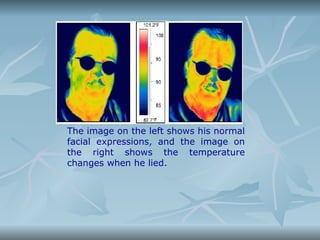
The document discusses biometrics, which is the study of methods for uniquely recognizing humans based on physical and behavioral traits. Some examples of physiological biometrics are fingerprint, face recognition, DNA, hand and palm geometry, and iris recognition. Behavioral biometrics include typing rhythm, gait, and voice. The document then explains the process of biometric systems which involves capturing biometric data, creating a template, storing it in a database, and comparing new captures against stored templates to authenticate users. It discusses some challenges with biometric technologies including privacy issues, discrimination concerns, and the permanence of biometrics.