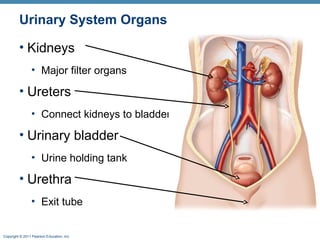
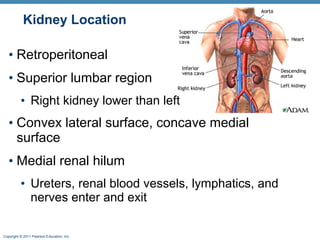
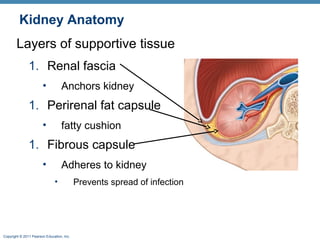
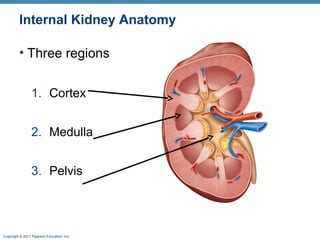
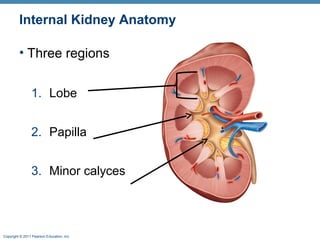
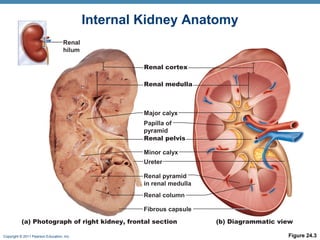
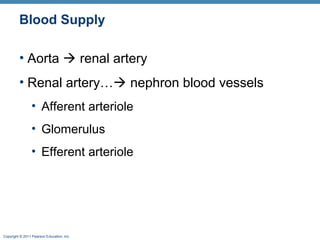
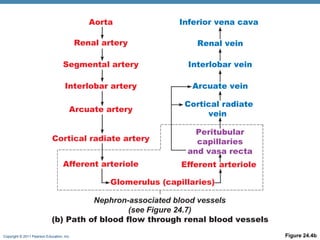
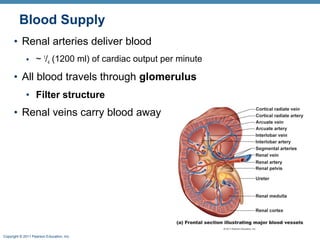
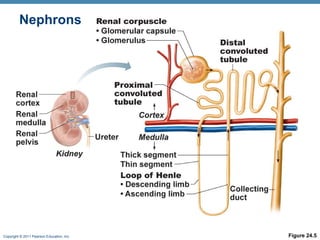
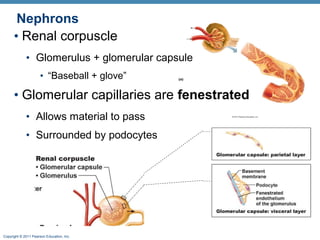
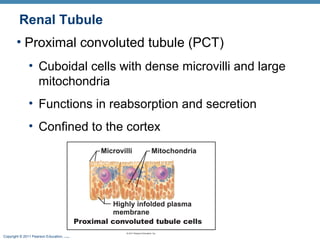
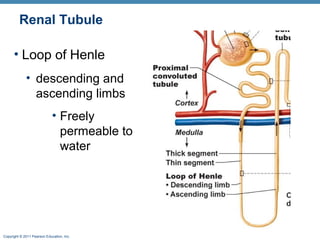
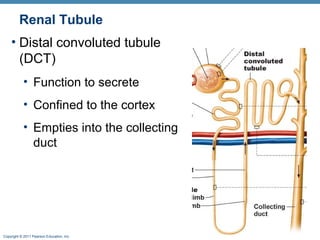
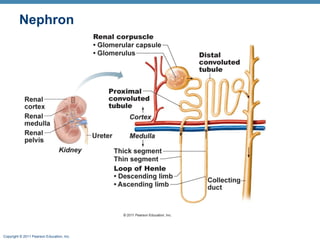
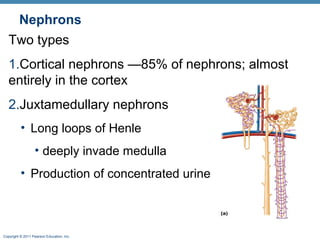
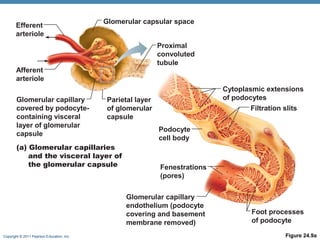
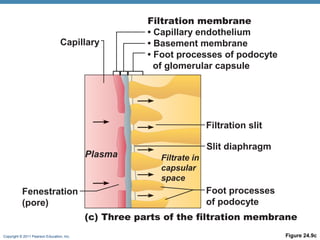
This document provides an overview of the structure and function of the urinary system. It discusses the key organs - kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. It then focuses on kidney anatomy, including internal structures like the cortex, medulla and nephrons. Nephrons are described as the functional units that form urine, consisting of a glomerulus for filtration and renal tubules for processing. The mechanisms of blood filtration and urine production by nephrons are also summarized.