducted in an objective manner and be detached from bias.
- There are different types of research including descriptive, analytical, applied, fundamental, quantitative, qualitative, conceptual, and empirical.
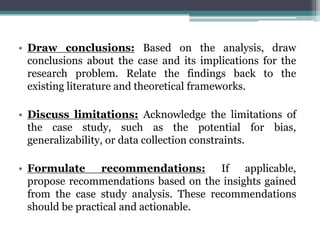
- The business research process involves formulating the problem, conducting a literature review, developing hypotheses, designing the study, collecting and analyzing data, testing hypotheses, and reporting conclusions.