This document discusses the relationship between humans and the natural environment. It defines the environment as including both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components that affect human life. The natural environment consists of naturally occurring landforms, climate, soils, and minerals, while the cultural environment includes human settlements, infrastructure, and other manmade additions. The document then examines interactions within ecosystems between biotic and abiotic factors, different types of ecosystems, energy and nutrient flows, and the importance of maintaining environmental balance.






![Interactions in environmentInteractions in environment
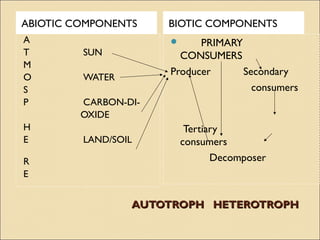
THERE ARE MANY INTERACTIONS BETWEEN
BIOTIC [LIVING] AND ABIOTIC [NON LIVING]
COMPONENTS.
ALL THE BIOTIC COMPONENTS DEPEND ON
EACH OTHER.WE BREATHE AIR THAT MEANS
THERE IS AN INTERACTION BETWEEN
US[LIVING] AND THE AIR [NON LIVING]
PLANTS MAKE PRODUCE THEIR FOOD USING
SOLAR ENERGY.THAT MEANS THERE IS AN
INTERACTION BETWEEN ABIOTIC AND
BIOTIC COMPONENTS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mannaturalenvironment-130904002302-/85/Man-natural-environment-7-320.jpg)