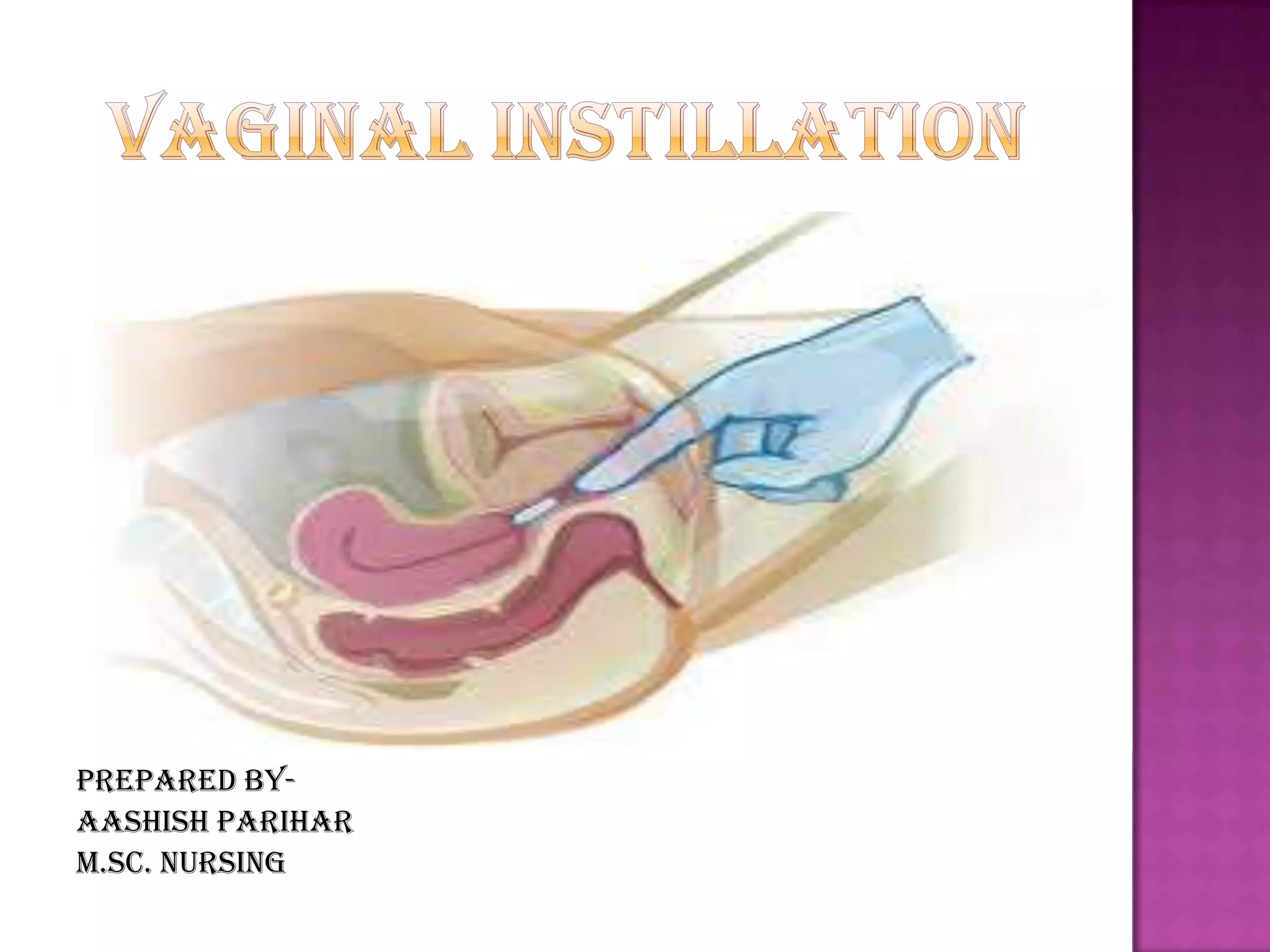
The document provides a comprehensive overview of vaginal medication administration, discussing its advantages such as prolonged release and minimal systemic side effects, while also noting disadvantages like patient incompliance and limited drug options. It outlines various forms of vaginal medication, general instructions for administration, and detailed procedural steps for both administration and aftercare. The document emphasizes the importance of aseptic technique and patient education throughout the process.