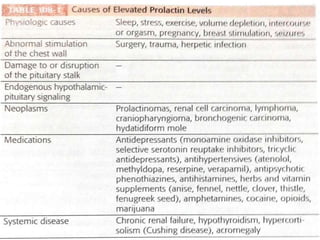
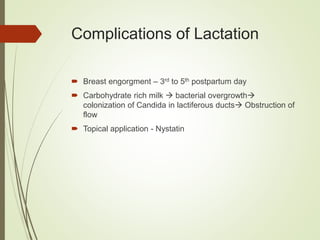
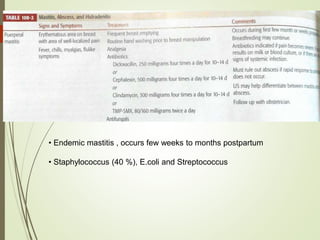
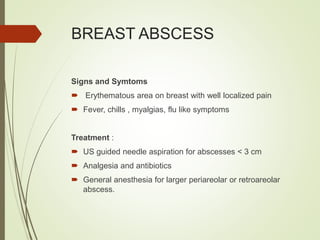
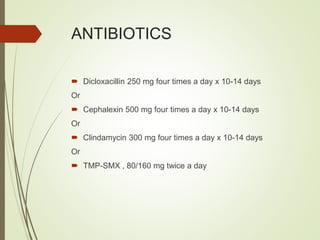
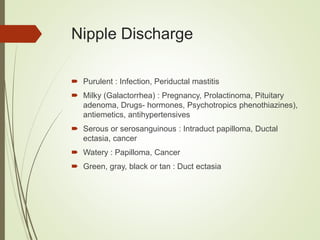
This document discusses common breast disorders and their management. It covers topics such as breast masses, pain, nipple discharge, infections, lactation complications, mastitis, abscesses, inflammatory and non-inflammatory painful conditions. Diagnosis involves history, examination and investigations like ultrasound and mammography. Management depends on the condition and may include antibiotics, analgesia, drainage procedures or surgery. Benign and malignant breast conditions are also differentiated.