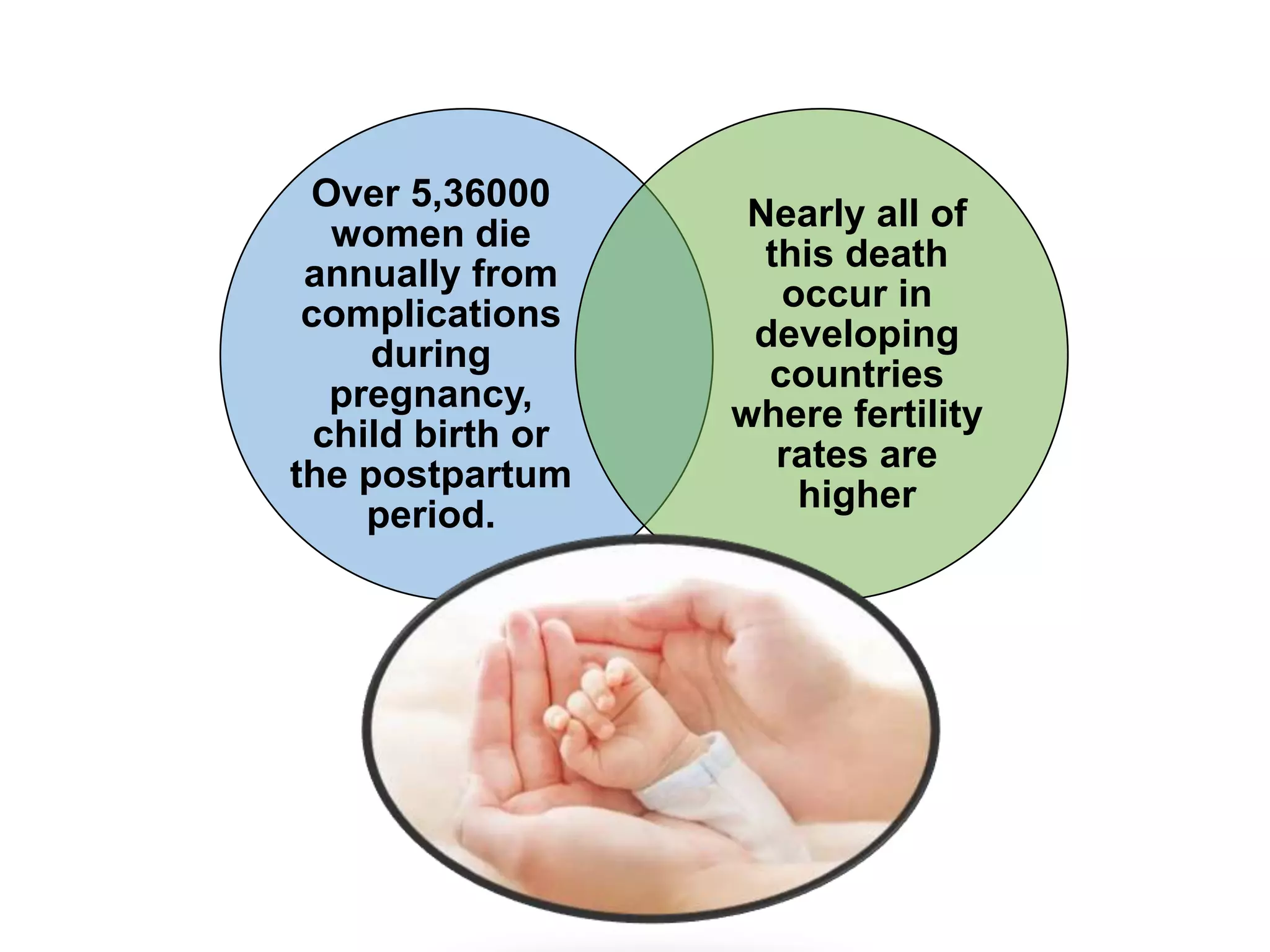
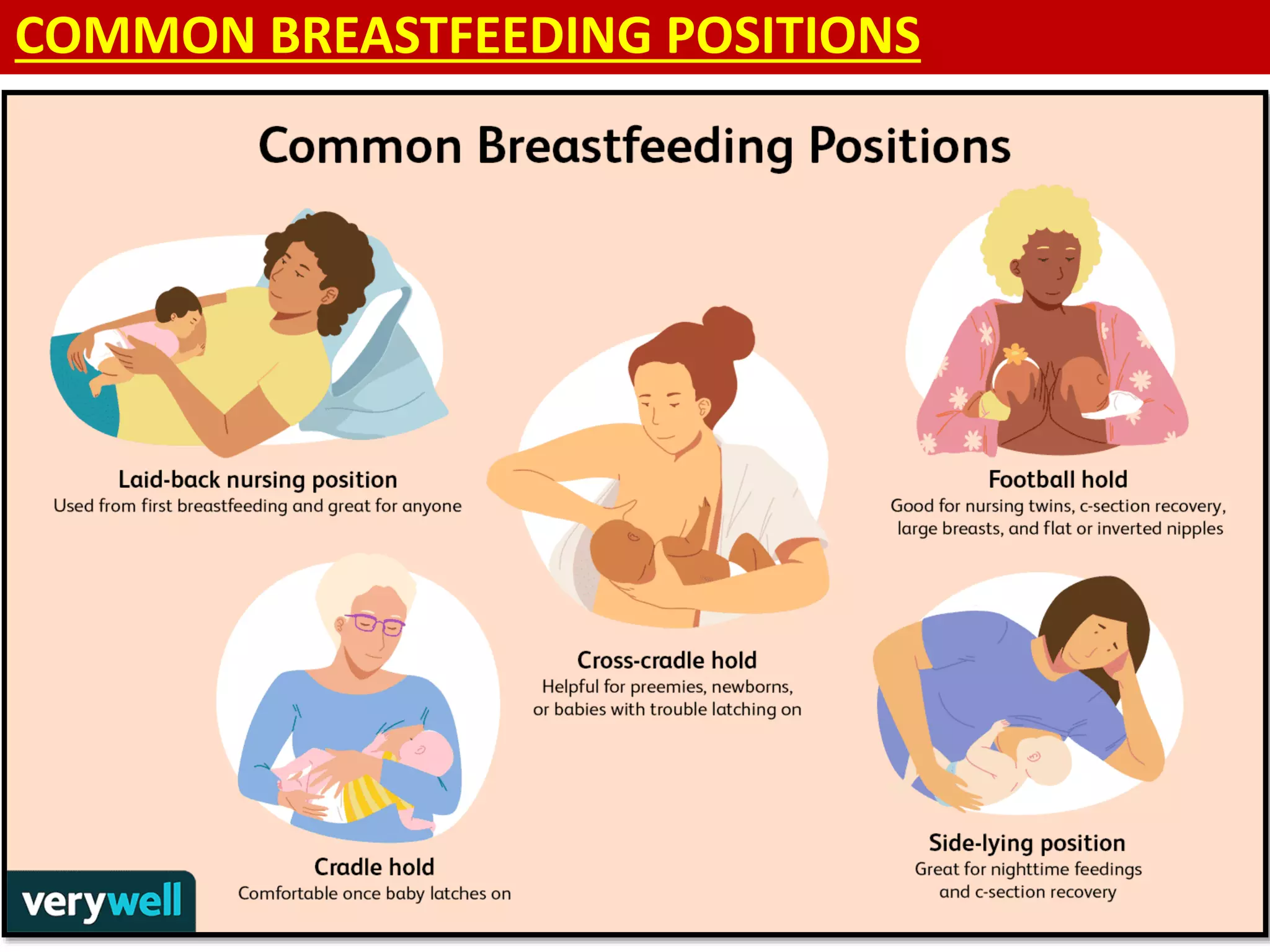
Over 536,000 women die annually from complications during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period, nearly all occurring in developing countries with higher fertility rates. Postnatal care involves examining both the mother and baby after birth and providing advice on health, breastfeeding, immunizations, family planning, and signs of complications. The mother is assessed for issues like bleeding, breast health, bladder function, bowel movements, and emotional state while the baby is examined and the mother educated on newborn care.