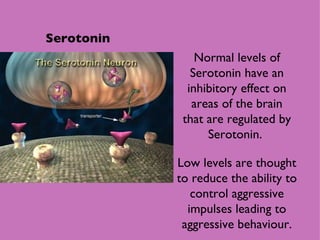
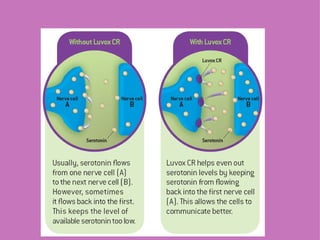
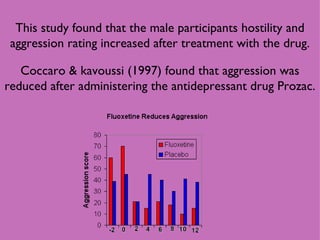
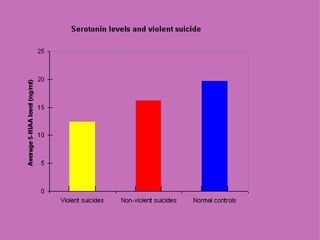
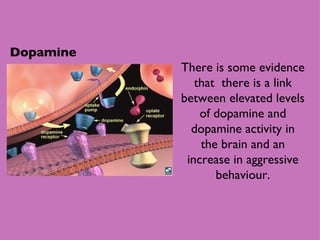
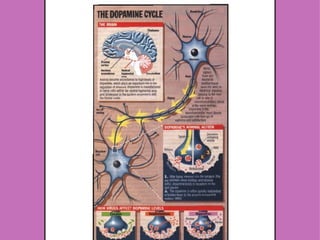
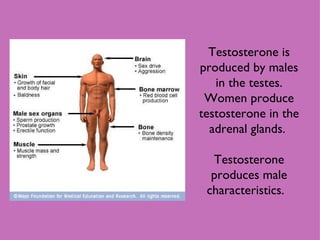
1) Neural and hormonal mechanisms influence aggressive behavior. Low levels of serotonin and high levels of dopamine have been linked to increased aggression. Testosterone has also been correlated with aggression, though the evidence is mixed.
2) Studies manipulating or measuring serotonin and dopamine levels in humans and animals support their role in aggression. However, low serotonin may instead lead to more serotonin receptors in the prefrontal cortex.
3) While some studies found a link between testosterone and aggression, others found no association, and high testosterone is more clearly linked to dominance than aggression. Testosterone supplements have also reduced depression in older males.