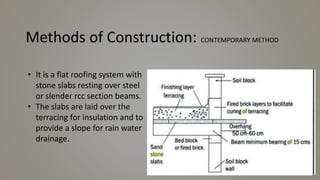
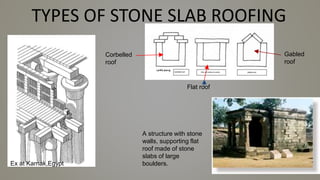
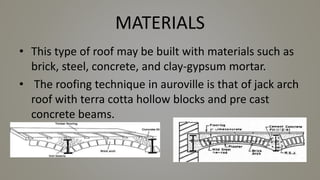
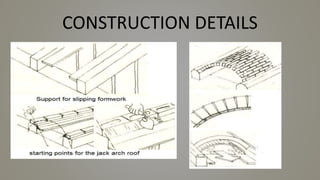
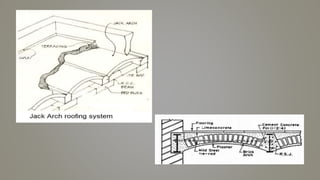
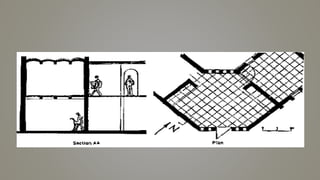
Stone slab roofing, jack arch roofing, Madras roofing, and deck roofing are alternative roofing materials that can replace conventional reinforced concrete roofing. Stone slab roofs used large flat stones laid without mortar traditionally, while jack arch roofs used a flat structural element to provide support. Madras roofing involved wooden beams with bricks and plaster to create a sloped roof. Deck roofing consisted of flat open roof areas made of materials like steel, wood, or concrete to support vertical loads and weather barriers. These alternative roofing methods are historically appropriate, cost effective, and suitable for various climates.