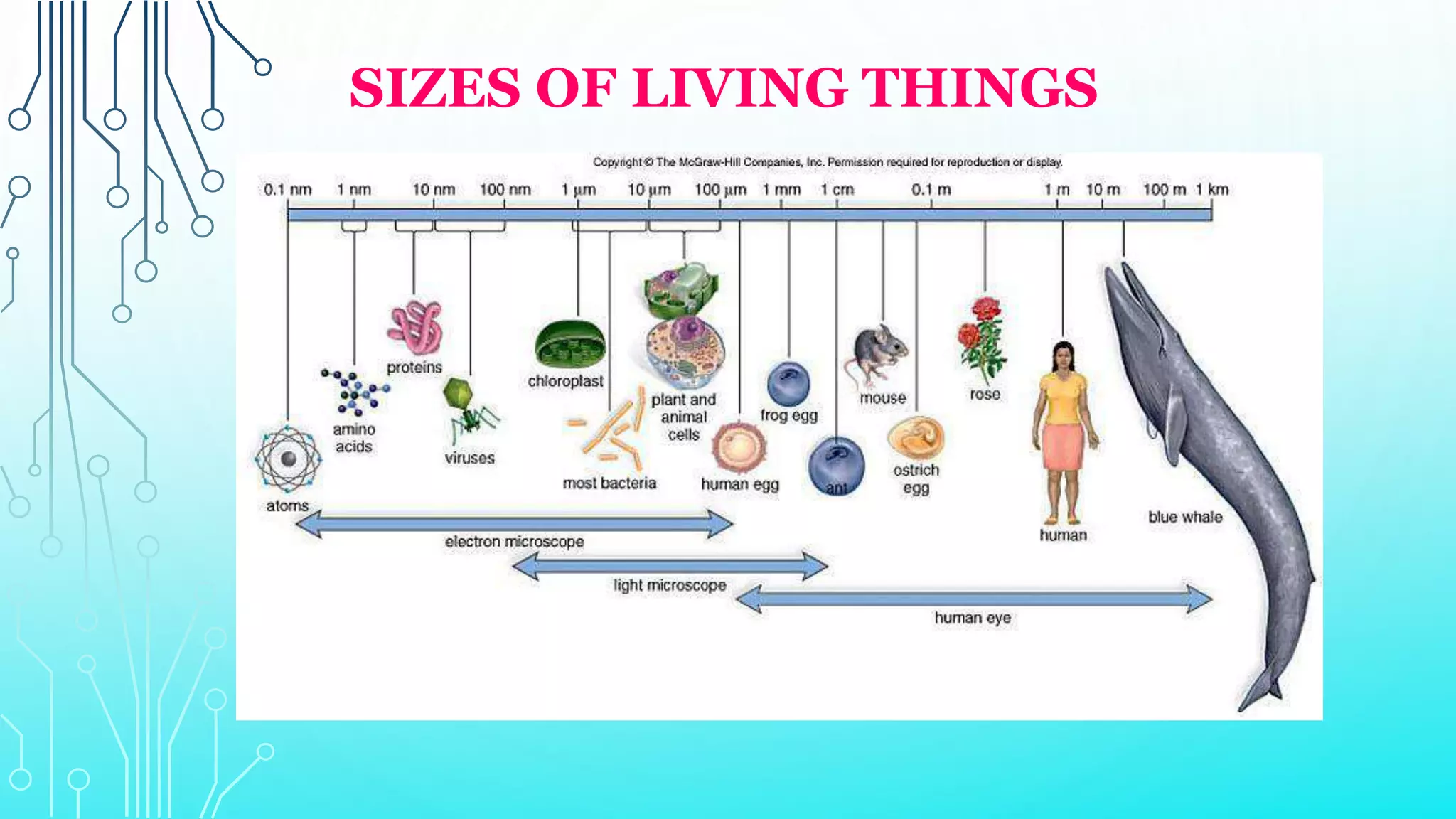
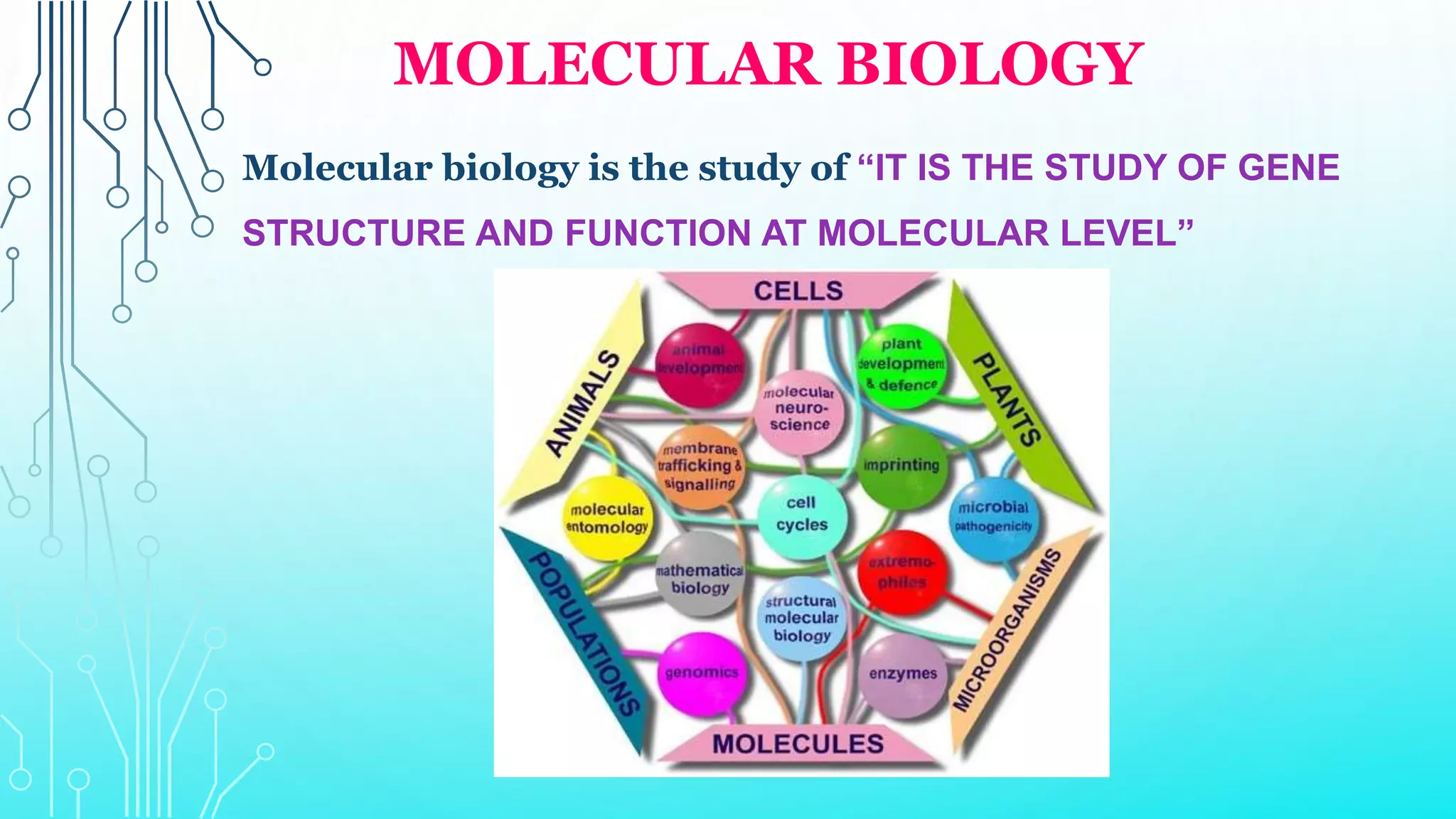
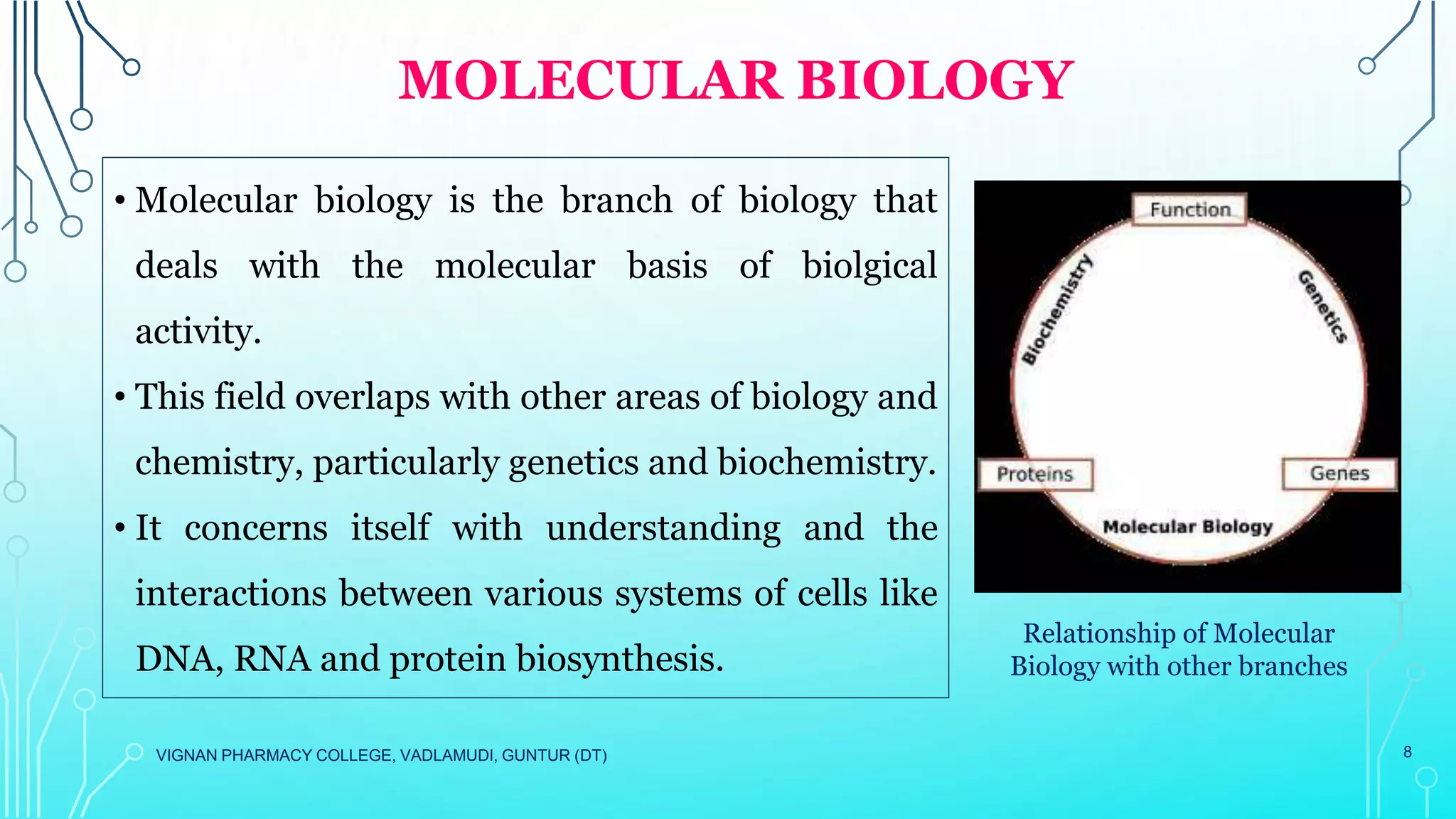
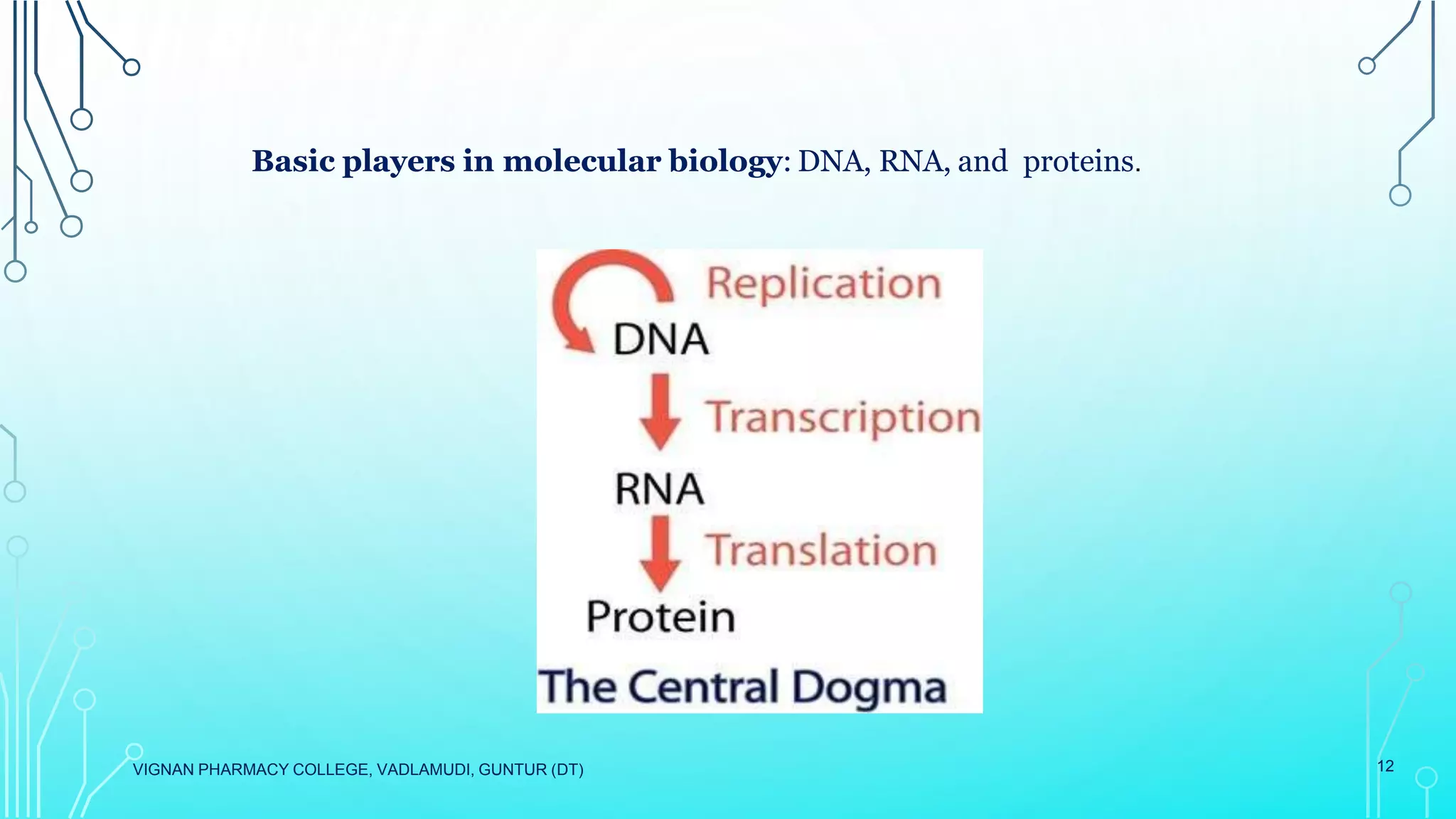
This document provides an overview of cell and molecular biology. It defines cells as the basic structural and functional units of life and describes their components and characteristics. The development of cell theory by Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow is summarized. Molecular biology is introduced as the study of gene structure and function at the molecular level, involving DNA, RNA, proteins, and their interactions. Common techniques used in molecular biology like PCR and DNA sequencing are listed.