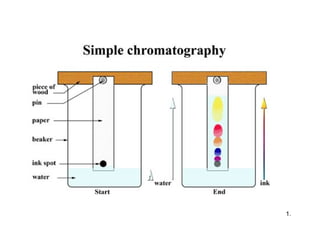
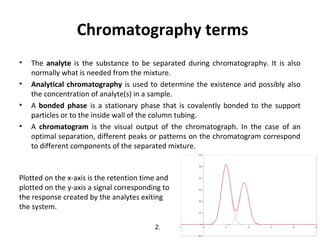
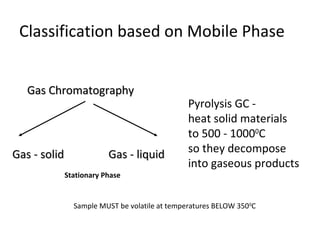
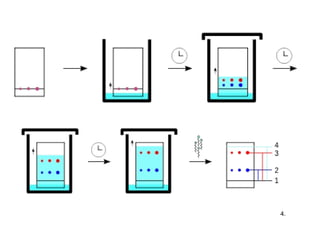
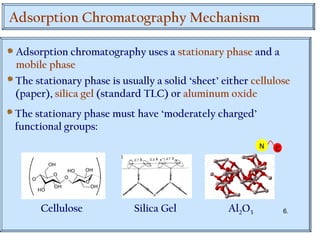
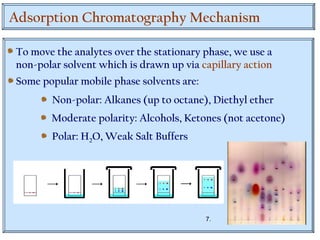
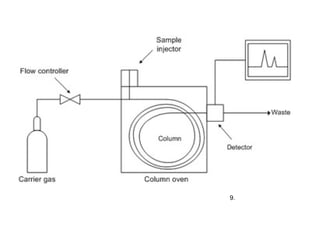
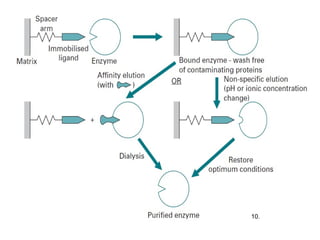
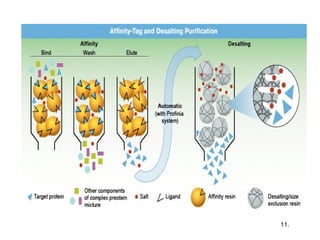
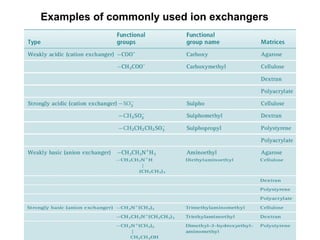
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures by distributing components between two phases - a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The mixture is dissolved in the mobile phase which carries it through a column containing the stationary phase. Components travel at different speeds depending on how they partition between the phases, allowing separation. Chromatography can be used for analytical purposes to determine the presence and proportions of components, or preparatively to purify components for further use. Key terms include the mobile phase, stationary phase, retention time, and resolution.