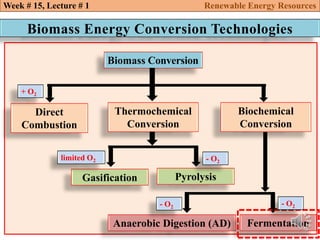
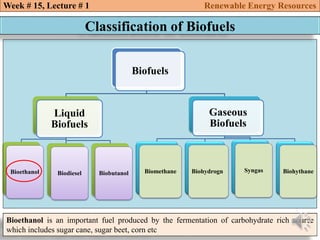
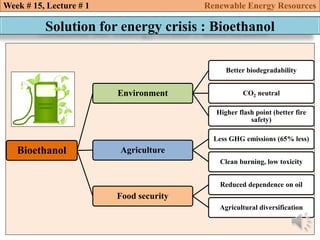
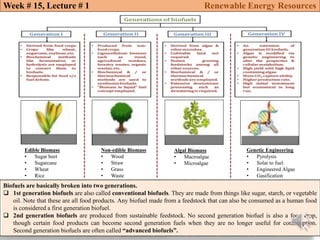
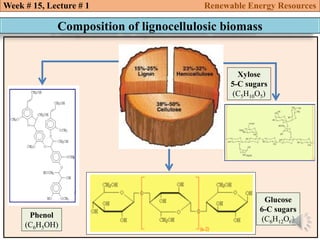
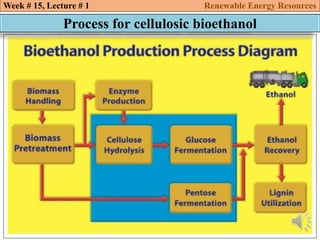
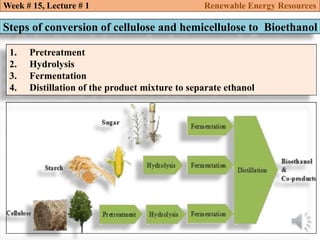
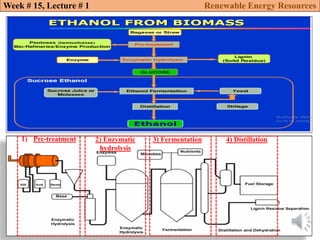
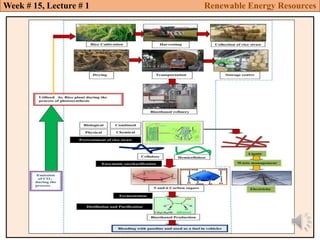
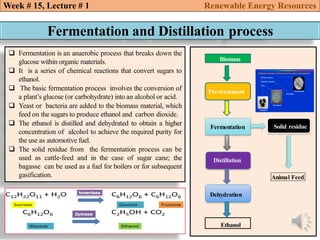
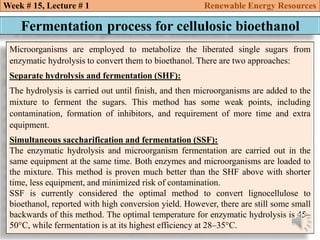
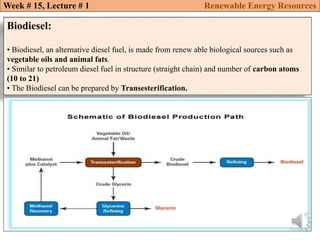
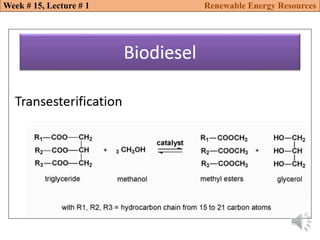
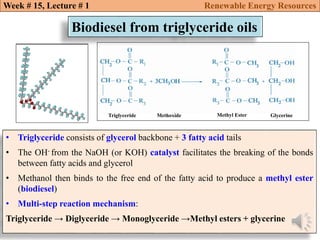
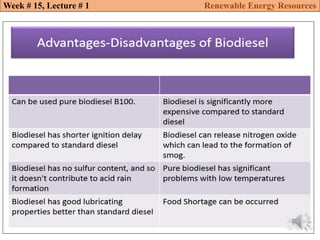
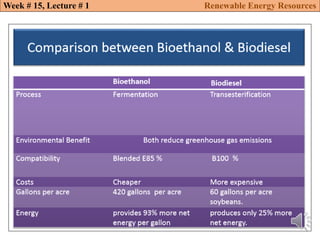
This document summarizes a lecture about renewable energy resources, focusing on bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass. It discusses the classification of biofuels as first or second generation. The process of producing cellulosic bioethanol involves pretreating lignocellulosic biomass, followed by enzymatic hydrolysis to break it down into sugars and fermentation to convert the sugars to ethanol. Advantages of bioethanol include cleaner exhaust, reduced greenhouse gases, and energy security. Challenges include the amount of land required and potential impacts on food production. Biodiesel production via transesterification of vegetable oils is also summarized.