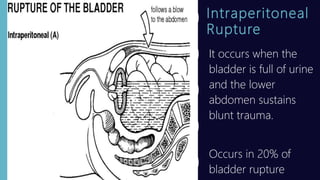
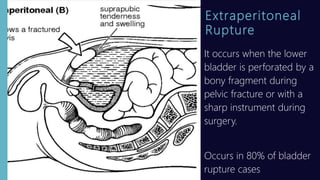
This document discusses bladder injury, including causes, classifications, clinical manifestations, diagnostic procedures, medical and nursing management. Bladder injury usually results from blunt or penetrating trauma and can be classified as contusion, intraperitoneal rupture, extraperitoneal rupture, or a combination. Signs include inability to void, hematuria, pain, and rigid abdomen. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging, and cystography. Treatment depends on type and severity of injury but generally involves stabilizing the patient, facilitating urinary drainage, controlling pain, and educating on self-care.