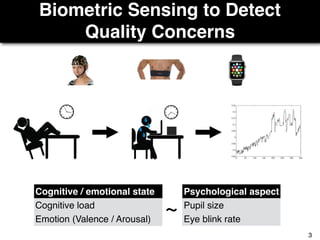
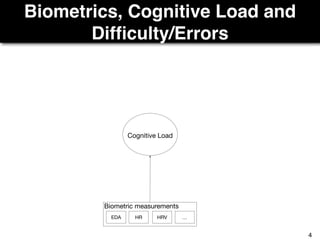
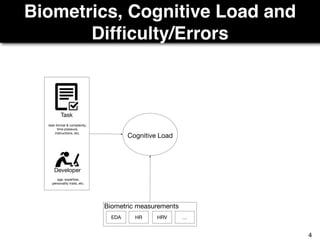
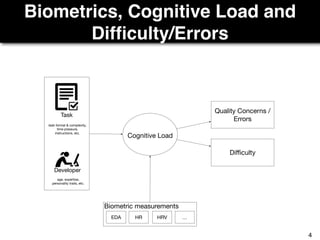
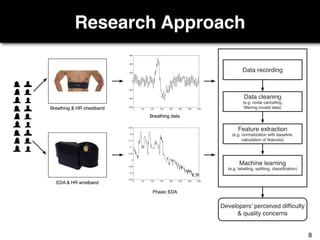
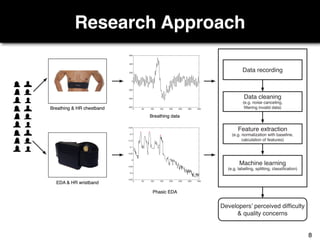
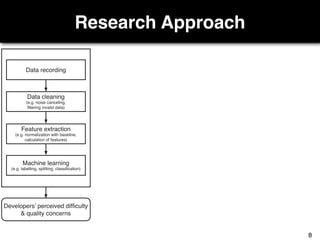
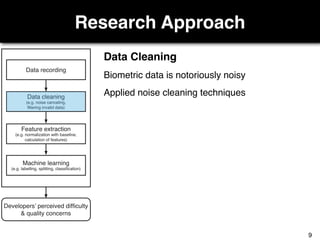
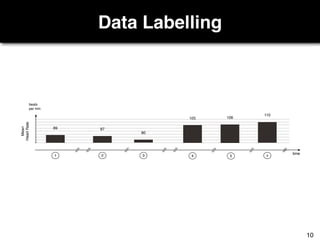
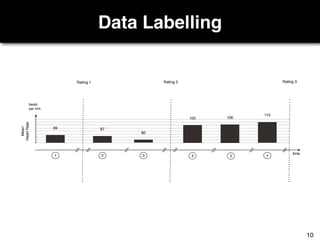
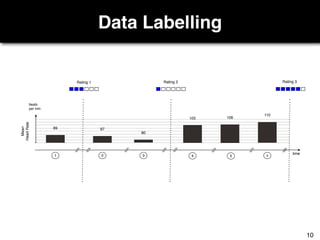
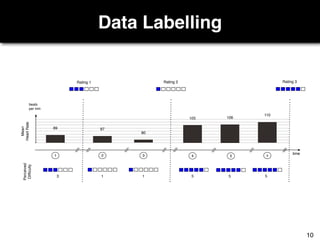
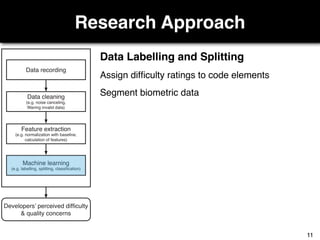
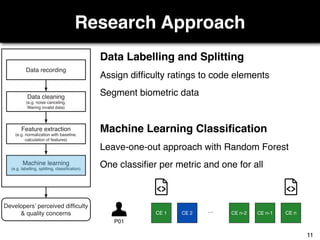
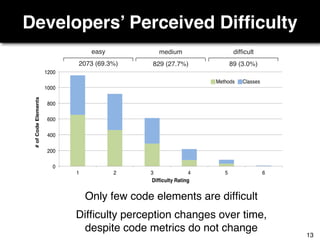
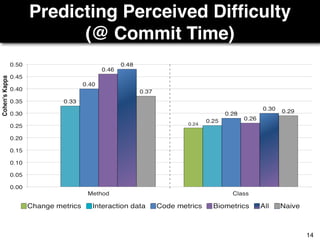
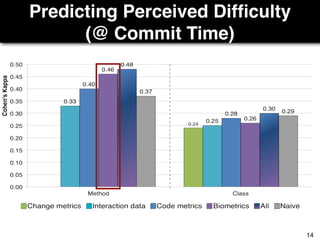
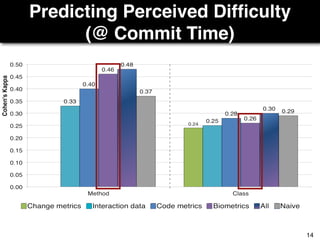
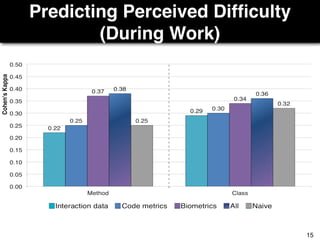
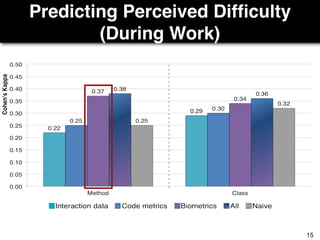
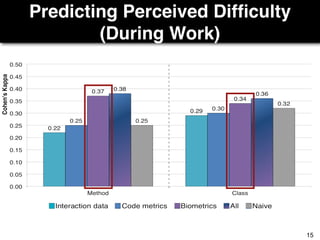
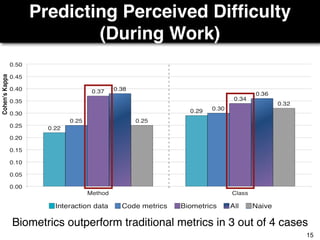
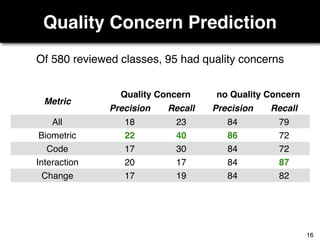
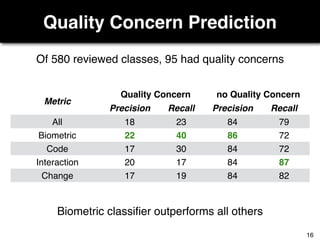
The document discusses a study by Sebastian Müller and Thomas Fritz on using biometric sensing to predict code quality and identify quality concerns in software development. It outlines research questions, methodologies involving professional developers, and biometric data collection, indicating that biometrics can outperform traditional metrics in identifying code difficulties and quality issues. The findings suggest potential for using biometric data to enhance developer support and intervene when developers face challenges.