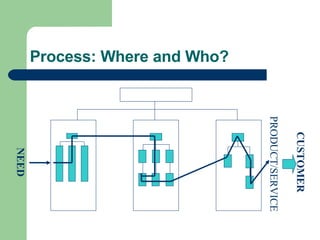
Business process reengineering (BPR) involves fundamentally rethinking and radically redesigning business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical performance measures like cost, quality, service, and speed. It seeks to optimize intra-functional and inter-functional processes within an organization and inter-organizational processes along the entire supply chain. Successful BPR requires top management support, cross-functional process teams, and treating it as a managed project with clear communication.















![Next Steps For more information email V. Mahajan at: [email_address] Or Skype at – Vmahajan Or Phone +1-630-303-9881 (VOIP Call with Voice Mail) Would like to hear from you.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/business-process-reengineering-ls-logo-1219486580310025-8/85/BPR-An-Introduction-17-320.jpg)