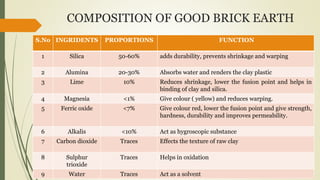
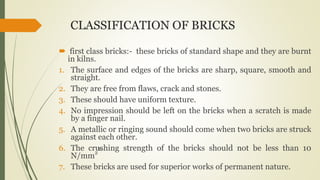
The document provides an overview of bricks, detailing their types, qualities, composition, and uses. It classifies bricks into four categories based on their characteristics and applications, highlighting first and second class bricks for permanent structures and third and fourth class bricks for temporary uses. Additionally, it outlines the ideal composition of brick earth and the necessary qualities for good brick-making.