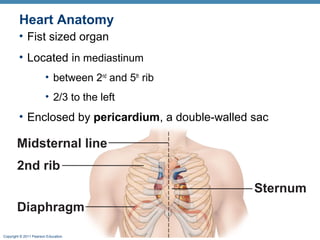
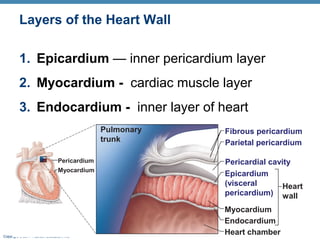
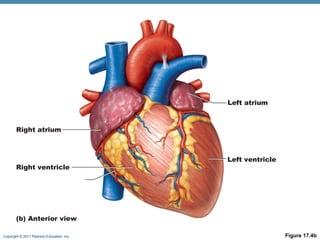
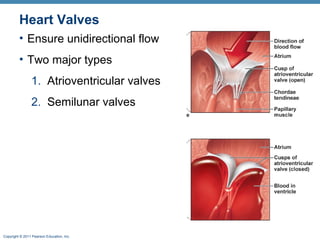
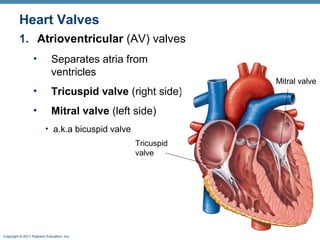
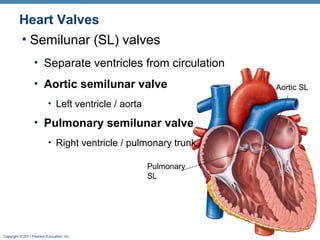
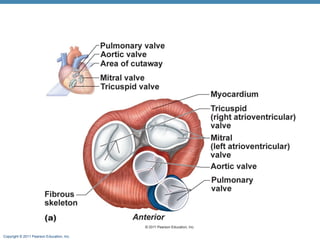
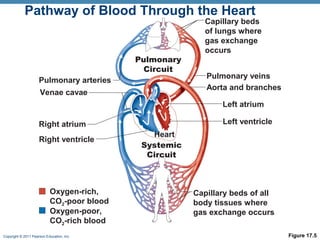
The document summarizes the anatomy and function of the heart. It describes the layers of the heart tissue, including the epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. It outlines the four chambers of the heart - the right and left atria which receive blood, and the right and left ventricles which pump blood out. It details the heart valves that ensure one-way blood flow, including the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary and aortic valves. It explains the pathway of blood through the heart in both the pulmonary and systemic circuits.