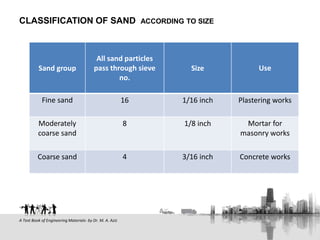
The document discusses the characteristics, types, and uses of sand in construction, including pit sand, river sand, sea sand, and crushed stone sand. It emphasizes the properties of good sand, such as cleanliness, durability, and absence of impurities, and details methods to test for silt, clay, and organic matter. Recommendations for best practices in sand selection and usage for various construction applications are also provided.