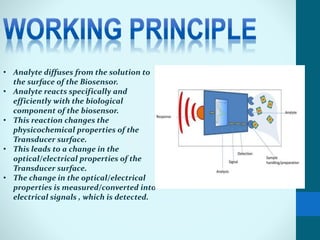
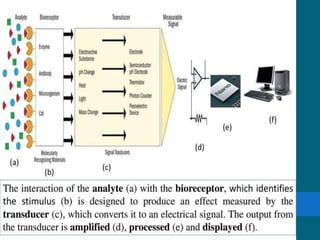
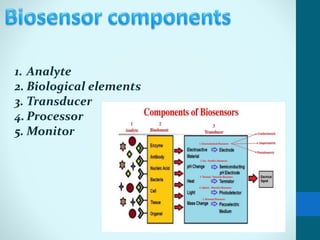
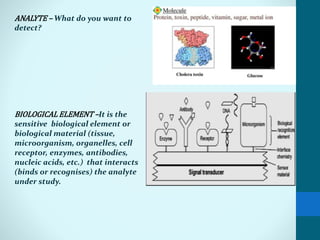
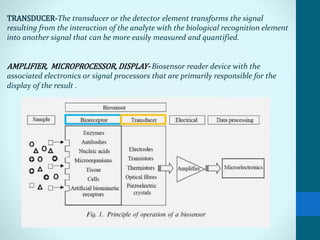
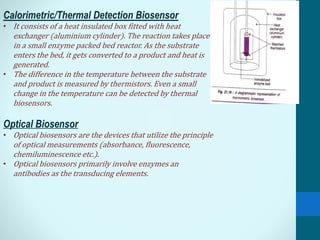
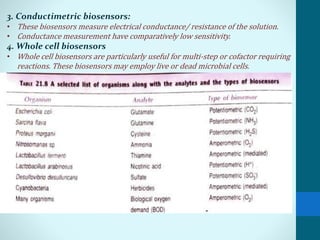
Leland Clark invented the Clark oxygen electrode, a pivotal biosensor that allows real-time monitoring of blood oxygen levels during surgery. A biosensor consists of a biological material like an enzyme or antibody immobilized on a transducer. When an analyte binds to the biological material, it produces a signal like electrons that are converted by the transducer into measurable electrical signals. Biosensors have important applications in clinical diagnostics like glucose monitoring, environmental monitoring of pollutants, and industrial processes like fermentation. Their low cost, small size, and sensitivity make them useful analytical tools.