This document discusses the importance and benefits of breastfeeding. It provides information on:
- The nutritional and developmental benefits of breastmilk for infants in their first 6 months of life.
- Recommendations that infants be exclusively breastfed for 6 months with continued breastfeeding for up to 2 years.
- Common challenges with breastfeeding in India such as delaying initiation, discarding colostrum, and prelacteal feeding.
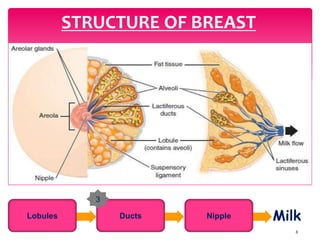
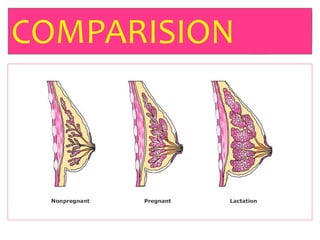
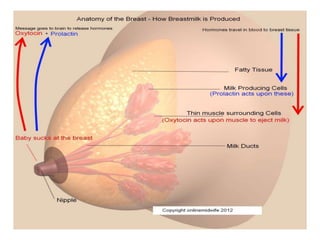
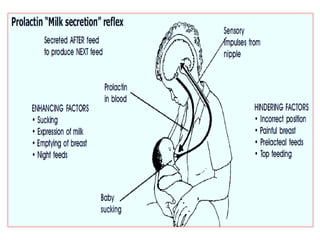
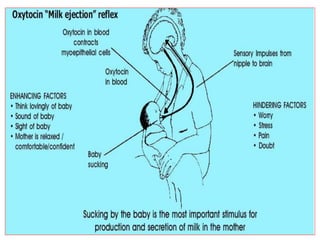
- The physiology of lactation and milk production.
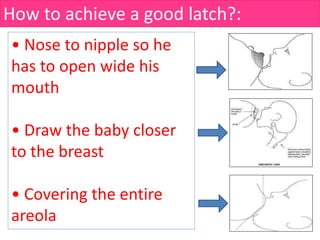
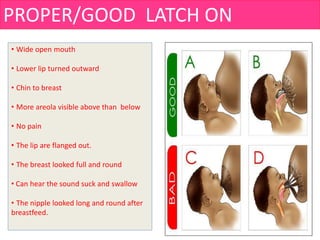
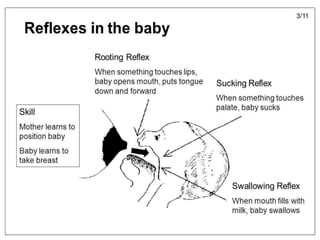
- Techniques for proper latching and positioning during breastfeeding.


![“A newborn has only three demands” :
They are warmth in the arms of its mother, food from
her breasts and security in the knowledge of her
presence.
Breastfeeding satisfies all three” . [Grantly Dick Read]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/breastfeeding-190405154056/85/Breast-Feeding-3-320.jpg)












![ADVANTAGES OF BREAST MILK
BABY
PERFECT FOOD FOR INFANTS
Easily digested and well absorbed
Protects against infection and allergies
Promotes emotion bonding b/w Baby and mother
Better brain growth
EHANCES IMMUNE SYSTEM
PROVIDES ADEQUATE H2O FOR HYDRATION
PROVIDES SUPERIOR NUTRITION FOR OPTIMUM GROWTH
RICH IN ALL NUTRIENTS, BABY
NEEDS[CHO,F,P,M,V]
REDUCE RISK OFCHILDHOOD CANCER
MOTHER
PROTECTS MOTHERS HEALTH
HELPS DELAY A NEW PREGNANCY
HELPS A MOTHER RETURN TO PRE-PREGNANCY WEIGHT
[BURN OFF EXTRA FAT ACCULUMATED DURING PREGNANCY]
REDUCE THE RISK OF BREAST AND OVARIAN CANCER
REPLENISHES CA LEVELS DURING LACTATION
DELAYS M.CYCLE / VOL OF B.FLOW DURING M.CYCLE
REDUCES THE RISK OF UTERINE BLEEDING AND HELPS THE
UTERUS TO RETURN TO ITS PREVIOUS SIZE
FAMILY
&
SOCIETY
Saves money [More economical than Artificial feed]
Promotes family planning
Decreases need for hospitalization of children's
Reduces Infant mortality](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/breastfeeding-190405154056/85/Breast-Feeding-25-320.jpg)



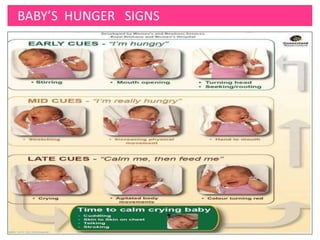
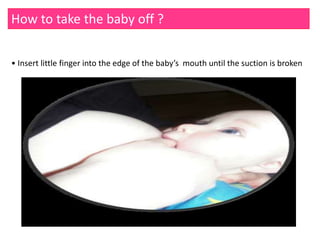



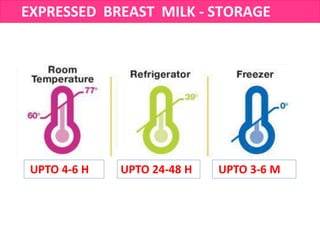
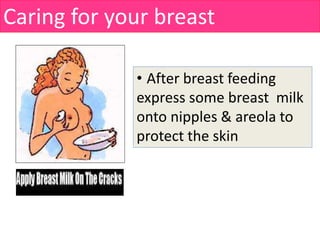

![How to breastfeed?:
Wash hands,
Be comfortable,
Relay Your shoulders.
• Head and body in straight line
• Whole body supported[Baby’s body turned
towards the mother]
• Nose to nipple
• Tummy to tummy [Baby’s body touching
mother’s abdomen]
• Support your breast. Thumb is on top and
fingers are below the breast](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/breastfeeding-190405154056/85/Breast-Feeding-38-320.jpg)