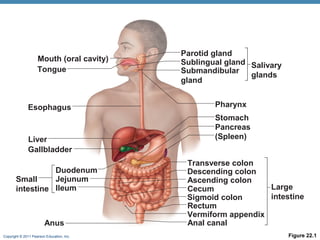
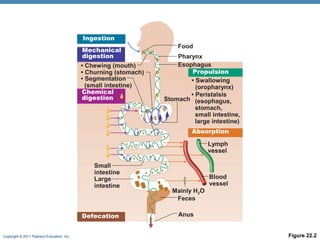
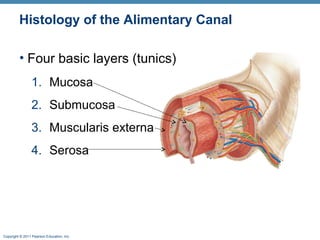
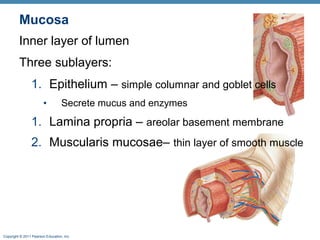
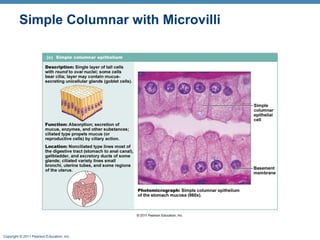
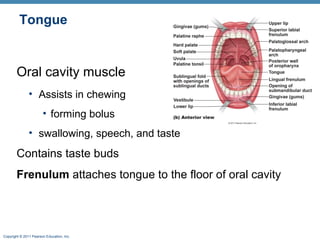
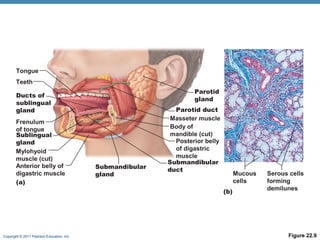
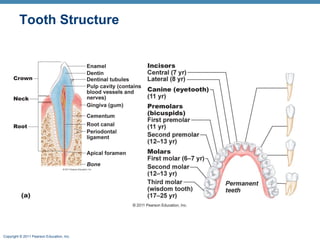
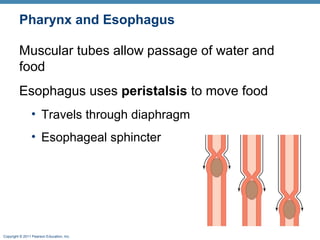
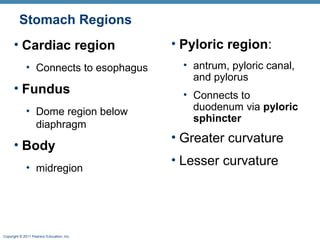
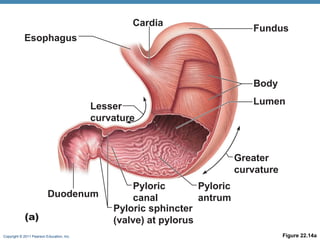
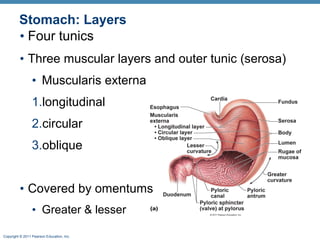
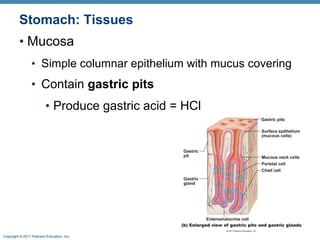
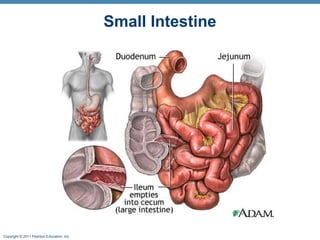
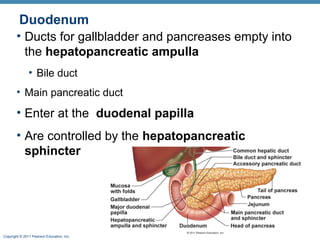
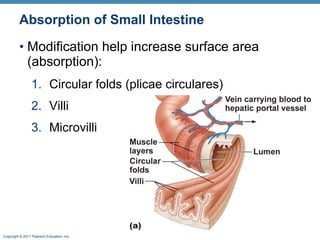
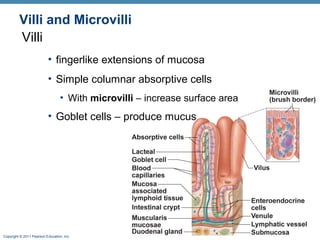
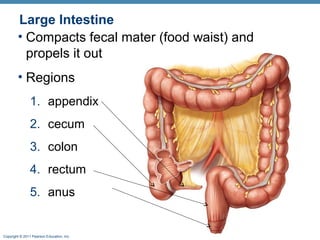
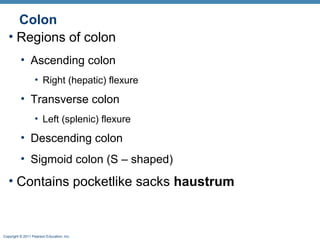
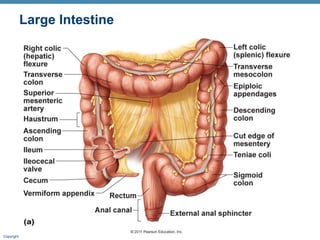
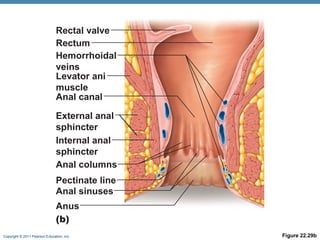
The digestive system consists of two main parts: the alimentary canal and accessory organs. The alimentary canal includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines and digests and absorbs food through mechanical and chemical processes. Accessory organs like the liver, pancreas and salivary glands produce enzymes that aid digestion. Food is ingested, propelled through the system, digested, absorbed in the small intestine, and waste is eliminated as feces in the large intestine and rectum.