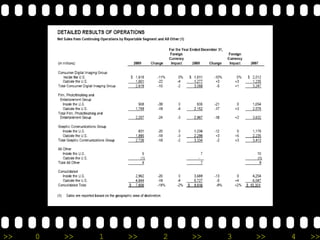
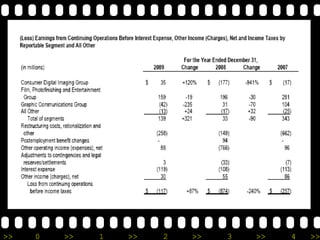
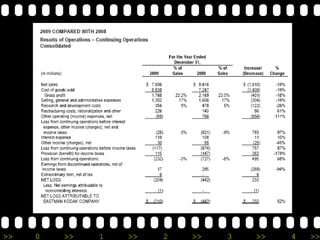
Eastman Kodak Company is a multinational corporation founded in 1880 that pioneered many innovations in photography. It grew through strategic acquisitions and new product lines but faced increasing competition in the late 20th century from Japanese firms and a decline in film use. Kodak underwent massive restructuring and workforce reductions to cut costs while transitioning to digital technologies and services.