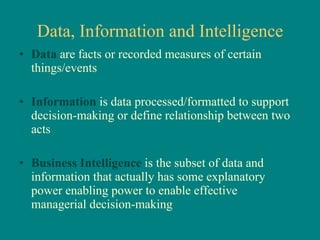
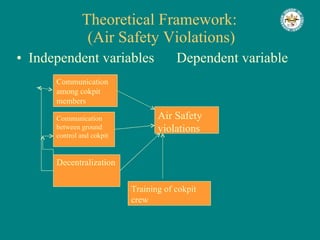
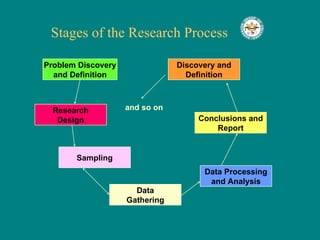
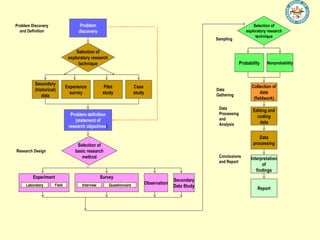
The document discusses the importance of effective communication in organizations. It outlines key strategies for improving interpersonal interactions and emphasizes the role of clarity and active listening. Additionally, the document highlights the positive impact of strong communication on team collaboration and overall organizational success.



































































![Thank you Dr. Muhammad Ramzan [email_address] , 03004487844](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week1-businessresearchprocessdesignandproposal-120207041816-phpapp01/85/business-research-process-design-and-proposal-76-320.jpg)