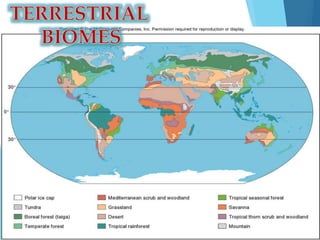
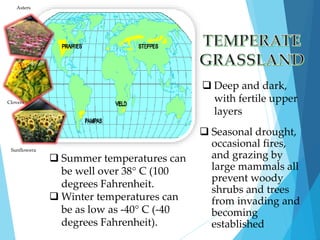
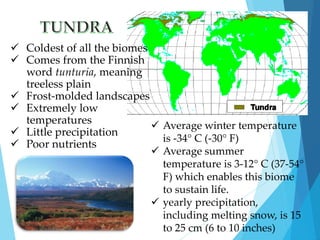
The document discusses various biomes, detailing the characteristics, adaptations of plants and animals, and the impact of human activity on these ecosystems. It emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts, such as sustainable agriculture, education, and restoration initiatives to protect biodiversity. Each biome, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, grasslands, and deserts, is described in terms of abiotic factors and species interactions.