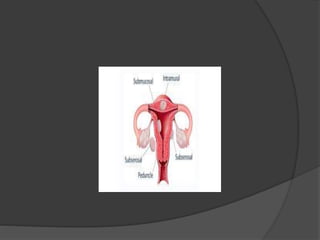
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that develop from the uterus. The most common type, interstitial fibroids, form within the uterine wall. Symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure. Treatment options include expectant management for asymptomatic fibroids, medication to reduce bleeding, and surgery such as myomectomy or hysterectomy to remove the fibroids. Ovarian cysts can also be functional or non-functional tumors of the ovaries. Functional cysts are normal occurrences during ovulation while non-functional cysts like dermoid or mucinous cysts may require surgery if symptomatic.

![DEFINITION
A uterine fibroid is a [non cancerous] tumor that
originates from the smooth muscle layer and the
accompanying connective tissue of the uterus.
Fibroids develop with the
uterine wall or attach to it .
They may grow as a single tumor
or in clusters.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cystsandfibroids-190705062122/85/Cysts-and-fibroids-2-320.jpg)