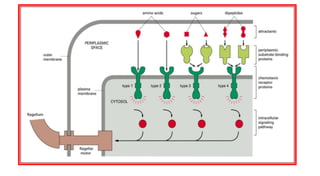
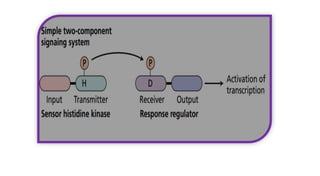
This document summarizes two-component signaling systems in bacteria and plants. It describes how in bacteria, like E. coli, membrane receptors detect extracellular signals and phosphorylate response regulators to control flagella rotation and chemotaxis. A similar system in plants involves cytokinin receptors phosphorylating histidine phosphotransfer proteins and response regulator proteins to control gene expression and cellular responses to cytokinin. The molecular mechanisms of both systems involve a phosphorylation cascade from a sensor kinase to response regulators that control downstream effects.