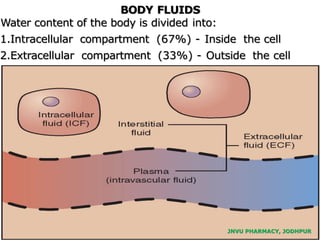
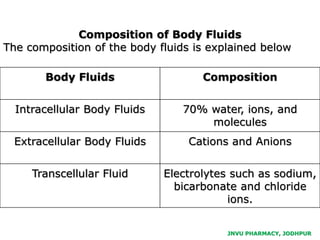
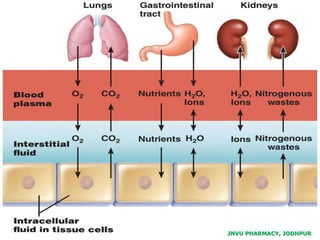
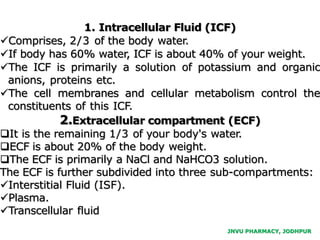
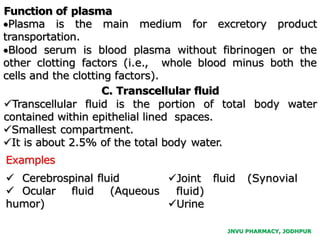
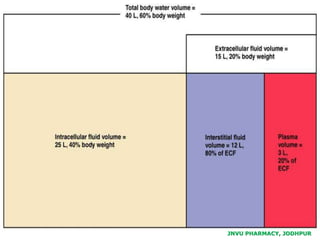
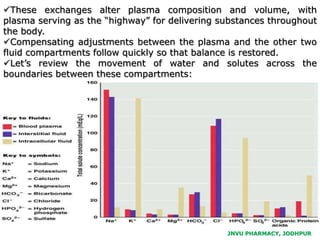
The document provides an overview of body fluids, emphasizing the roles and compositions of blood and lymph, which are critical for transportation, temperature regulation, and metabolism. It explains the distinctions between intracellular and extracellular fluid compartments, their compositions, and functions, including interstitial and plasma fluids. Additionally, the document covers factors affecting body water content and the movement of fluids and solutes across cellular membranes.