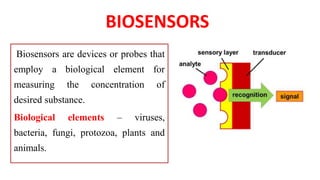
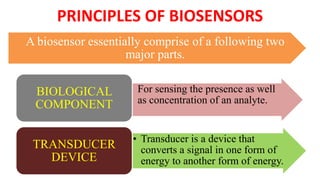
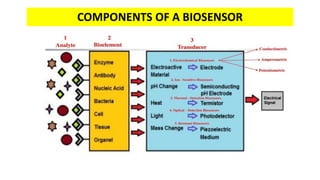
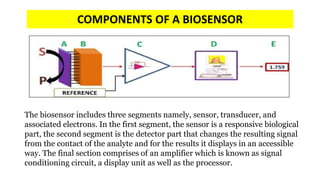
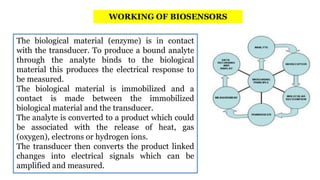
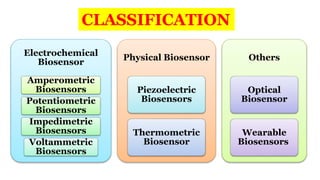
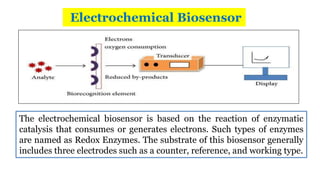
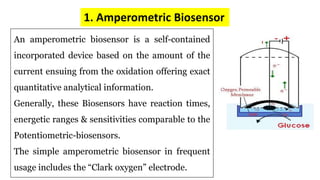
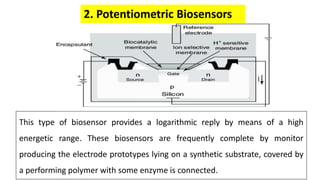
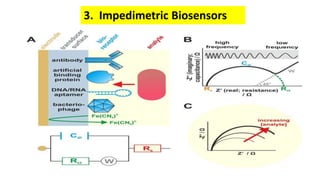
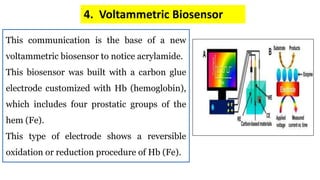
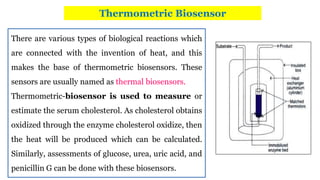
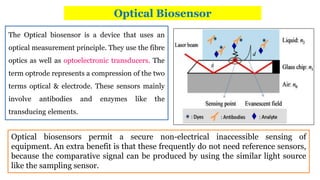
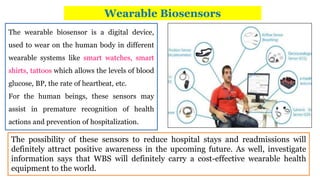
A biosensor consists of three main components: a biological recognition element, a transducer, and associated electronics. The biological element interacts selectively with the target analyte and this interaction is converted to an electrical signal via the transducer. Common types of biosensors include electrochemical, physical, and optical biosensors. Electrochemical biosensors detect the product of an enzymatic reaction that generates or consumes electrons. Physical biosensors respond to physical stimuli like mass, temperature, or acoustic waves. Optical biosensors use optical signals like fluorescence. Biosensors provide rapid, specific, and reagent-free measurement of various targets with applications in food/environmental monitoring, healthcare diagnostics, and more.