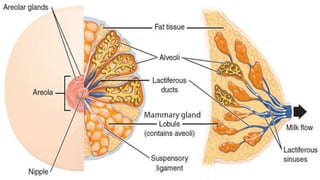
The document discusses breastfeeding, including its benefits for both mother and baby. It recommends exclusive breastfeeding for six months, then continuing while introducing other foods for up to two years or longer. Breast milk provides optimal nutrition for newborns and protects against disease. The document outlines proper breastfeeding techniques and potential issues for mothers and babies, as well as dietary guidelines to support breastfeeding.