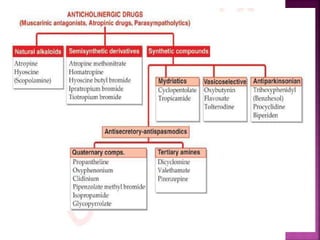
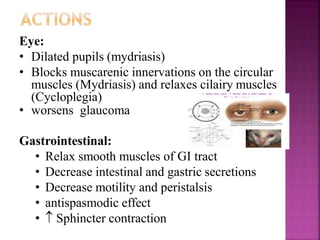
Anticholinergic drugs, also known as parasympatholytics or antimuscarinics, work by competitively blocking acetylcholine receptors in the parasympathetic nervous system. This results in effects such as decreased secretions, relaxed smooth muscles, dilated pupils, and increased heart rate. Common uses include treating asthma, COPD, peptic ulcers, overactive bladder, and Parkinson's disease. Side effects include dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention, and CNS effects like agitation. Atropine is the prototype drug and physostigmine is used as an antidote for anticholinergic overdose.