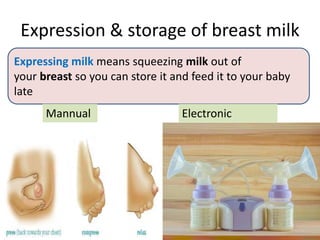
Human milk storage and banking involves expressing, collecting, processing, and distributing breast milk to support infants who cannot be breastfed directly. Milk is expressed manually or electrically and stored safely in the refrigerator or freezer. Donor milk undergoes pasteurization and screening before being distributed to hospitals. The milk is labeled and stored according to guidelines to ensure its safety and quality for premature and sick infants. Well-established human milk banks play an important role in supporting the nutritional needs of high-risk newborns.













![• The International Milk Banking Initiative (IMBI),
was founded at the International HMBANA
Congress in 2005.
• It lists 33 countries with milk bank programs.[6]
• Mothers' Milk Bank (MMB) says, this service
provides mothers with an alternative to infant
formula
• The World Health Organization (WHO) states
that the first alternative to a biological mother
not being able to breast feed is the use of
human milk from other sources.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanmilkstoragebanking1-200902050113/85/Human-milk-storage-banking-16-320.jpg)





![Processing
• All batches of collected raw breast milk should be
refrigerated
• Fresh raw milk should not be added to the frozen milk
• While mixing fresh raw breast milk to frozen raw breast
milk previously collected from same donor, it should be
chilled before adding to frozen milk [18].
• For sick or preterm babies, it is advisable to use a new
container for each pumping.
• Before pasteurization, pooling and mixing may be carried
out from multiple donors to ease the process of processing
and storage.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanmilkstoragebanking1-200902050113/85/Human-milk-storage-banking-23-320.jpg)





