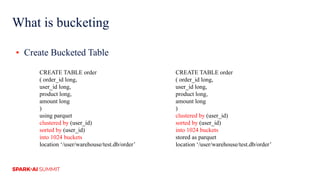
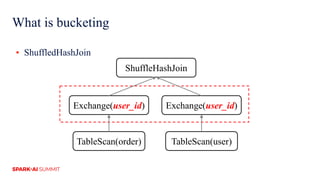
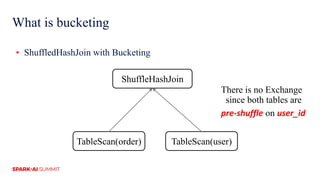
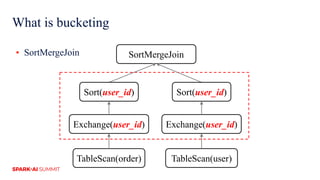
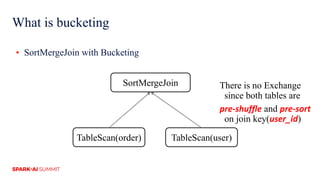
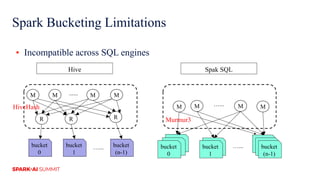
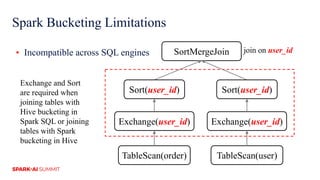
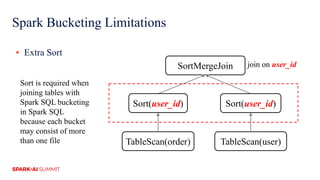
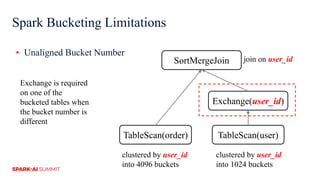
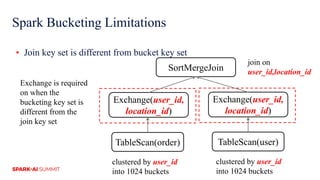
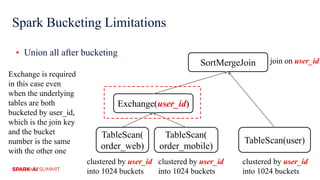
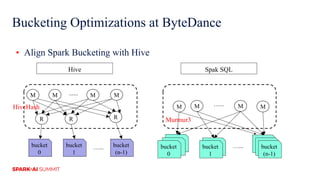
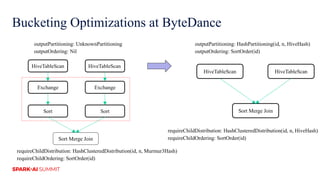
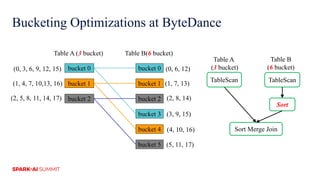
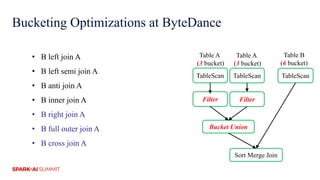
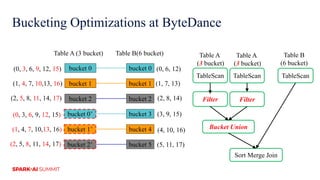
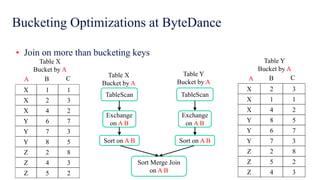
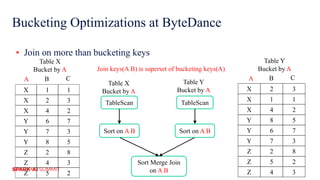
The document discusses improvements in Spark SQL performance through bucketing optimizations implemented by ByteDance's data engine team. It covers the limitations of Spark bucketing, such as small file generation and incompatibility across SQL engines, while also detailing strategies for aligning Spark bucketing with Hive's mechanisms. Additionally, the document presents various optimizations to enhance bucketing efficiency in large-scale data processing scenarios.