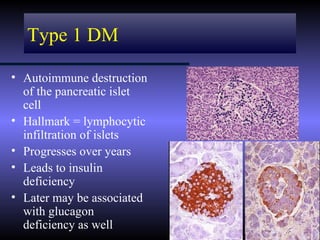
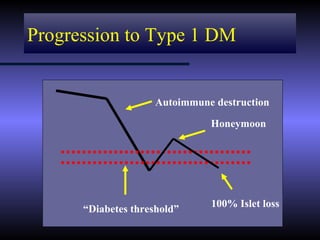
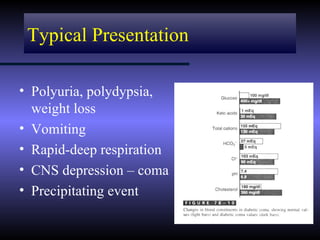
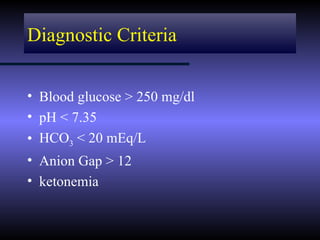
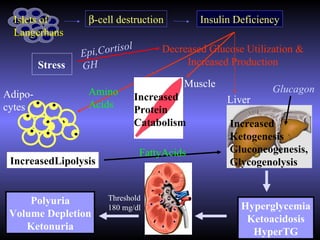
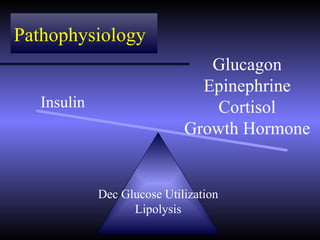
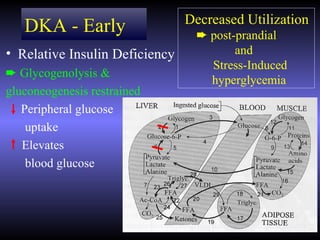
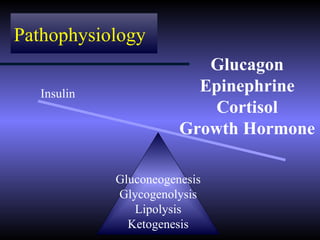
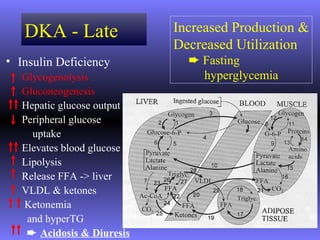
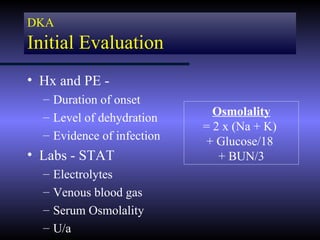
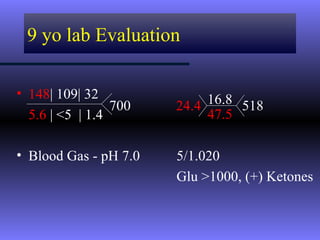
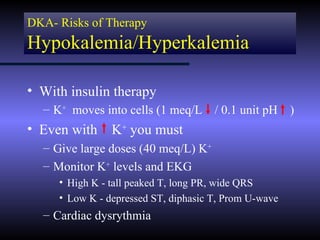
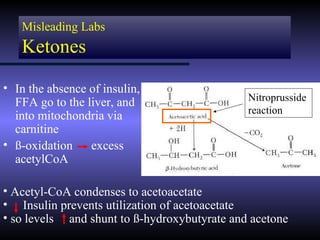
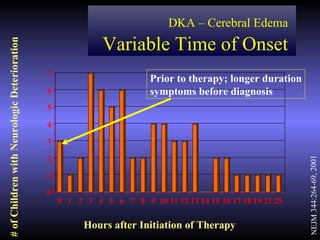
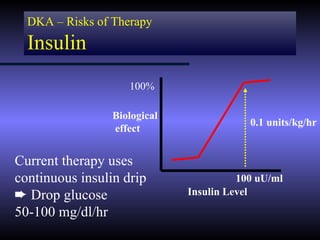
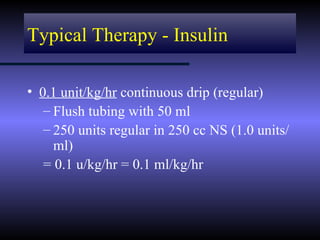
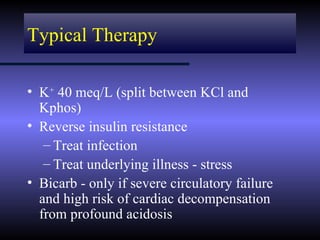
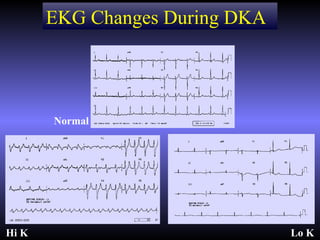
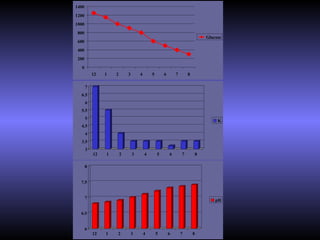
The document discusses diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), including its pathophysiology caused by a lack of insulin leading to gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and ketone production. It outlines the clinical presentation of DKA with symptoms like vomiting, rapid breathing, and altered mental status. The treatment of DKA involves rehydration with intravenous fluids, administration of insulin to promote glucose uptake and utilization and reverse acidosis, and replacing electrolyte losses with sodium and potassium.