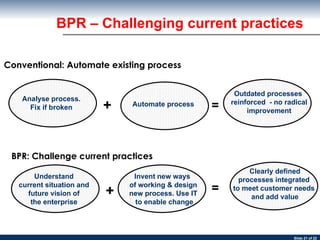
The document provides an introduction and history of business process re-engineering (BPR). It discusses how BPR aims to fundamentally rethink and radically redesign business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in performance. BPR focuses on completely redesigning processes from scratch rather than automating existing processes. It emphasizes starting without preconceptions and focusing on what processes should be, rather than what they are currently.