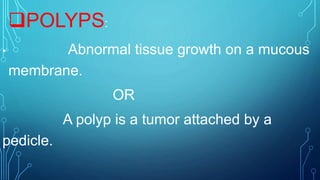
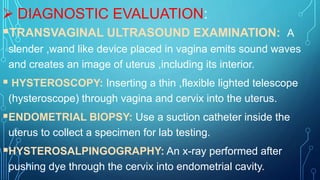
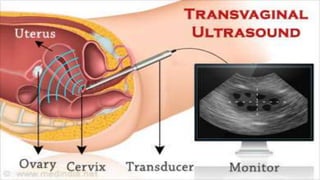
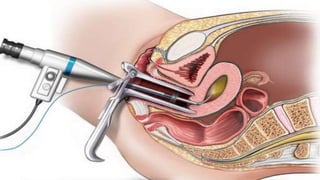
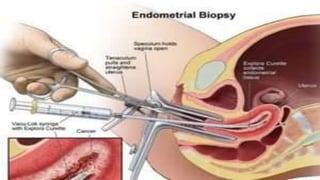
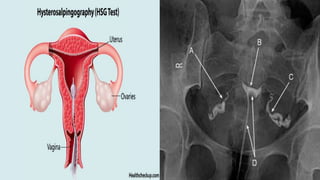
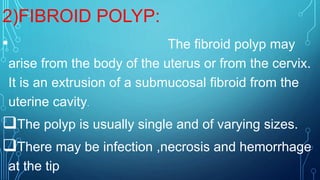
Uterine polyps are abnormal tissue growths that can form on the uterus or cervix. There are two main types: mucoid polyps arising from the endometrium and fibroid polyps arising from submucosal fibroids. Polyps may cause irregular bleeding but often have no symptoms. Diagnosis involves transvaginal ultrasound, hysteroscopy, or endometrial biopsy. Small polyps are removed by twisting with forceps, while larger polyps require procedures like hysteroscopy or morcellation. Complications can include infertility or cervical injury.