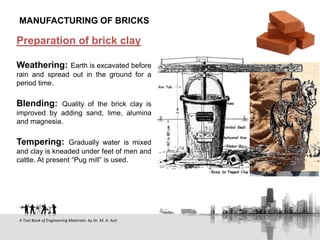
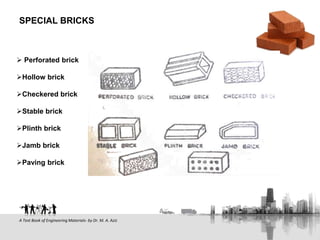
This document discusses bricks, including their manufacturing process and key properties. It describes how chemical composition, clay preparation, drying, and burning affect brick quality. Ideal bricks are uniform in color, size and shape, compact, crack-free, and withstand wetting without changing volume. The document also outlines common brick classifications, sizes used in Bangladesh, and special brick types.