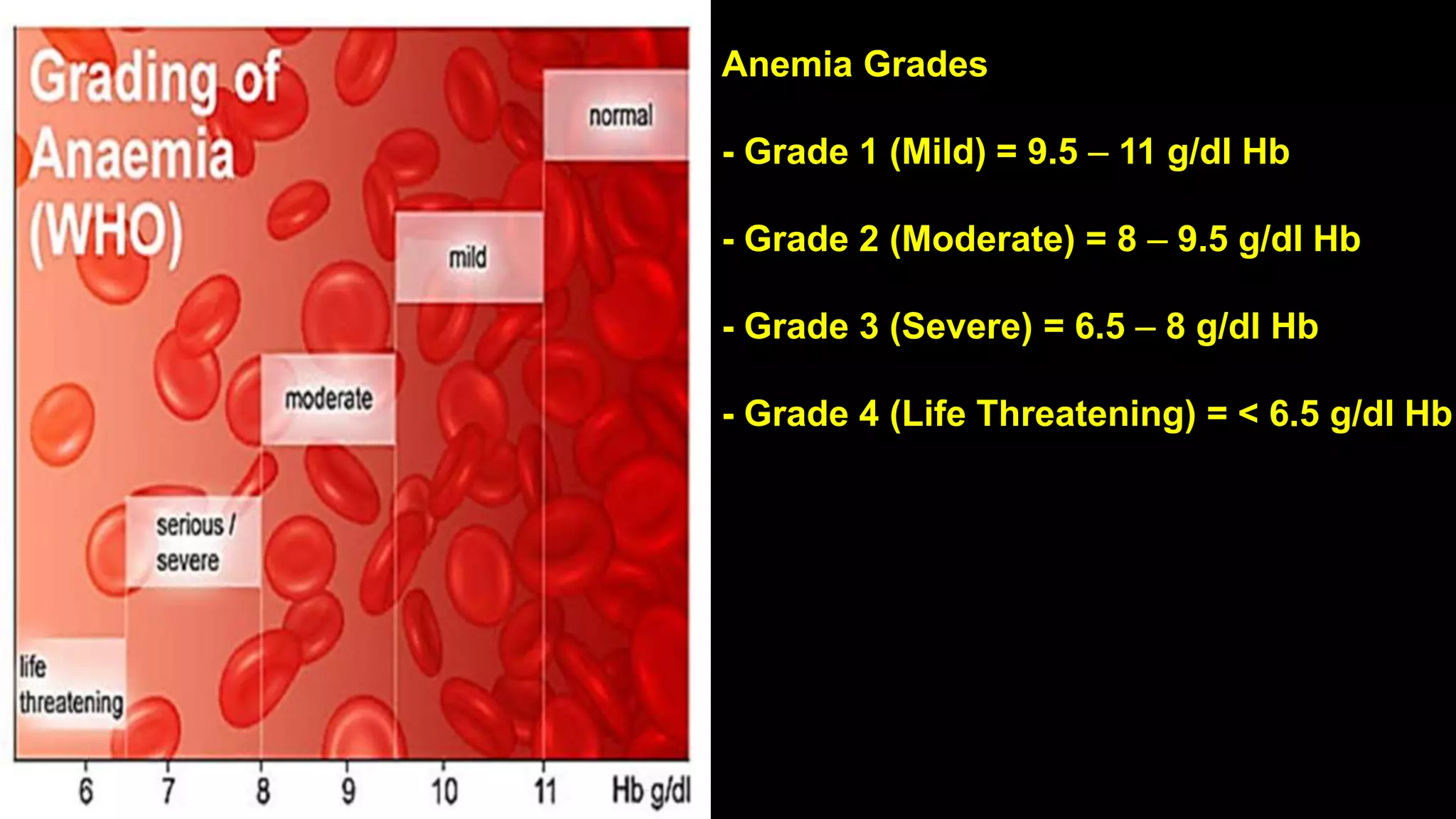
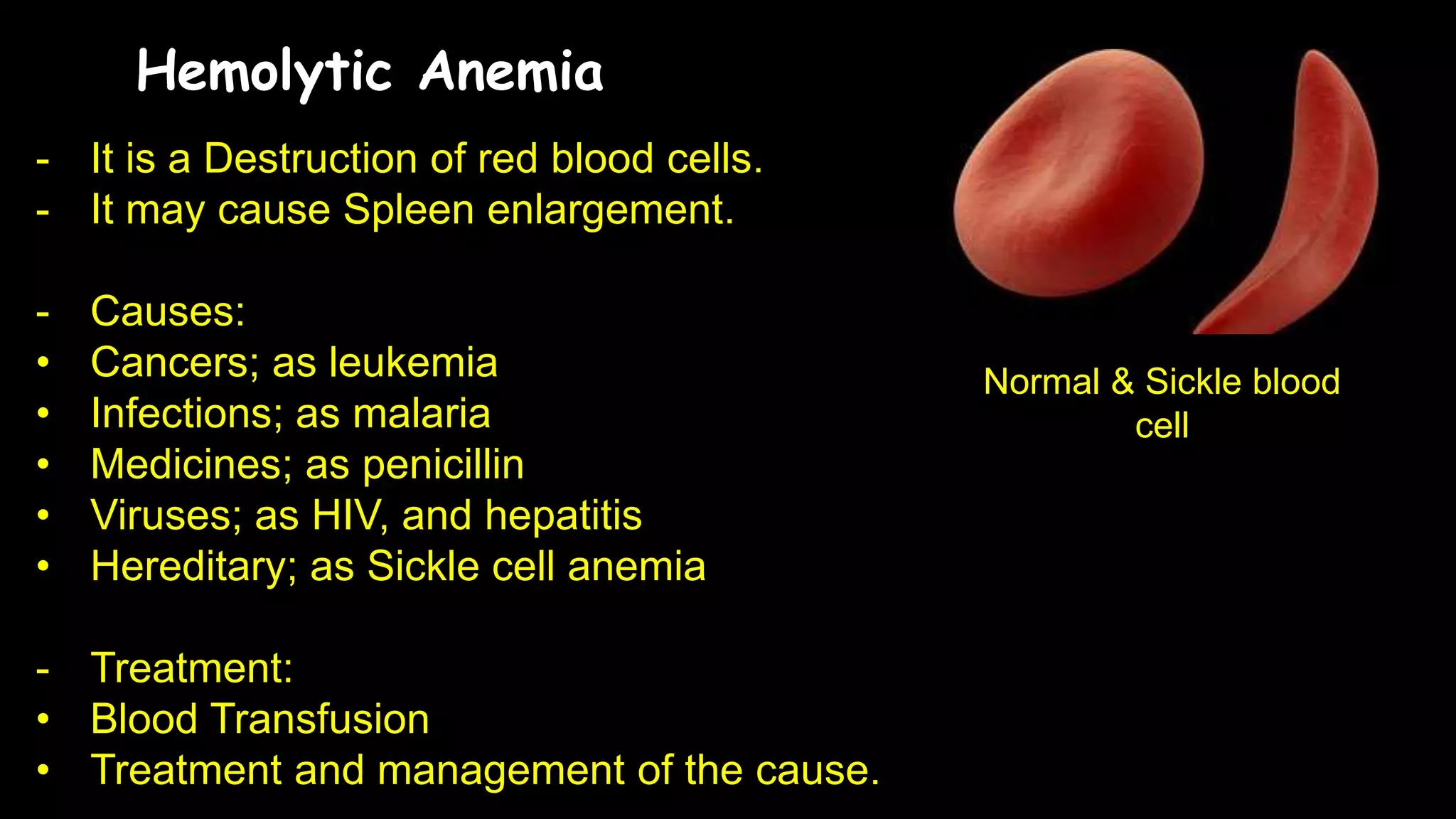
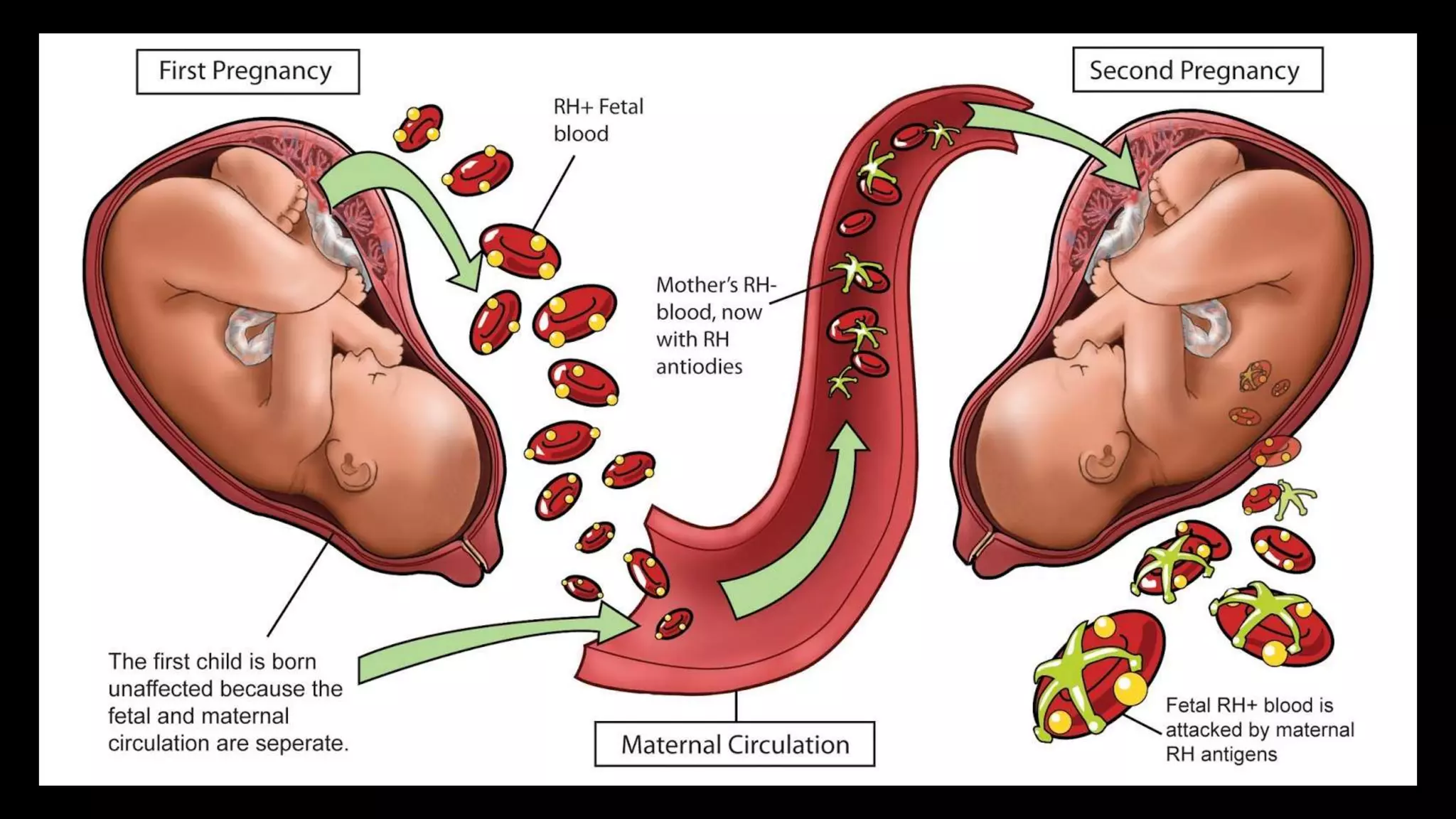
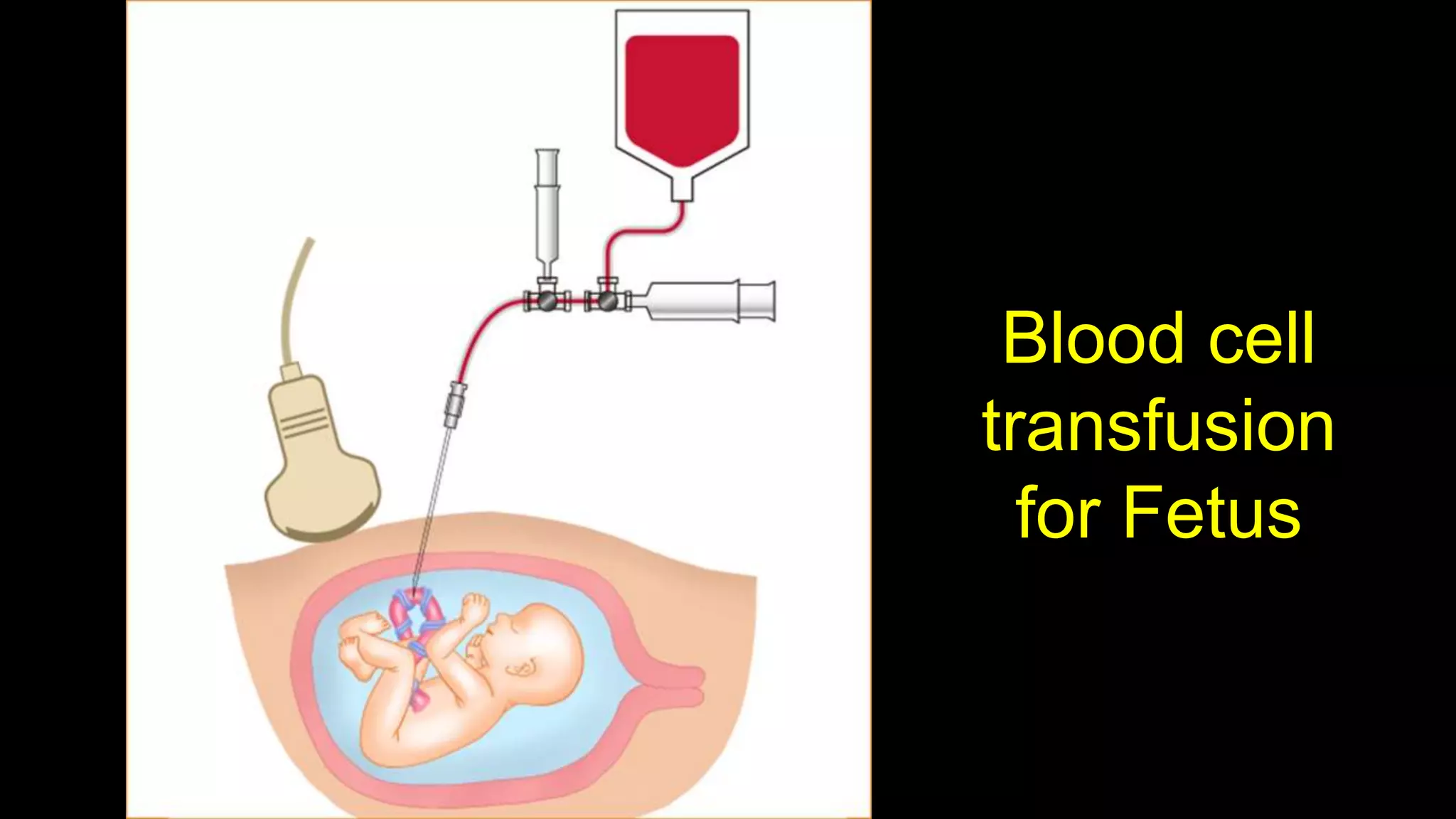
Anemia in pregnancy is characterized by inadequate healthy red blood cells to supply oxygen, with specific hemoglobin thresholds defining its severity. The condition increases risks for both mothers and babies, such as postpartum complications and neural tube defects, and is often caused by iron deficiency, folate deficiency, or vitamin B12 deficiency. Management includes dietary modifications, iron supplements, folate tablets, and blood transfusions where necessary, especially for severe cases.