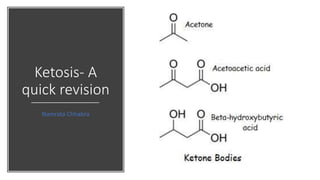
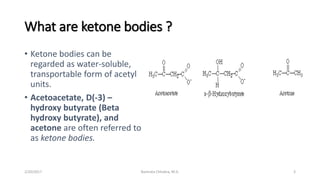
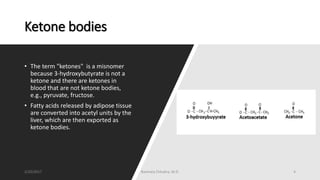
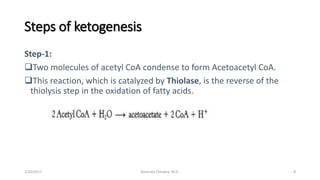
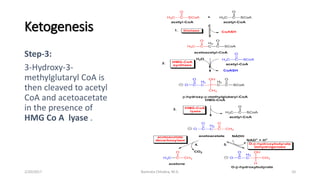
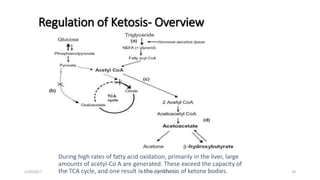
This document discusses ketone bodies and ketosis. It defines ketone bodies as water-soluble transporters of acetyl units produced in the liver from fatty acids during periods of low carbohydrate availability. The three main ketone bodies are acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. Ketone bodies serve as an alternative fuel for tissues like the brain during glucose deprivation. The document outlines the pathways of ketone body synthesis in the liver and utilization in other tissues, as well as conditions that cause excess ketone production (ketosis).